
How to Use pca9685: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
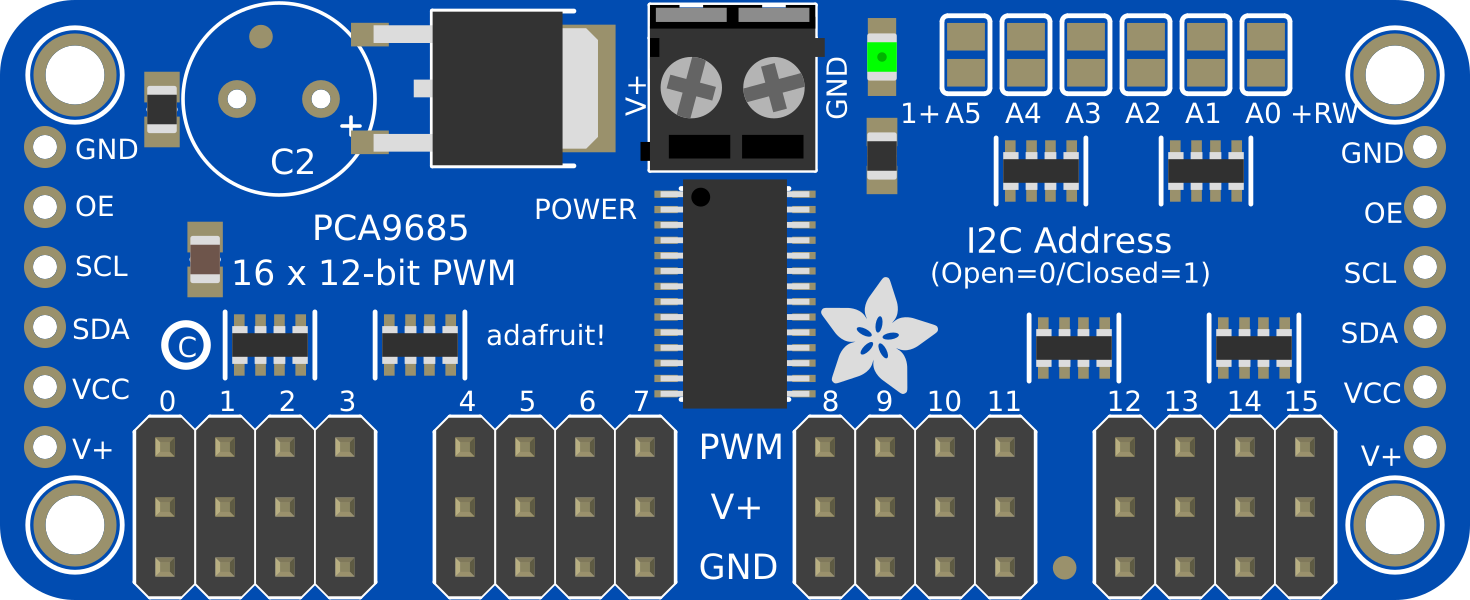
 Design with pca9685 in Cirkit Designer
Design with pca9685 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PCA9685 is a 16-channel, 12-bit PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller that communicates via the I2C protocol. It is widely used in robotics, automation, and lighting projects due to its ability to control up to 16 independent PWM outputs with high precision. This component is particularly useful for driving servos, LEDs, and other devices requiring PWM signals, while offloading the processing burden from the microcontroller.
