
How to Use 4 Point Terminal Block: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 4 Point Terminal Block in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4 Point Terminal Block in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 4 Point Terminal Block is a type of electrical connector designed to facilitate the secure and organized connection of multiple wires to a single point. It features four terminals, each capable of accommodating a wire, making it an essential component in electrical and electronic systems. Terminal blocks are widely used in control panels, junction boxes, and other applications where reliable and modular wiring is required.
Explore Projects Built with 4 Point Terminal Block
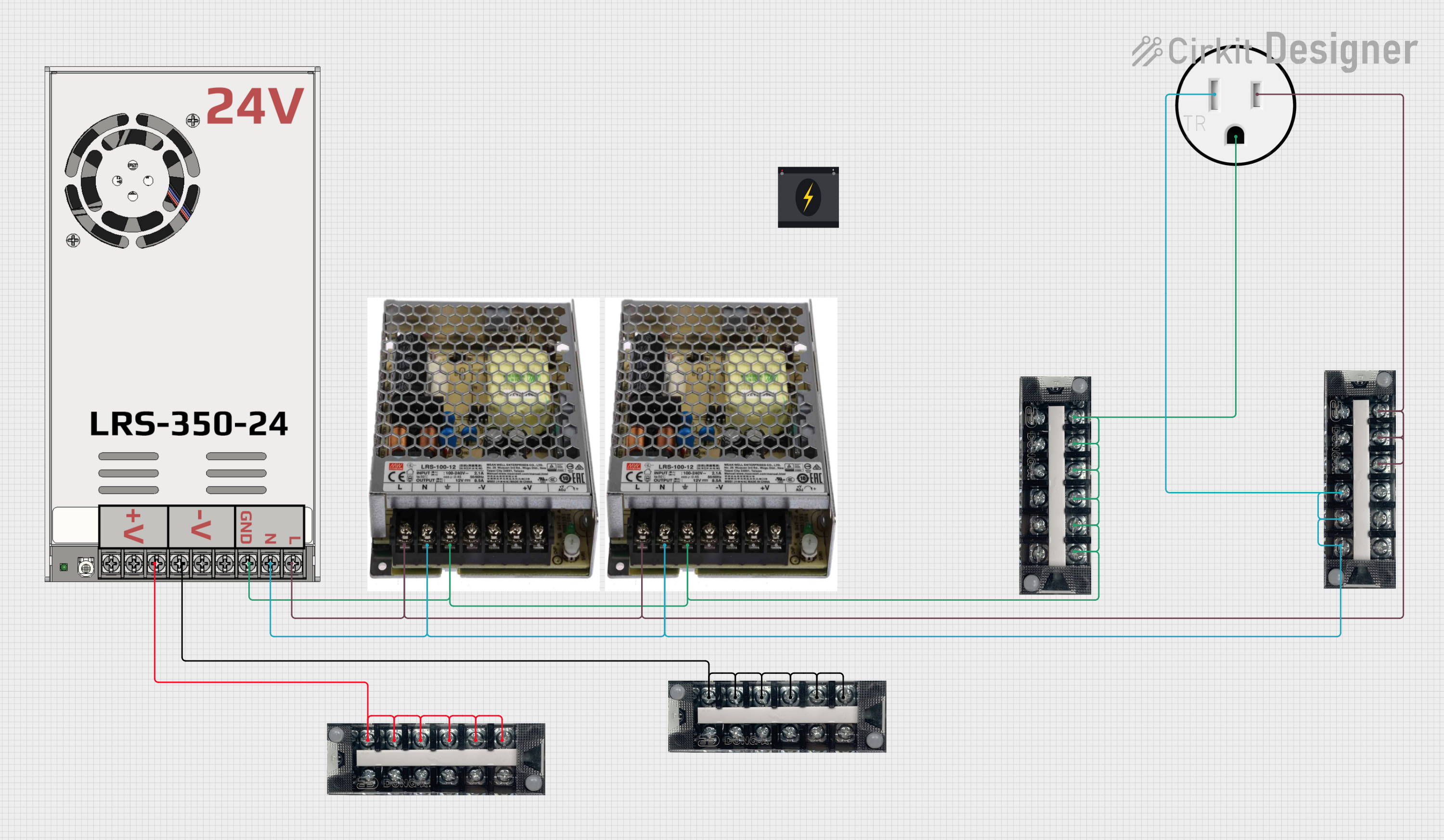
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer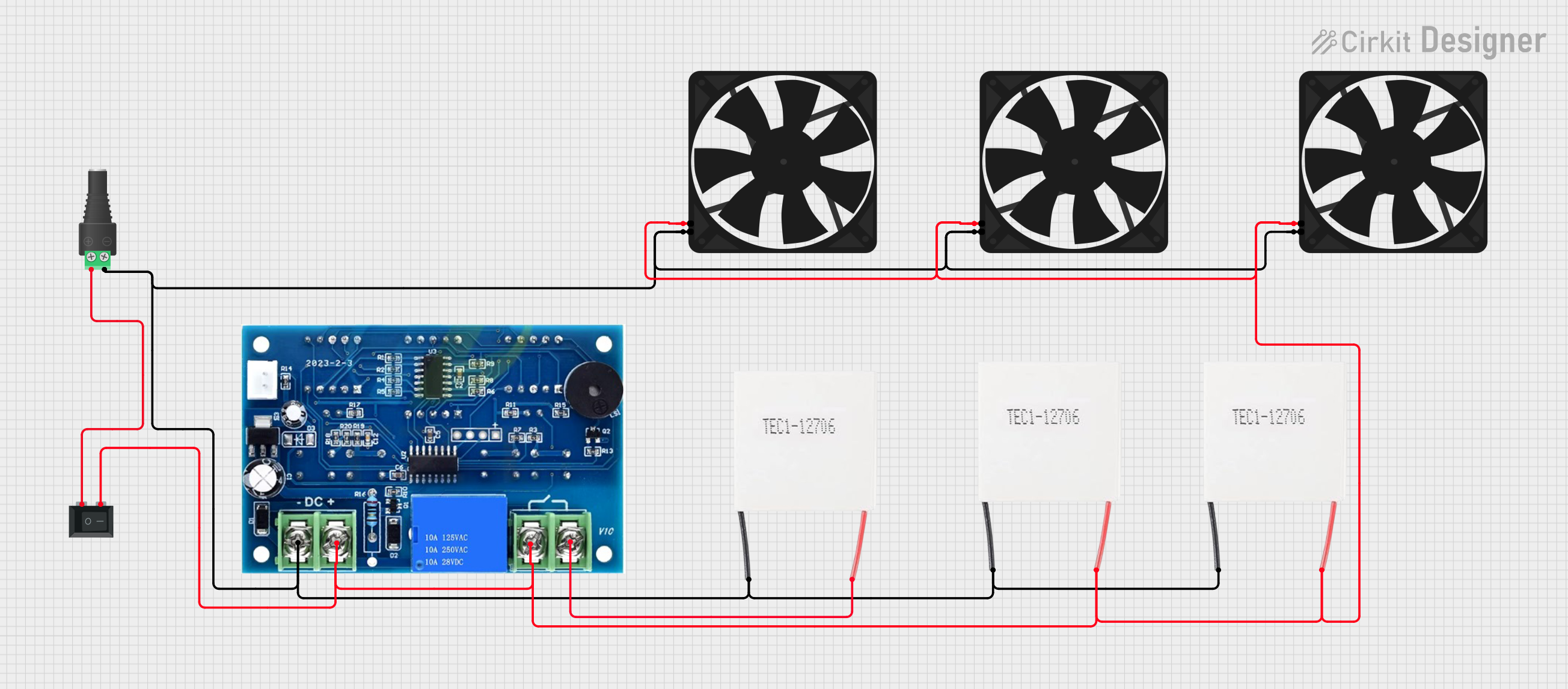
