
How to Use W5500: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
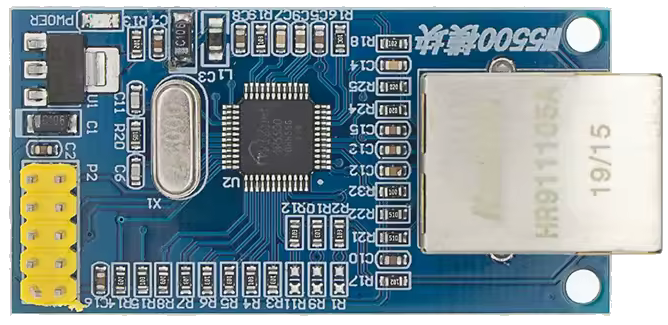
 Design with W5500 in Cirkit Designer
Design with W5500 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The W5500 is a standalone Ethernet controller designed to simplify the process of connecting microcontrollers to the Internet. It features an integrated TCP/IP stack, which supports protocols such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, IPv4, ARP, IGMP, and PPPoE. This makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring reliable and efficient network communication. The W5500 communicates with microcontrollers via an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), ensuring compatibility with a wide range of systems.
Explore Projects Built with W5500
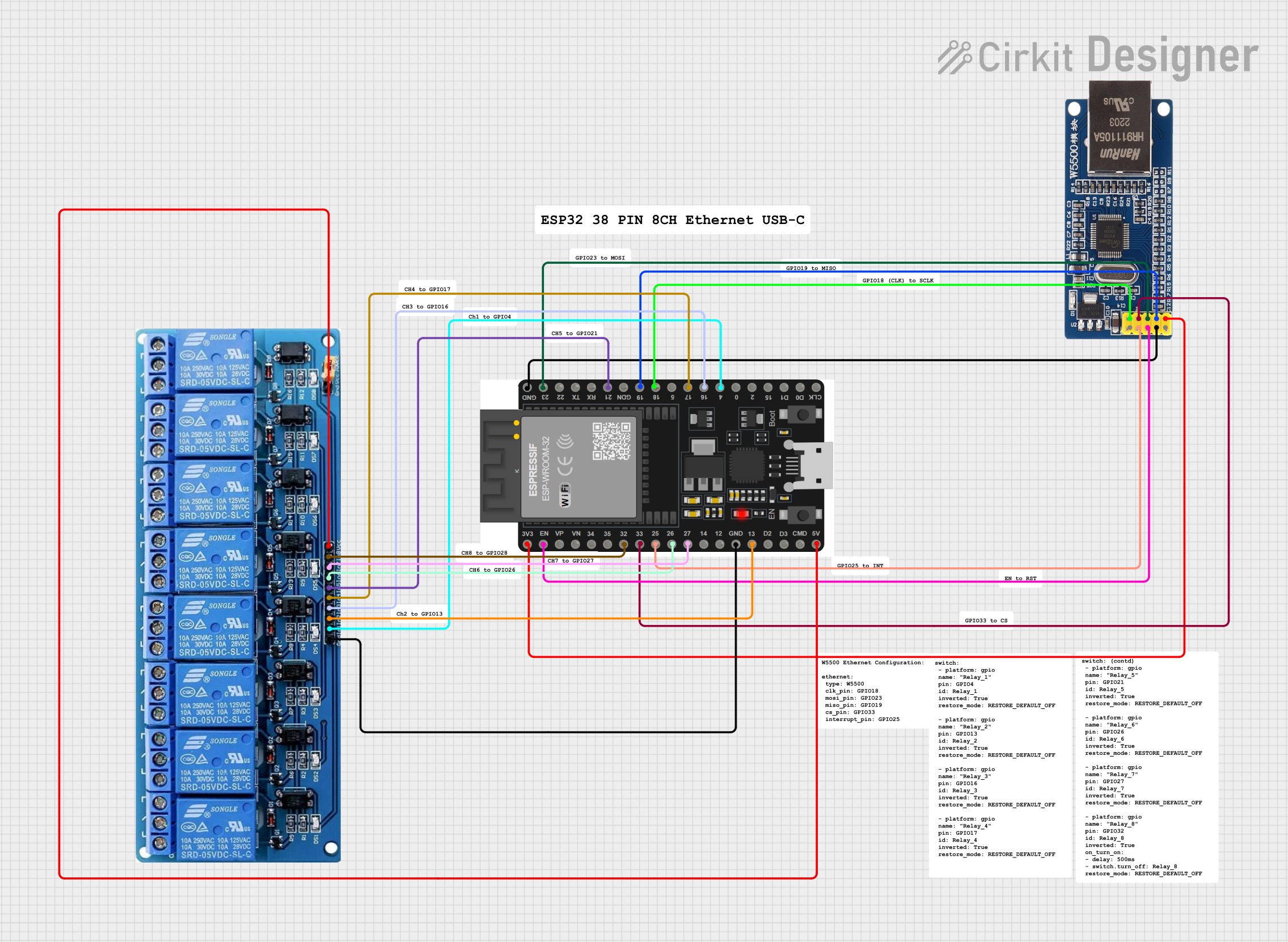
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer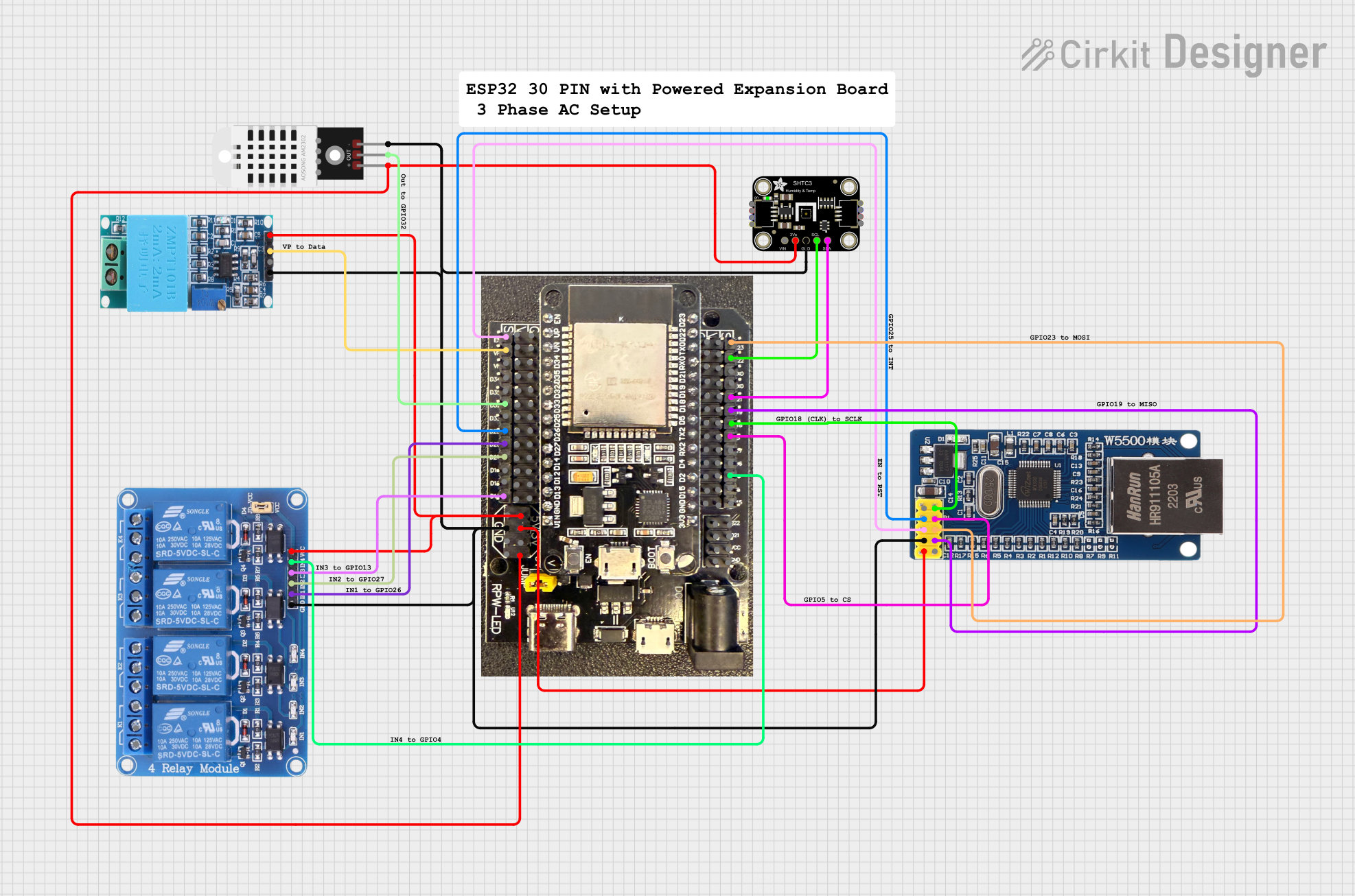
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer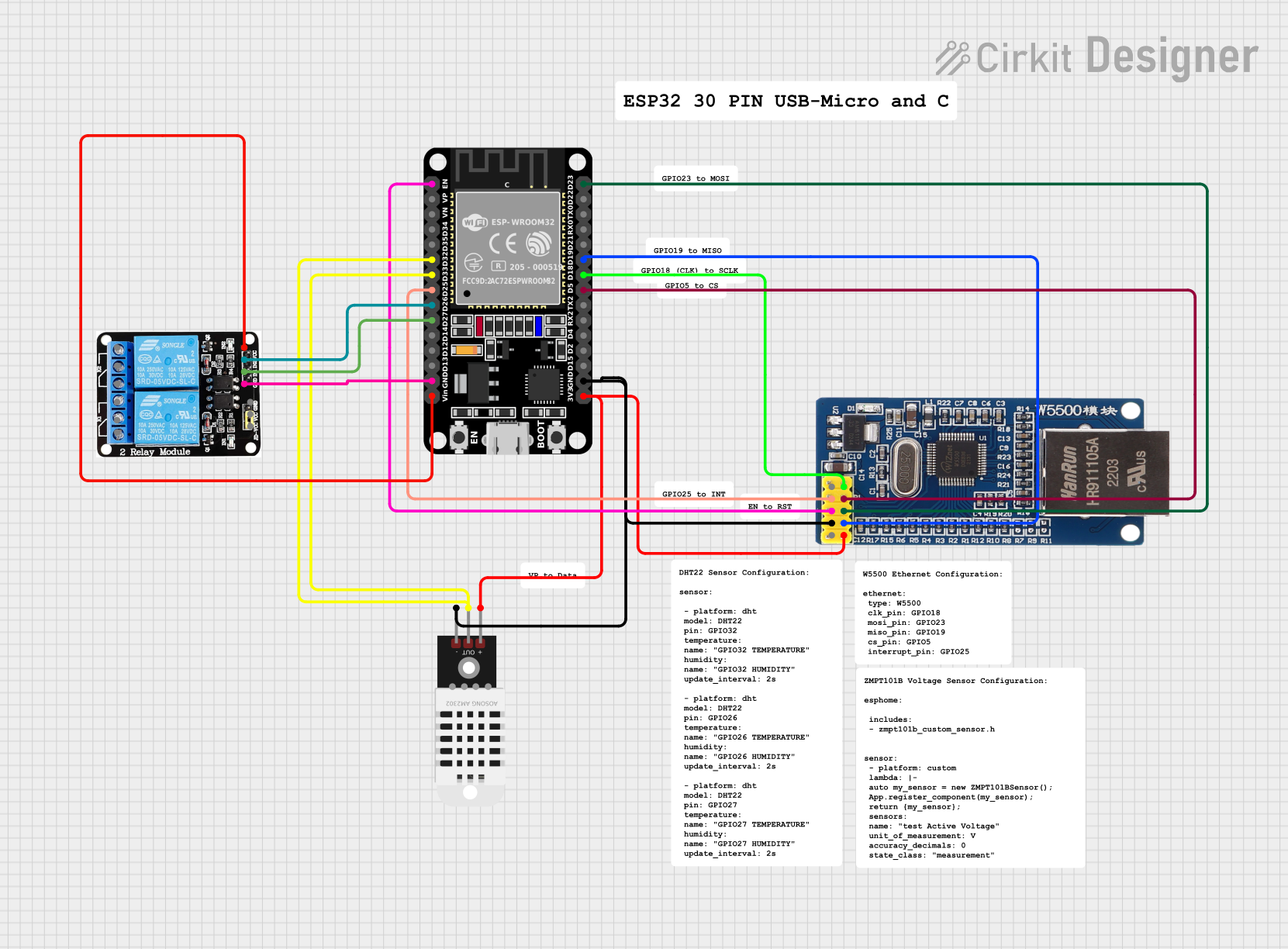
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer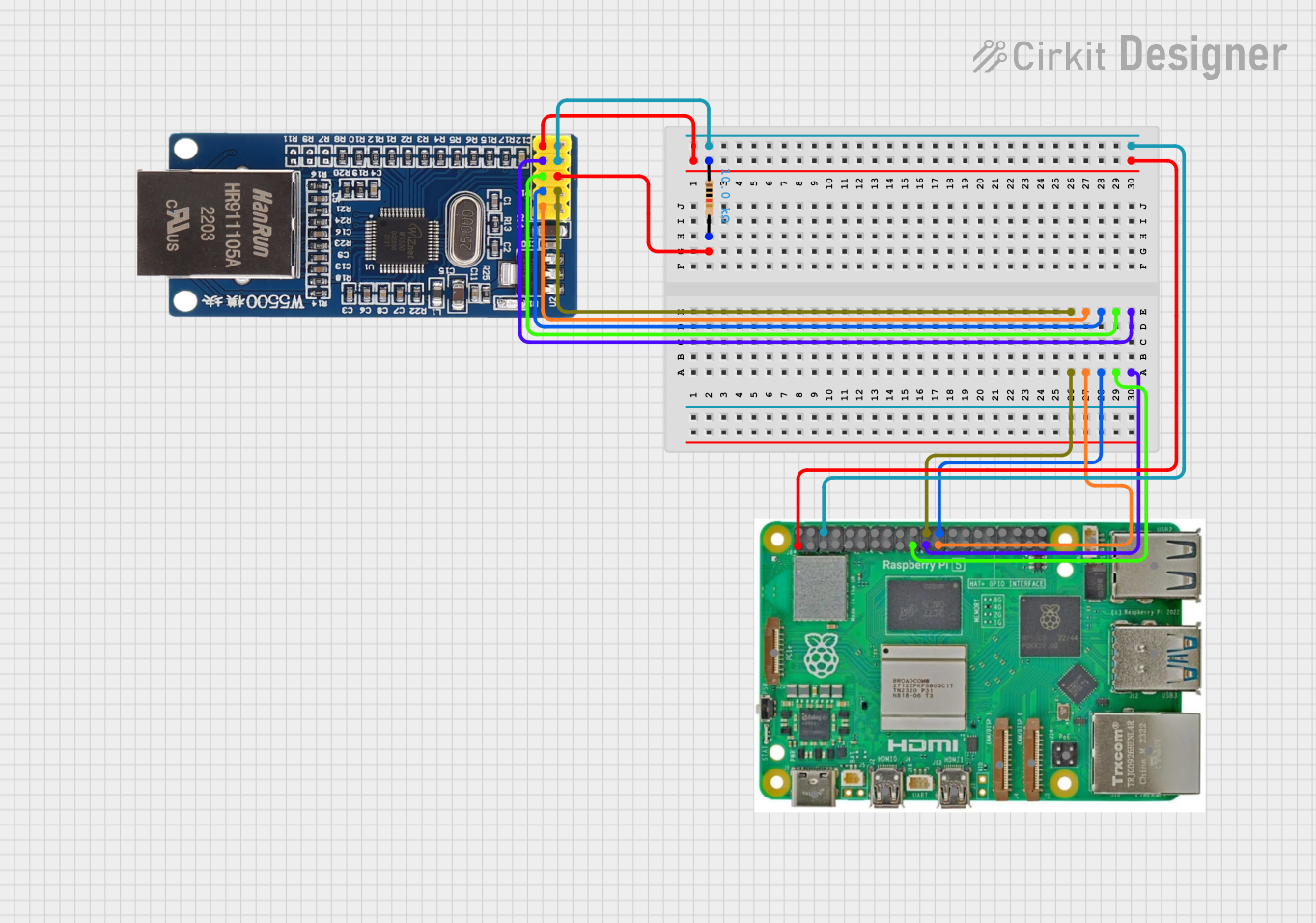
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with W5500

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Home automation systems
- Industrial control and monitoring
- Network-enabled embedded systems
- Data logging and remote monitoring
- Web servers and networked sensors