Explore Projects Built with pca9685
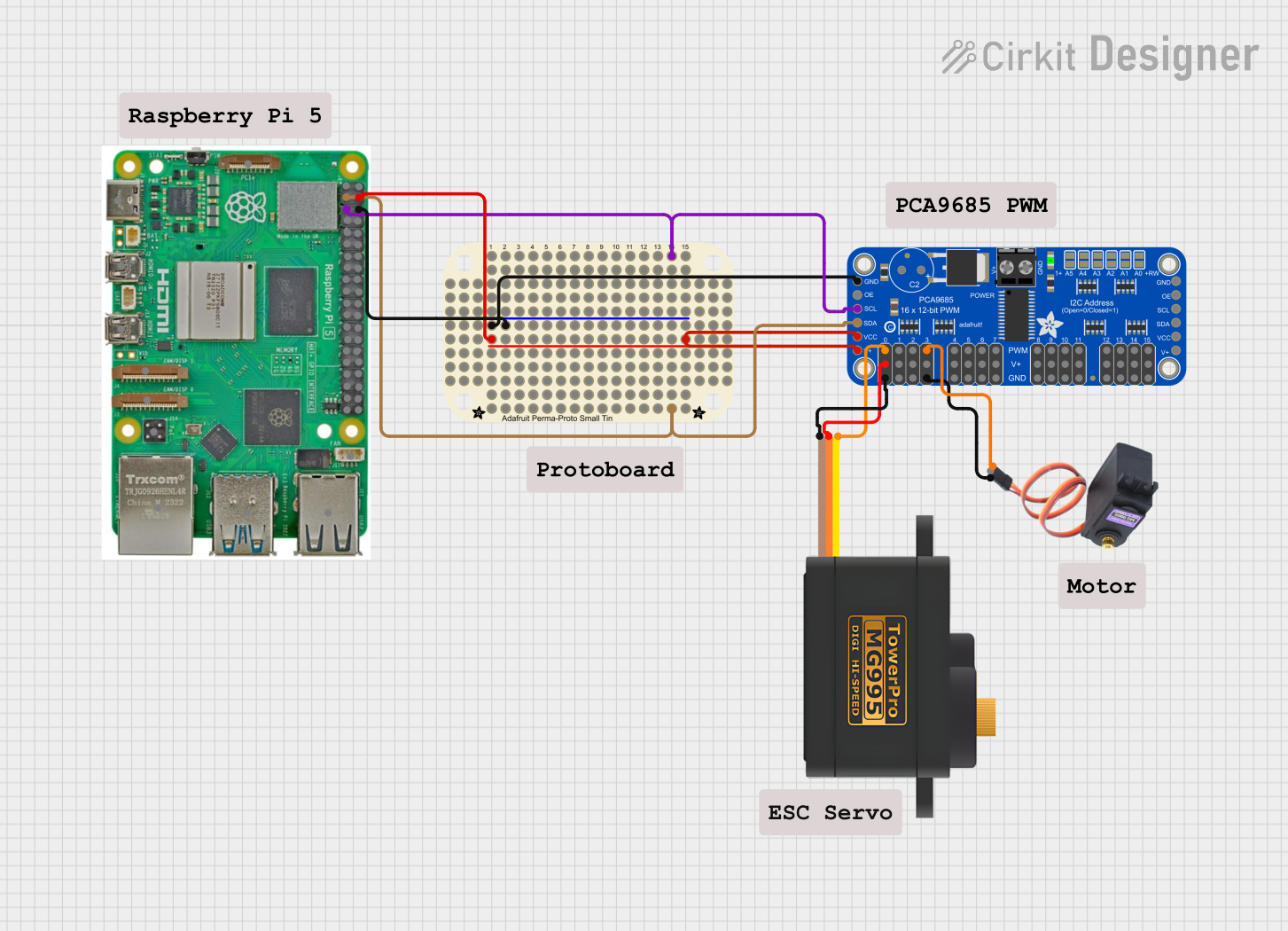
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer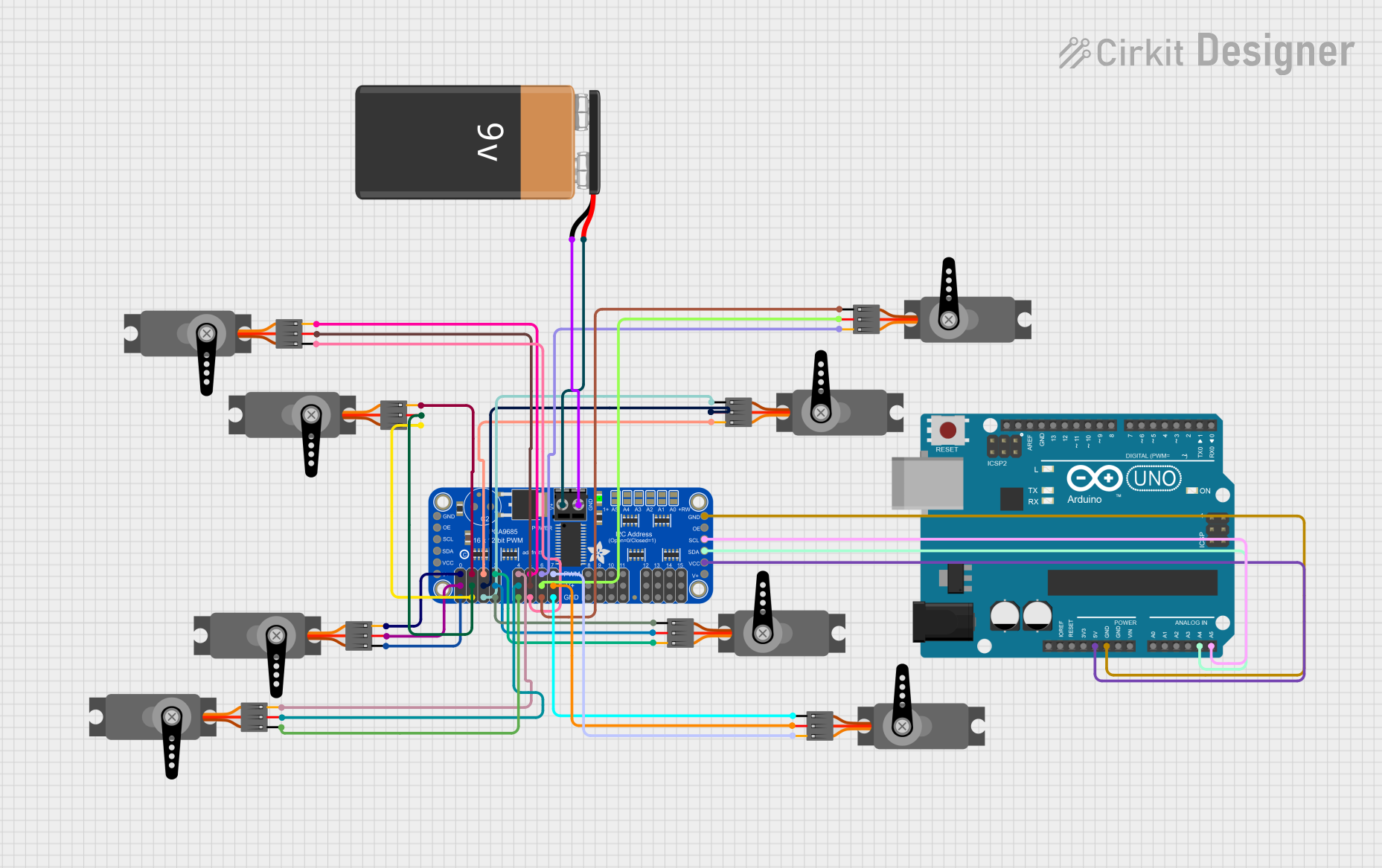
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer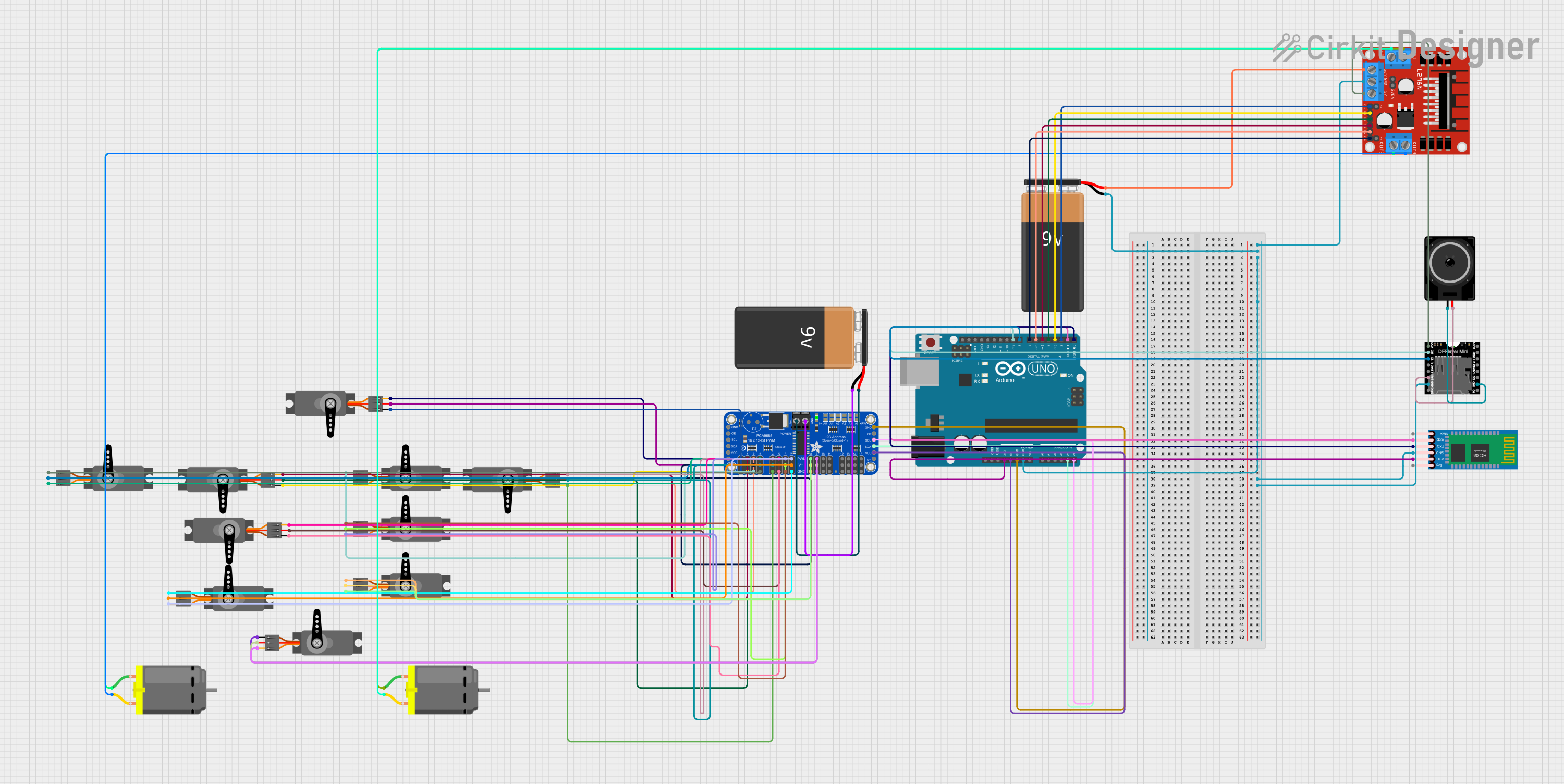
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer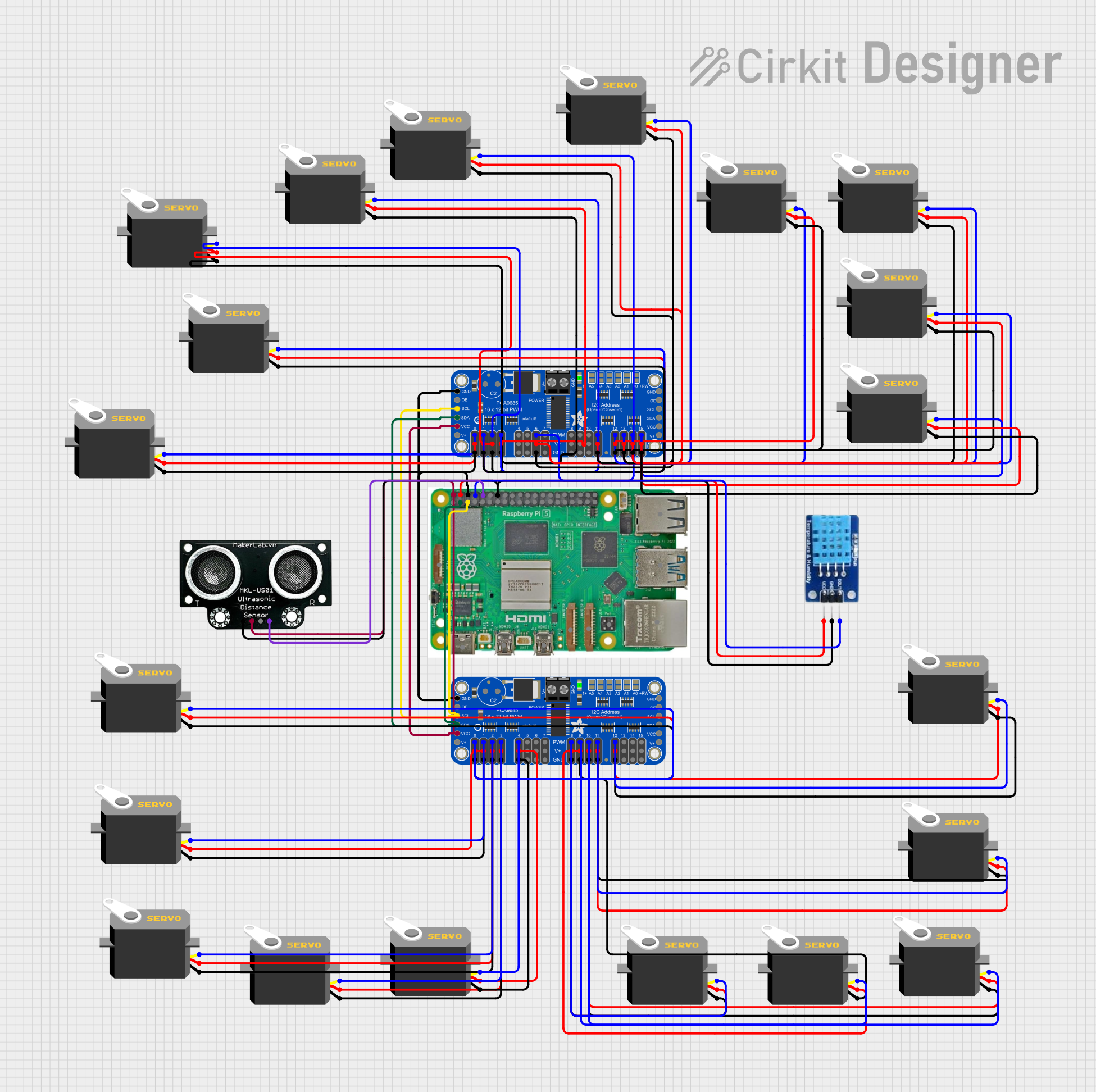
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with pca9685

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Controlling servo motors in robotic arms, drones, and RC vehicles
