
How to Use MCB 1 Phase: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MCB 1 Phase in Cirkit Designer
Design with MCB 1 Phase in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MCB 1 Phase (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is a compact, electromechanical device designed to protect single-phase electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions, such as overloads and short circuits. It automatically disconnects the circuit when the current exceeds a predefined threshold, ensuring the safety of connected devices and reducing the risk of electrical fires.
Explore Projects Built with MCB 1 Phase

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer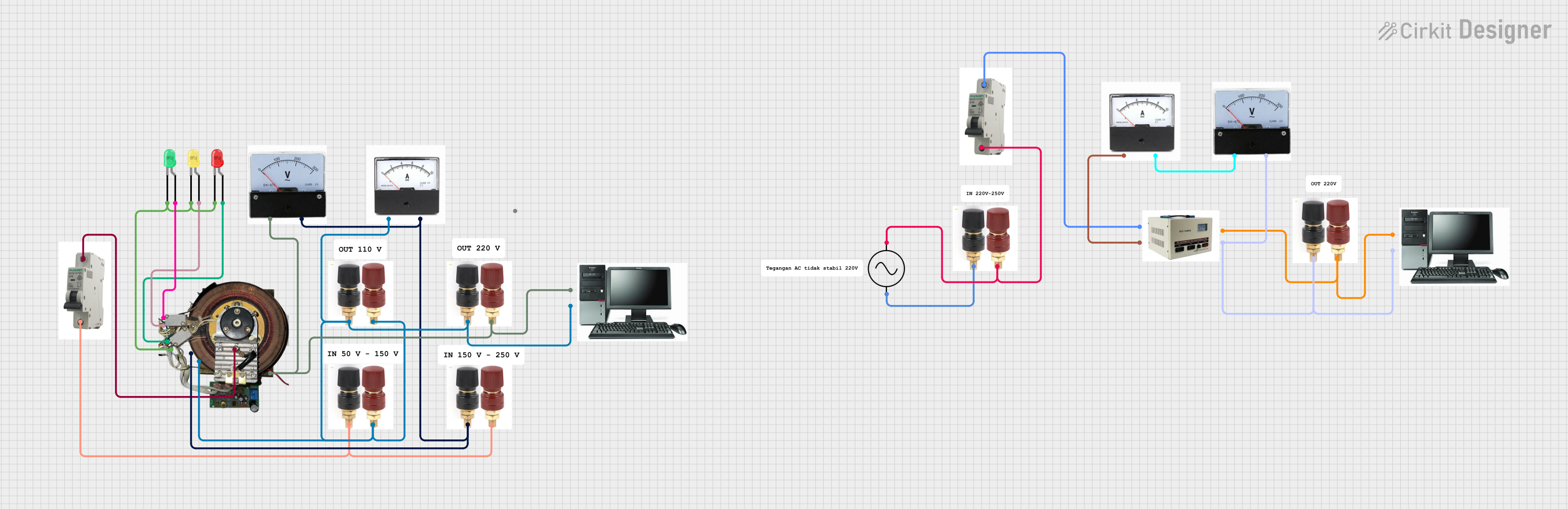
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer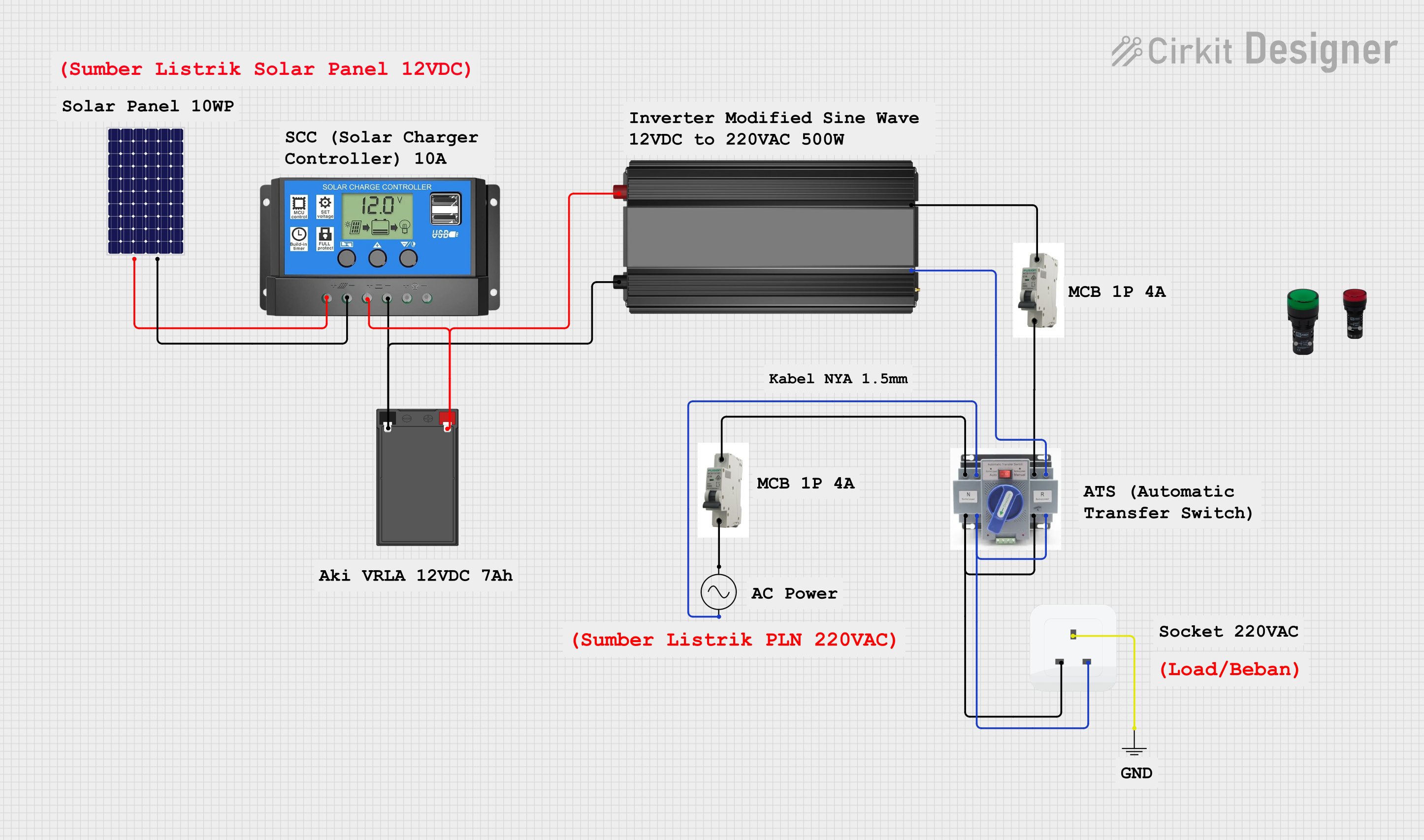
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer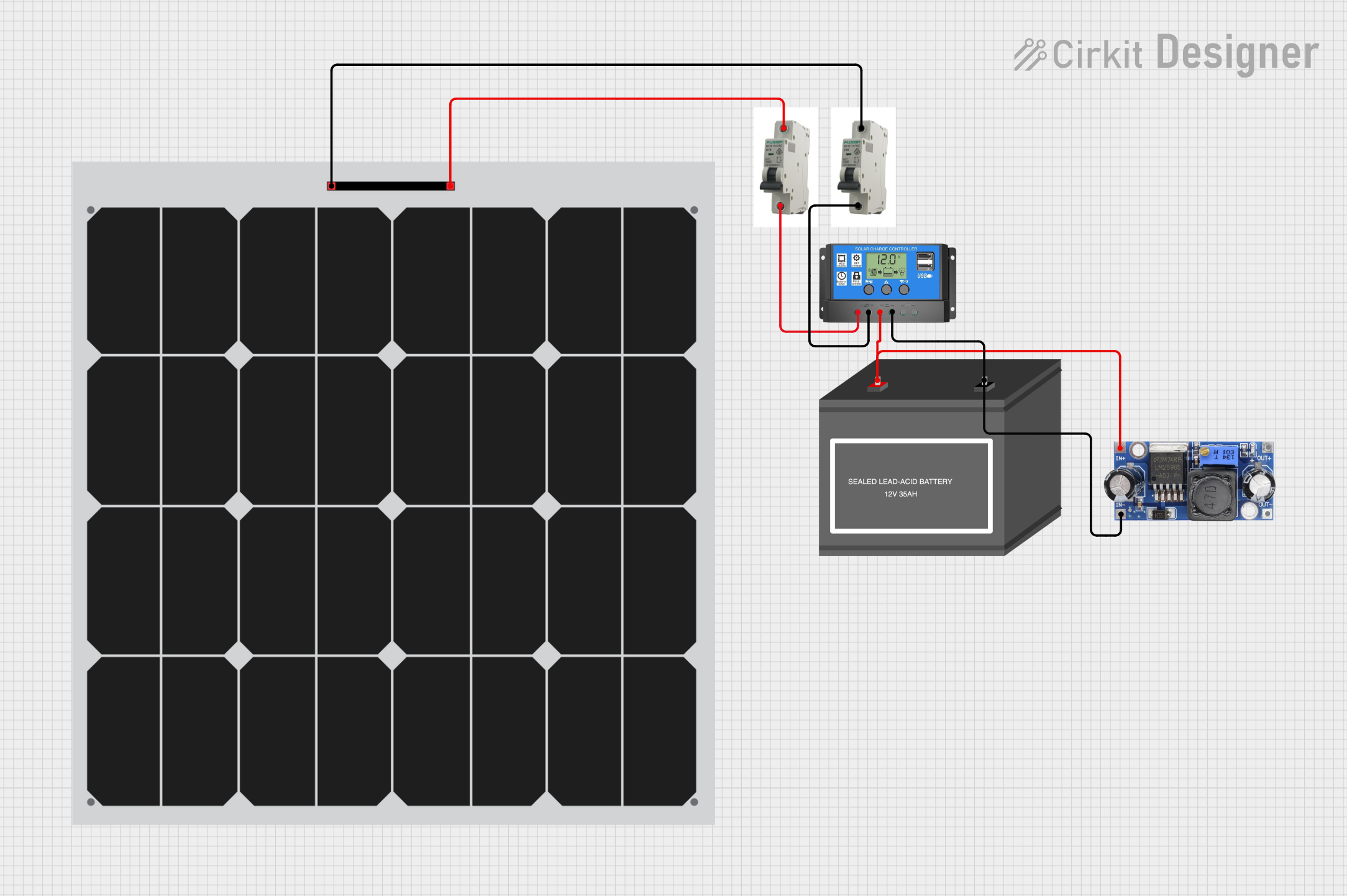
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MCB 1 Phase

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial electrical systems
- Protection of lighting circuits, appliances, and power outlets
- Industrial control panels and machinery
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar inverters)
- Backup power systems and generators
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 230V AC |
| Rated Current | 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 32A, 40A |
| Breaking Capacity | 6kA (6000A) |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Tripping Curve | B, C, or D (depending on model) |
| Number of Poles | 1 (Single Phase) |
| Operating Temperature | -5°C to +40°C |