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer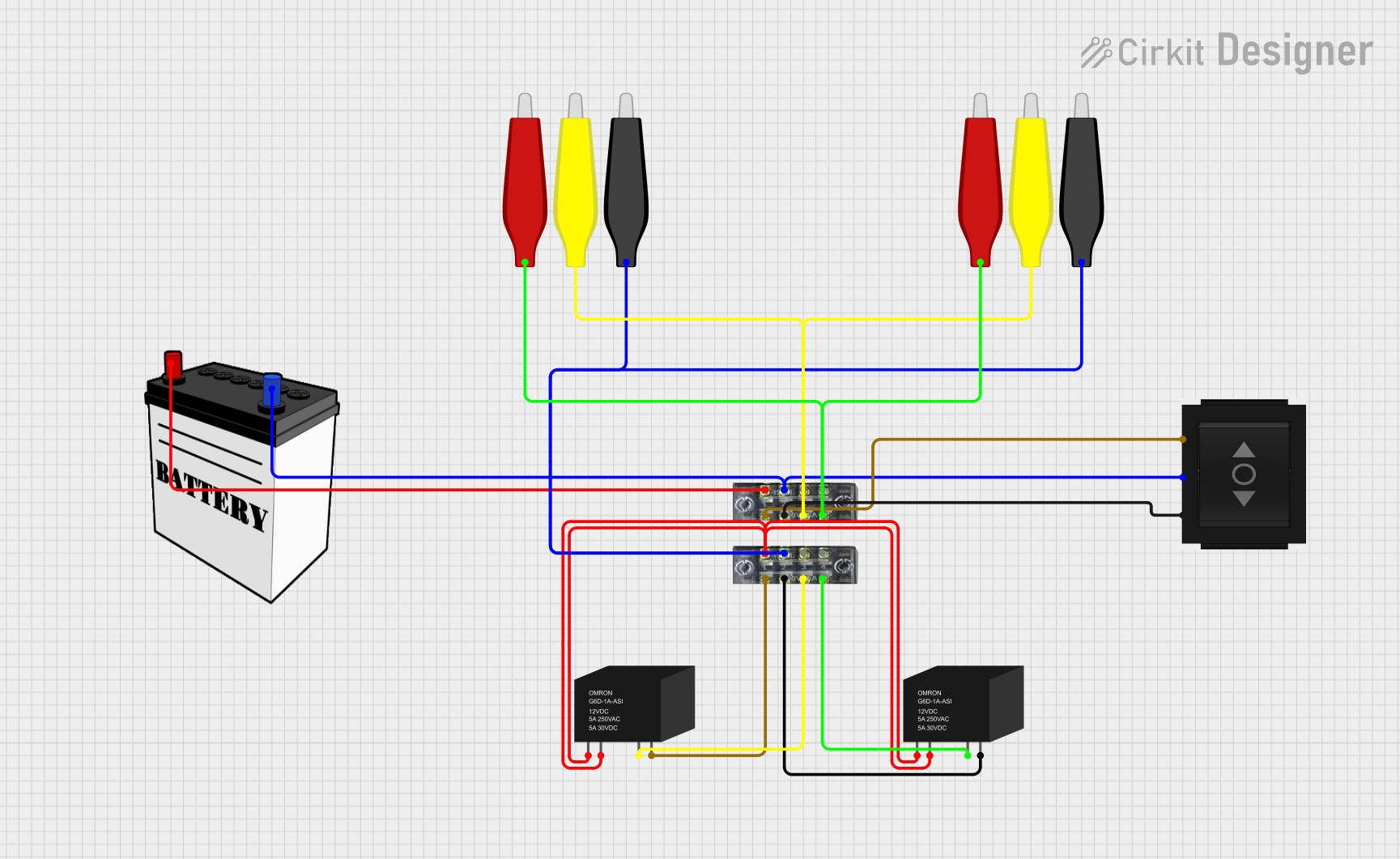
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4 Point Terminal Block

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Control Panels: For connecting sensors, actuators, and other devices to controllers.
- Junction Boxes: To organize and distribute electrical connections.