- LED dimming and RGB lighting control
- Stepper motor control
- General-purpose PWM signal generation for automation systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Number of Channels: 16 independent PWM outputs
- Resolution: 12-bit (4096 steps per channel)
- Communication Protocol: I2C (up to 1 MHz)
- Operating Voltage: 2.3V to 5.5V
- Output Voltage: Matches supply voltage (VCC)
- Output Current: Up to 25 mA per channel (sink), 10 mA (source)
- PWM Frequency: Adjustable from 24 Hz to 1526 Hz
- I2C Address Range: 0x40 to 0x7F (configurable via address pins)
- Package: TSSOP-28 or SOIC-28
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PCA9685 has 28 pins. Below is a description of the key pins:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power | Supply voltage (2.3V to 5.5V). |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection. |
| SDA | Input/Output | I2C data line. |
| SCL | Input | I2C clock line. |
| OE | Input | Output enable (active low). Disables all outputs when high. |
| A0–A5 | Input | Address pins for configuring the I2C address. |
| OUT0–OUT15 | Output | PWM output channels. |
| EXTCLK | Input | External clock input (optional). |
| V+ | Power | External power supply for driving servos or LEDs (separate from VCC). |
| RESET | Input | Resets the device when pulled low. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the PCA9685 in a Circuit
Powering the PCA9685:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- If driving servos or LEDs, connect an external power source to the V+ pin.