| Mounting Type | DIN Rail (35mm standard) |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 60898-1, IS/IEC 60947-2 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MCB 1 Phase does not have traditional pins but instead features screw terminals for input and output connections. Below is a description of the terminals:
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Line (Input) | Connects to the live wire from the power source. |
| Load (Output) | Connects to the live wire of the load circuit. |
| Neutral | Not applicable (neutral wire bypasses the MCB). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MCB 1 Phase in a Circuit
- Turn Off Power: Ensure the main power supply is turned off before installation.
- Mounting: Securely mount the MCB onto a 35mm DIN rail in the distribution box.
- Wiring:
- Connect the live wire from the power source to the Line (Input) terminal.
- Connect the live wire of the load circuit to the Load (Output) terminal.
- Ensure all connections are tight to prevent arcing or overheating.
- Testing:
- Turn on the power supply and switch the MCB to the "ON" position.
- Test the MCB by pressing the test button (if available) to ensure proper tripping functionality.
- Operation:
- The MCB will automatically trip if an overcurrent condition occurs. Reset it by switching it back to the "ON" position after resolving the issue.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Select an MCB with the appropriate current rating and tripping curve (B, C, or D) based on the load type:
- B Curve: For resistive loads (e.g., lighting, heating).
- C Curve: For inductive loads (e.g., motors, transformers).
- D Curve: For high inrush current loads (e.g., industrial equipment).
- Avoid exceeding the rated current and voltage of the MCB.
- Regularly inspect the MCB for signs of wear, overheating, or damage.
