
How to Use TDs sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) sensor is an electronic device used to measure the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid. These dissolved solids include minerals, salts, and organic matter, which affect the conductivity of the liquid. The sensor provides a TDS value in parts per million (ppm), which is a key indicator of water quality.
Explore Projects Built with TDs sensor
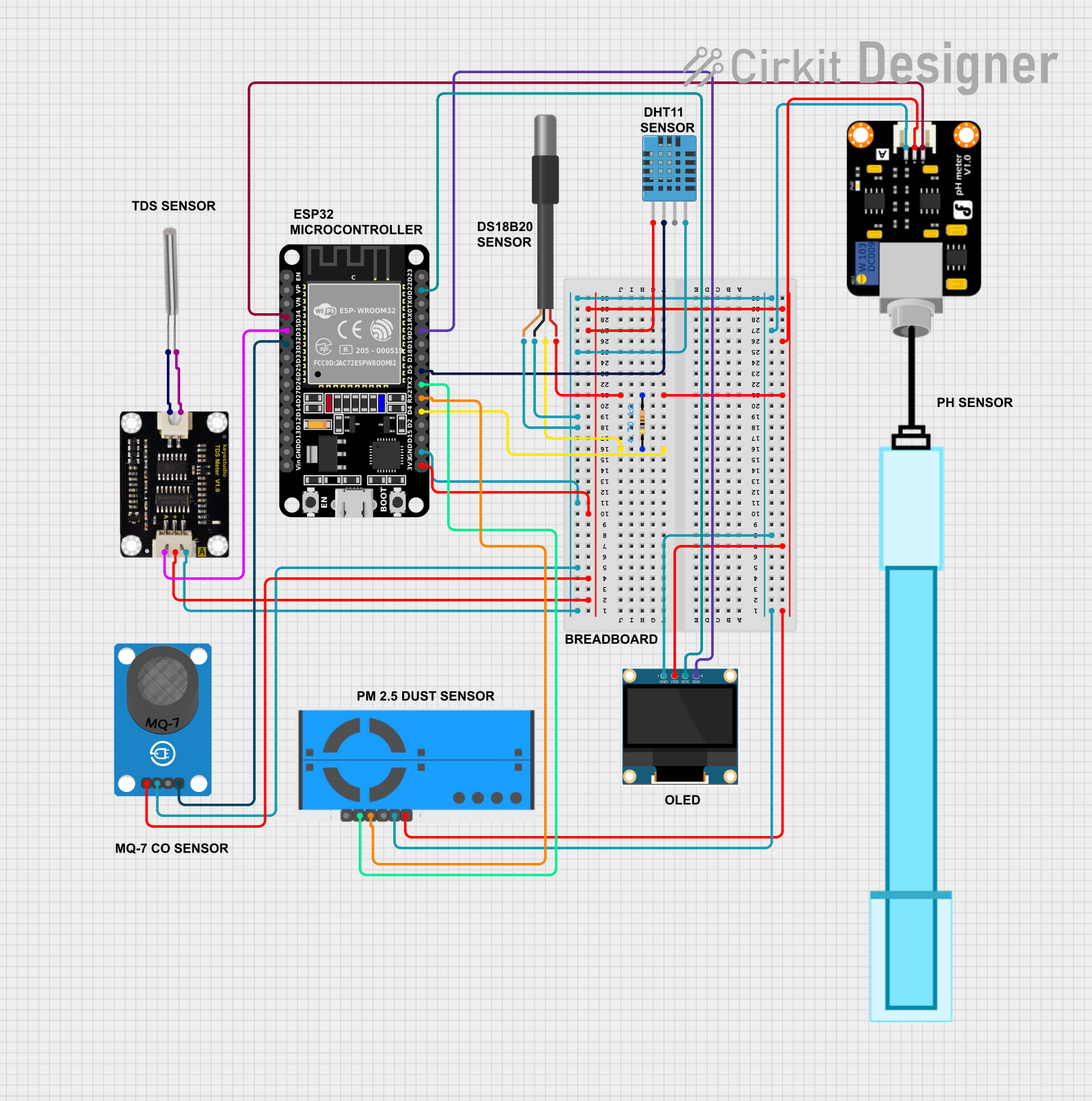
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer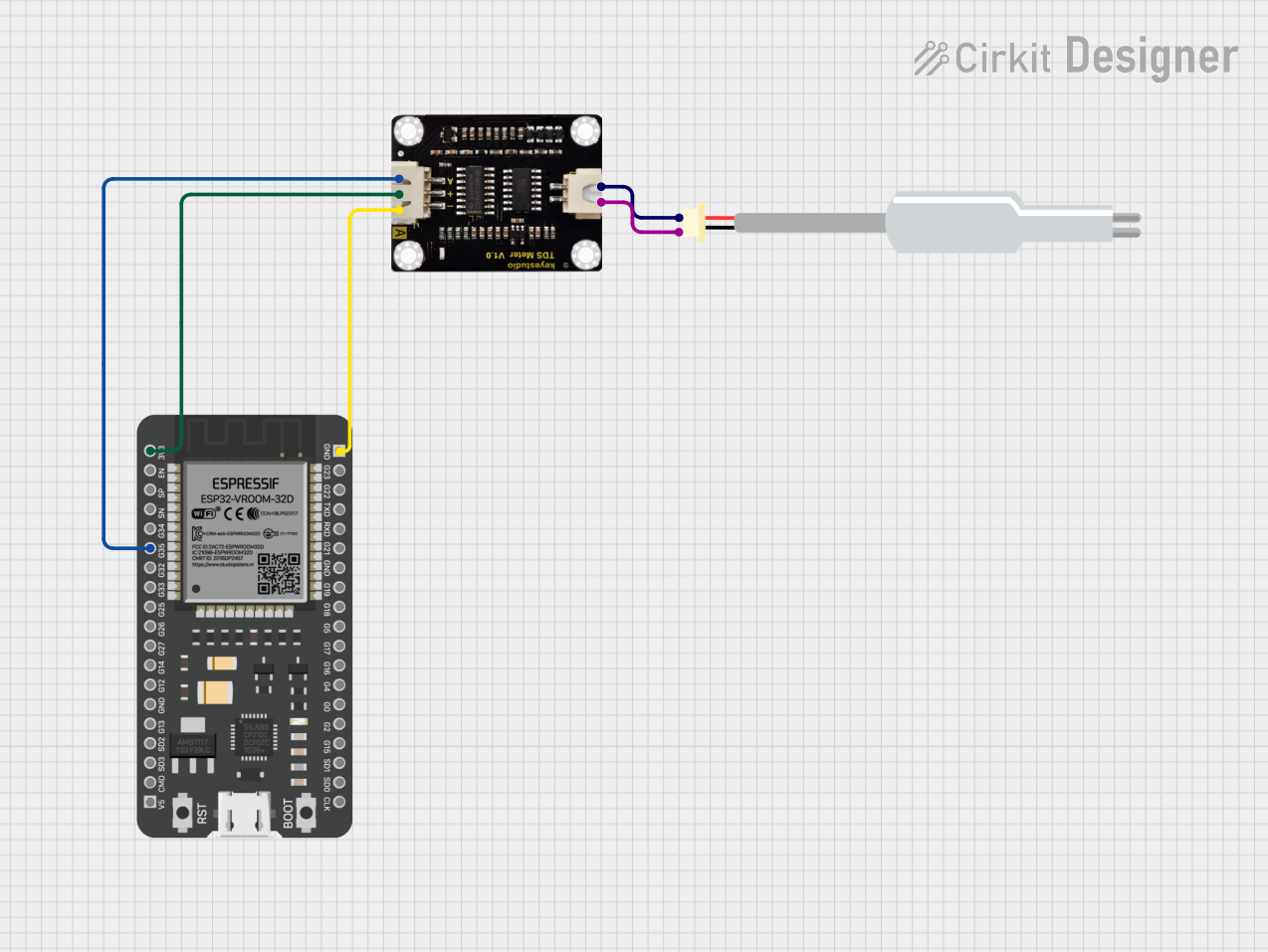
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer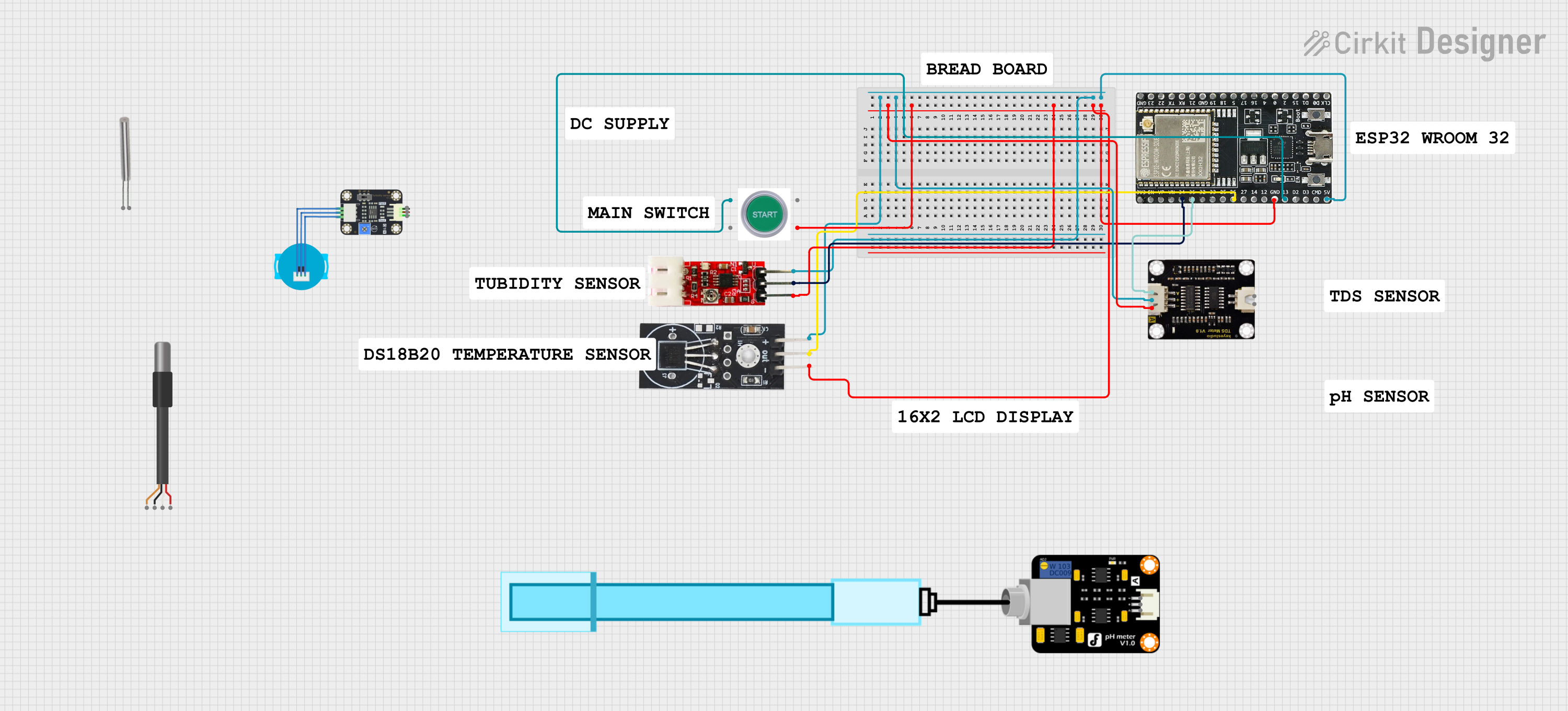
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TDs sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Water quality monitoring in aquariums, hydroponics, and swimming pools
- Drinking water purification systems
- Industrial water treatment processes
- Environmental monitoring of rivers, lakes, and groundwater
- Agricultural irrigation systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical TDS sensor module:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5.0V |
| Operating Current | 3-6 mA |
| Measurement Range | 0 - 1000 ppm |
| Accuracy | ±10% (25°C calibration) |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0-2.3V typical) |
| Temperature Compensation | Supported (via external probe) |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C - 60°C |
Pin Configuration
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5.0V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| AOUT | Analog output signal proportional to TDS value |
| TEMP | Optional connection for temperature probe input |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TDS Sensor in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5.0V power source and theGNDpin to the ground. - Connect the Analog Output: Connect the