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 3.3V (with 5V-tolerant I/O pins) |
| Operating Current | 132 mA (typical) |
| Communication Interface | SPI (up to 80 MHz) |
| Network Protocols | TCP, UDP, ICMP, IPv4, ARP, IGMP, PPPoE |
| Ethernet Speed | 10/100 Mbps |
| Internal Memory | 32 KB for TX/RX buffers |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | LQFP-48 or QFN-48 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The W5500 has 48 pins, but the most commonly used pins for interfacing are listed below:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VDD | 1 | 3.3V power supply input |
| GND | 2 | Ground |
| SCLK | 3 | SPI clock input |
| MISO | 4 | SPI master-in/slave-out data line |
| MOSI | 5 | SPI master-out/slave-in data line |
| CS | 6 | SPI chip select (active low) |
| RESET | 7 | Reset input (active low) |
| INT | 8 | Interrupt output (active low) |
| RDY | 9 | Ready signal for SPI communication |
| TX+ | 10 | Ethernet transmit positive |
| TX- | 11 | Ethernet transmit negative |
| RX+ | 12 | Ethernet receive positive |
| RX- | 13 | Ethernet receive negative |
For a complete pinout, refer to the W5500 datasheet.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the W5500 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a 3.3V power source and GND to ground. Ensure the power supply is stable and capable of providing sufficient current.