- Do not use the MCB as a regular switch for turning circuits on and off.
Arduino UNO Integration
While MCBs are not directly connected to microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, they can be used in circuits powered by Arduino to protect against overcurrent. For example, an MCB can safeguard the power supply line to an Arduino-based project.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| MCB trips frequently | Overload or short circuit in the load | Check the load for faults or reduce the load. |
| MCB does not trip during a fault | Faulty MCB or incorrect wiring | Replace the MCB or verify wiring connections. |
| MCB feels hot during operation | Loose connections or overload | Tighten connections or reduce the load. |
| MCB cannot be reset | Persistent fault in the circuit | Identify and fix the fault before resetting. |
FAQs
Can I use an MCB 1 Phase for DC circuits?
- No, this MCB is designed for AC circuits. Use a DC-rated MCB for DC applications.
What is the difference between B, C, and D tripping curves?
- The tripping curve defines the MCB's response to overcurrent:
- B Curve: Trips at 3-5 times the rated current.
- C Curve: Trips at 5-10 times the rated current.
- D Curve: Trips at 10-20 times the rated current.
- The tripping curve defines the MCB's response to overcurrent:
How do I select the correct MCB rating?
- Calculate the total current of the connected load and choose an MCB with a slightly higher rating. Ensure the MCB's rating matches the wire gauge and circuit design.
Can I use an MCB as a substitute for a fuse?
- Yes, MCBs are a modern alternative to fuses, offering resettable protection and faster response times.
By following this documentation, users can safely and effectively integrate the MCB 1 Phase into their electrical systems.