AOUTpin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino). - Optional Temperature Compensation: If your sensor supports temperature compensation, connect the external temperature probe to the
TEMPpin. - Calibrate the Sensor: Use a known TDS solution to calibrate the sensor for accurate readings. Adjust the calibration potentiometer on the module if available.
- Read the Output: The sensor outputs an analog voltage proportional to the TDS value. Use an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to read and process the signal.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Corrosion: Do not leave the sensor submerged in water for extended periods to prevent electrode corrosion.
- Temperature Effects: Use temperature compensation for accurate readings in varying temperature conditions.
- Clean the Sensor: Rinse the sensor with distilled water after each use to prevent residue buildup.
- Avoid High TDS Levels: The sensor is designed for TDS levels up to 1000 ppm. Exceeding this range may damage the sensor or produce inaccurate readings.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use a TDS sensor with an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect
VCCto the Arduino's5Vpin. - Connect
GNDto the Arduino'sGNDpin. - Connect
AOUTto the Arduino'sA0pin.
Arduino Code
// TDS Sensor Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Reads the analog output from the TDS sensor and converts it to a TDS value.
const int TDS_PIN = A0; // Analog pin connected to the TDS sensor's AOUT
float voltage; // Variable to store the sensor's output voltage
float tdsValue; // Variable to store the calculated TDS value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