- Industrial Automation: For wiring PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and other equipment.
- Prototyping and Testing: For creating temporary or modular connections in circuits.
- Power Distribution: To split or combine power lines in low-voltage systems.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a standard 4 Point Terminal Block:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Number of Terminals | 4 |
| Rated Voltage | 300V AC/DC (varies by model) |
| Rated Current | 10A to 30A (depending on wire gauge) |
| Wire Size Compatibility | 22 AWG to 12 AWG |
| Insulation Material | Polyamide (PA66) or similar |
| Terminal Type | Screw-type or spring-loaded |
| Mounting Style | DIN rail or panel mount |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +105°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 4 Point Terminal Block does not have "pins" in the traditional sense but instead features four terminals for wire connections. Below is a description of the terminal layout:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Connection point for the first wire |
| Terminal 2 | Connection point for the second wire |
| Terminal 3 | Connection point for the third wire |
| Terminal 4 | Connection point for the fourth wire |
Each terminal is typically labeled on the block for easy identification.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 4 Point Terminal Block in a Circuit
Prepare the Wires:
- Strip approximately 5-7 mm of insulation from the end of each wire.
- Ensure the wire ends are clean and free of frayed strands.
Connect the Wires:
- Loosen the screw or spring mechanism on the terminal block.
- Insert the stripped end of the wire into the terminal opening.
- Tighten the screw or engage the spring mechanism to secure the wire.
Verify Connections:
- Gently tug on each wire to ensure it is firmly secured.
- Double-check that no exposed wire is touching adjacent terminals.
Mount the Terminal Block:
- If using a DIN rail, snap the terminal block onto the rail.
- For panel mounting, use screws to secure the block to the panel.
Test the Circuit:
- Power on the system and verify that all connections are functioning as intended.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Wire Gauge: Ensure the wire gauge is compatible with the terminal block's specifications.
- Tightening Torque: Do not overtighten screws, as this may damage the wire or terminal.
- Insulation Clearance: Ensure no exposed wire is visible outside the terminal to prevent short circuits.
- Environmental Conditions: Use terminal blocks rated for the operating temperature and humidity of your application.
- Labeling: Clearly label each terminal to avoid confusion during maintenance or troubleshooting.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
While a 4 Point Terminal Block is not directly connected to an Arduino UNO, it can be used to organize connections between the Arduino and external components. For example, you can use the terminal block to connect multiple sensors or actuators to the Arduino.
// Example: Controlling an LED and a motor using an Arduino UNO
// Wires from the terminal block connect to the Arduino pins and components.
// Define pin numbers
const int ledPin = 9; // Terminal 1 connects to LED
const int motorPin = 10; // Terminal 2 connects to motor driver
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motor pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on LED
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH); // Turn on motor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW); // Turn off motor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Loose Connections:
- Issue: Wires are not securely held in the terminal block.
- Solution: Ensure screws are tightened properly or the spring mechanism is fully engaged.
Short Circuits:
- Issue: Exposed wire strands are touching adjacent terminals.
- Solution: Strip the wire to the correct length and ensure no strands are frayed.
Overheating:
- Issue: Terminal block becomes hot during operation.
- Solution: Verify that the current does not exceed the terminal block's rated capacity.
Wire Slippage:
- Issue: Wires slip out of the terminal block.
- Solution: Check that the wire gauge matches the terminal block's specifications.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use a 4 Point Terminal Block for high-voltage applications?
A1: Most 4 Point Terminal Blocks are rated for up to 300V. For higher voltages, use a terminal block specifically designed for high-voltage applications.
Q2: Can I connect more than one wire to a single terminal?
A2: It is not recommended, as this may compromise the connection's reliability. Use a larger terminal block or a bus bar for such cases.
Q3: How do I clean a terminal block?
A3: Disconnect all wires and use a soft brush or compressed air to remove dust and debris. Avoid using water or solvents.
Q4: Can I use stranded wires with a terminal block?
A4: Yes, but it is recommended to use ferrules on the wire ends to prevent fraying and ensure a secure connection.