I2C Communication:
- Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller.
- Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines if not already present.
Configuring the I2C Address:
- Set the address pins (A0–A5) to either HIGH or LOW to configure the I2C address.
- The default address is 0x40 when all address pins are LOW.
Connecting Outputs:
- Connect servos, LEDs, or other devices to the OUT0–OUT15 pins.
- Ensure the total current draw does not exceed the PCA9685's limits.
Programming the PCA9685:
- Use an I2C library to communicate with the PCA9685.
- Set the PWM frequency and duty cycle for each channel as needed.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control servos using the PCA9685 with an Arduino UNO:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_PWMServoDriver.h>
// Create an instance of the PCA9685 driver
Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver();
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Initializing PCA9685...");
// Initialize the PCA9685
pwm.begin();
pwm.setPWMFreq(50); // Set PWM frequency to 50 Hz for servos
}
void loop() {
// Example: Move a servo connected to channel 0
int servoMin = 150; // Minimum pulse length (adjust for your servo)
int servoMax = 600; // Maximum pulse length (adjust for your servo)
// Sweep the servo from minimum to maximum position
for (int pulse = servoMin; pulse <= servoMax; pulse++) {
pwm.setPWM(0, 0, pulse); // Channel 0, start at 0, pulse width
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth movement
}
// Sweep the servo back to the minimum position
for (int pulse = servoMax; pulse >= servoMin; pulse--) {
pwm.setPWM(0, 0, pulse);
delay(10);
}
}
Important Considerations
- Use an external power supply for V+ when driving high-current devices like servos or LEDs.
- Ensure the total current draw does not exceed the PCA9685's maximum ratings.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the VCC and V+ pins to reduce noise.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Response from the PCA9685:
- Verify the I2C connections (SDA, SCL) and ensure pull-up resistors are present.
- Check the I2C address configuration and ensure it matches your code.
Servos or LEDs Not Working:
- Ensure the external power supply (V+) is connected and sufficient for your devices.
- Verify the PWM frequency and pulse width settings in your code.
Flickering LEDs or Erratic Servo Movement:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the V+ pin to stabilize the power supply.
- Check for loose or poor connections in the circuit.
Overheating:
- Ensure the total current draw does not exceed the PCA9685's limits.
- Use a heatsink or active cooling if necessary.
FAQs
Can I use multiple PCA9685 modules in one project? Yes, you can connect up to 62 PCA9685 modules on the same I2C bus by configuring their addresses.
What is the maximum PWM frequency? The PCA9685 supports PWM frequencies up to 1526 Hz.
Can I use the PCA9685 with a 3.3V microcontroller? Yes, the PCA9685 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
Do I need an external clock source? No, the PCA9685 has an internal oscillator, but you can use an external clock if higher precision is required.