pinMode(TDS_PIN, INPUT); // Set the TDS pin as an input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(TDS_PIN); // Read the analog value from the sensor
voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert ADC value to voltage
tdsValue = (voltage * 1000) / 2.3; // Convert voltage to TDS (ppm)
// Print the TDS value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("TDS Value: ");
Serial.print(tdsValue);
Serial.println(" ppm");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Inaccurate Readings
- Cause: Sensor not calibrated.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor using a standard TDS solution.
No Output Signal
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the power supply matches the sensor's requirements.
Fluctuating Readings
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable water conditions.
- Solution: Use a capacitor across the power supply pins to reduce noise. Ensure the water sample is stable.
Sensor Corrosion
- Cause: Prolonged exposure to water.
- Solution: Limit the sensor's immersion time and clean it after use.
FAQs
Q: Can the TDS sensor measure salinity?
A: While the TDS sensor measures dissolved solids, it is not specifically designed for salinity measurement. However, it can provide an approximate salinity value in ppm.
Q: How often should I calibrate the sensor?
A: Calibration is recommended every 2-3 months or whenever you notice inaccurate readings.
Q: Can I use the TDS sensor in hot water?
A: The sensor operates within a temperature range of 0°C to 60°C. Avoid using it in water outside this range to prevent damage.
Q: Is the TDS sensor waterproof?
A: The sensor probe is waterproof, but the module is not. Ensure the module remains dry during operation.