
How to Use selector switch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with selector switch in Cirkit Designer
Design with selector switch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A selector switch, manufactured by SA (Part ID: SA), is an electromechanical device designed to allow users to select between multiple circuit paths or functions. It typically features multiple positions, enabling control over various operations in a circuit. Selector switches are widely used in industrial control panels, machinery, and consumer electronics for their reliability and ease of use.
Explore Projects Built with selector switch
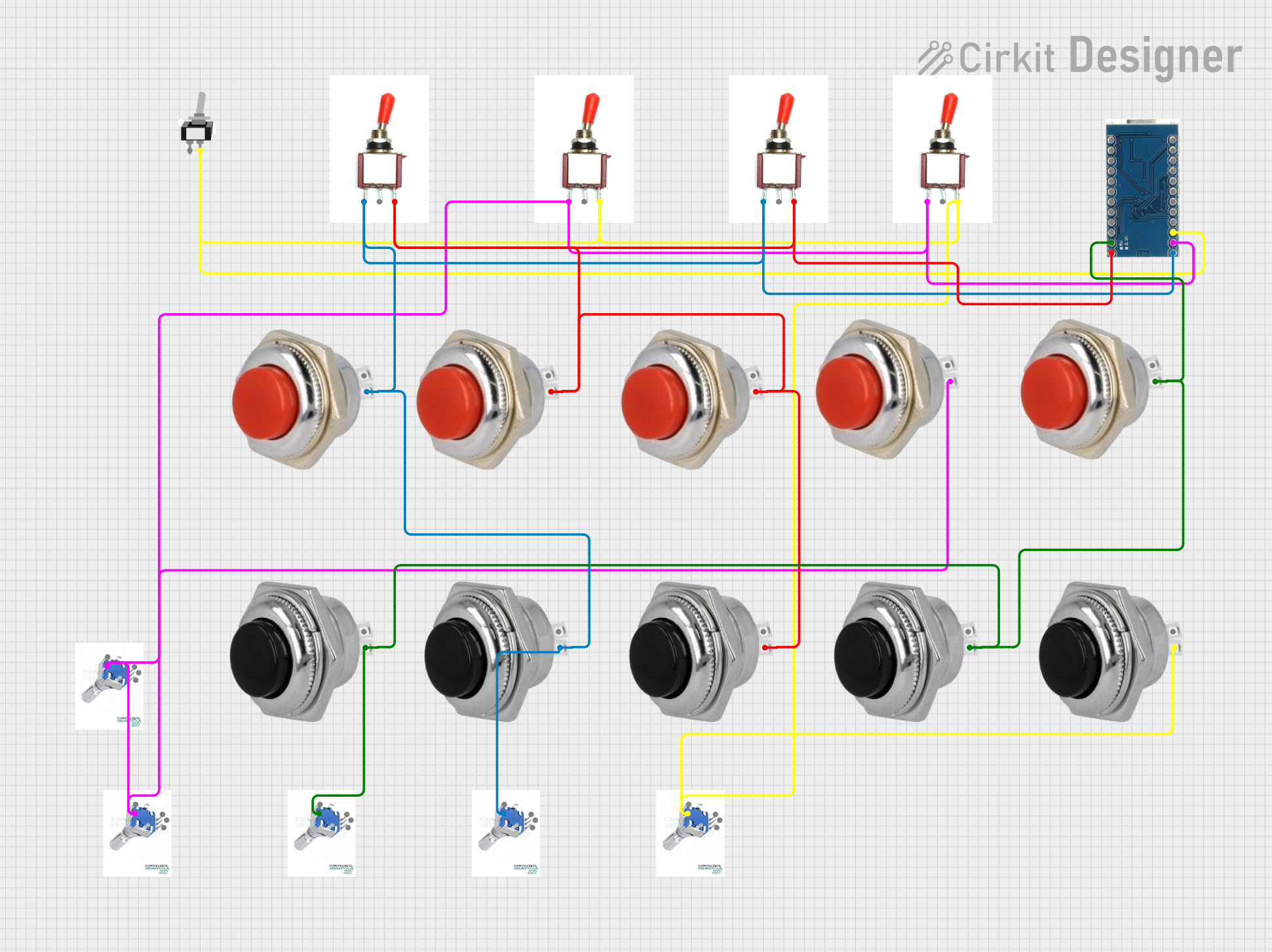
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer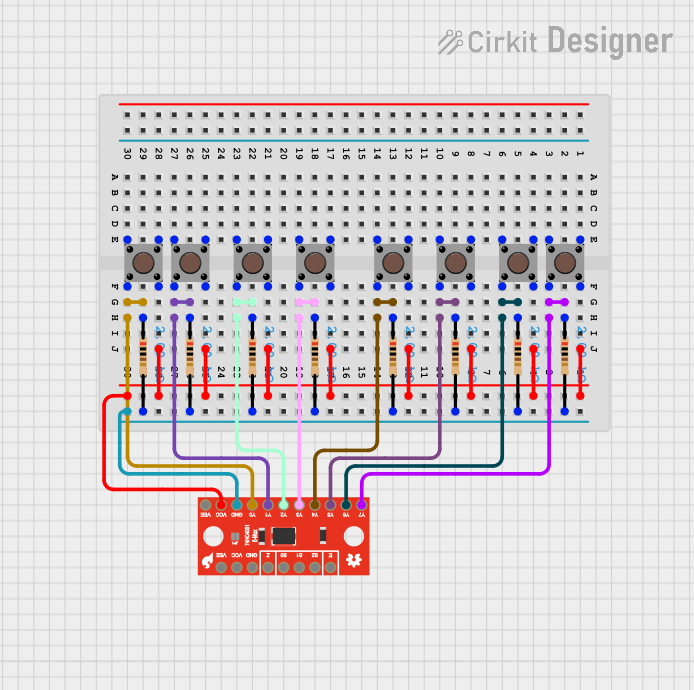
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer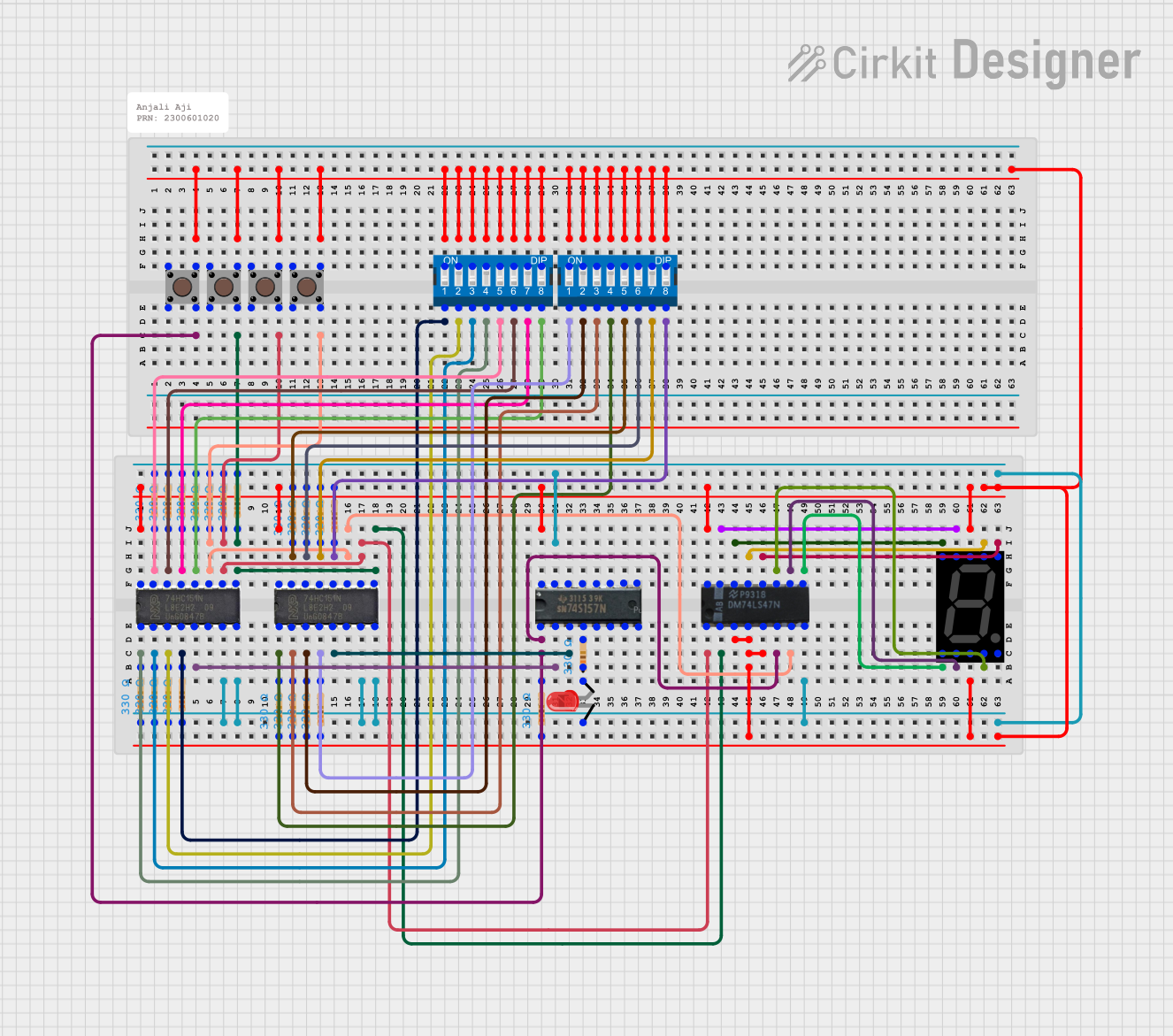
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with selector switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial control systems for selecting machine modes (e.g., manual, automatic, off).
- Consumer electronics for switching between different operational modes.
- Audio equipment for selecting input sources.
- Power distribution systems for routing power to different circuits.
- Test and measurement equipment for selecting test configurations.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: SA
- Part ID: SA
- Switch Type: Rotary or lever-based selector switch
- Positions: 2 to 12 positions (depending on the model)
- Contact Configuration: Single Pole Single Throw (SPST), Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT), or more complex configurations
- Voltage Rating: Up to 250V AC/DC (model-dependent)