- SPI Interface: Connect the SPI pins (SCLK, MISO, MOSI, and CS) to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors on the CS line if necessary.
- Ethernet Connection: Connect the TX+/TX- and RX+/RX- pins to an Ethernet transformer or RJ45 connector for network communication.
- Reset and Interrupt: Use the RESET pin to initialize the W5500 and the INT pin to handle interrupts for events like data reception.
- Crystal Oscillator: Connect a 25 MHz crystal oscillator to the XTAL1 and XTAL2 pins for clock generation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the VDD pin to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
- Ensure proper termination of Ethernet lines to avoid signal reflections and maintain signal integrity.
- Use a level shifter if interfacing with a 5V microcontroller, as the W5500 operates at 3.3V logic levels.
- Configure the SPI clock speed to match the W5500's specifications (up to 80 MHz).
- Initialize the W5500's internal registers and memory buffers before starting communication.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the W5500 with an Arduino UNO to establish a basic Ethernet connection:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
// MAC address and IP address for the W5500
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 100);
// Initialize the Ethernet server on port 80
EthernetServer server(80);
void setup() {
// Start the serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // Wait for the serial port to connect
}
// Initialize the Ethernet connection
if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0) {
Serial.println("Failed to configure Ethernet using DHCP");
// Manually configure the IP address if DHCP fails
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
}
// Start the server
server.begin();
Serial.print("Server is at ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
}
void loop() {
// Listen for incoming clients
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
Serial.println("New client connected");
// Read data from the client and send a response
while (client.connected()) {
if (client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
Serial.write(c); // Echo the received data to the serial monitor
// Send a basic HTTP response
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
client.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML>");
client.println("<html>Hello, W5500!</html>");
break;
}
}
// Close the connection
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client disconnected");
}
}
Notes:
- Replace the MAC and IP address with values suitable for your network.
- Ensure the Ethernet library is installed in your Arduino IDE.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Ethernet Connection:
- Verify the Ethernet cable is securely connected to the RJ45 jack.
- Check the TX+/TX- and RX+/RX- connections for proper wiring.
- Ensure the W5500 is powered correctly and the SPI interface is configured properly.
SPI Communication Fails:
- Confirm the SPI clock speed is within the W5500's supported range.
- Check the CS pin connection and ensure it is pulled low during communication.
- Verify the microcontroller's SPI pins are correctly connected to the W5500.
Device Not Responding:
- Reset the W5500 using the RESET pin and reinitialize the registers.
- Check for proper grounding and decoupling capacitors near the power pins.
Incorrect IP Address:
- Ensure the MAC and IP address are unique and do not conflict with other devices on the network.
- Use a static IP configuration if DHCP fails.
FAQs
Q: Can the W5500 be used with 5V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the W5500 has 5V-tolerant I/O pins, but it operates at 3.3V. Use a level shifter for optimal performance.
Q: What is the maximum SPI clock speed supported by the W5500?
A: The W5500 supports SPI clock speeds up to 80 MHz.
Q: Does the W5500 support IPv6?
A: No, the W5500 only supports IPv4.
Q: How much memory is available for data transmission and reception?
A: The W5500 has 32 KB of internal memory, which is shared between TX and RX buffers.
Q: Can the W5500 handle multiple simultaneous connections?
A: Yes, the W5500 supports up to 8 independent sockets for simultaneous connections.