- Current Rating: 5A to 20A (model-dependent)
- Mounting Style: Panel mount
- Material: High-durability plastic and metal contacts
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a selector switch depends on the number of positions and poles. Below is an example for a 3-position, Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) selector switch:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Common terminal (COM) |
| 2 | Output terminal for Position 1 |
| 3 | Output terminal for Position 2 |
For a more complex selector switch (e.g., 4-pole, 6-position), refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for detailed pinout information.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Selector Switch in a Circuit
- Identify the Terminals: Refer to the pin configuration table or the datasheet to identify the common terminal (COM) and the output terminals for each position.
- Connect the Common Terminal: Connect the common terminal to the input voltage or signal source.
- Connect the Output Terminals: Connect the output terminals to the desired circuit paths or devices.
- Mount the Switch: Secure the selector switch to a panel or enclosure using the provided mounting hardware.
- Test the Circuit: Rotate or toggle the selector switch to ensure proper operation and verify that the correct circuit paths are activated.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the selector switch is rated for the voltage and current of your application to avoid damage or failure.
- Debouncing: If the selector switch is used in a digital circuit, consider implementing debouncing techniques to prevent false triggering.
- Wiring: Use appropriate wire gauges and connectors to ensure reliable connections.
- Environmental Conditions: Avoid exposing the switch to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust unless it is specifically rated for such conditions.
Example: Connecting a Selector Switch to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a 3-position selector switch with an Arduino UNO to read its position:
// Define the pins connected to the selector switch
const int position1Pin = 2; // Pin connected to Position 1 terminal
const int position2Pin = 3; // Pin connected to Position 2 terminal
const int commonPin = 4; // Pin connected to Common terminal
void setup() {
// Set the selector switch pins as inputs
pinMode(position1Pin, INPUT);
pinMode(position2Pin, INPUT);
pinMode(commonPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // Use internal pull-up resistor
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the state of the selector switch
bool position1State = digitalRead(position1Pin);
bool position2State = digitalRead(position2Pin);
// Determine the switch position and print it
if (position1State == LOW) {
Serial.println("Selector Switch is in Position 1");
} else if (position2State == LOW) {
Serial.println("Selector Switch is in Position 2");
} else {
Serial.println("Selector Switch is in Neutral/Off Position");
}
delay(500); // Add a small delay for stability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Switch Not Functioning Properly:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the terminals are properly secured.
Intermittent Operation:
- Cause: Dirty or worn contacts inside the switch.
- Solution: Clean the contacts with a contact cleaner or replace the switch if necessary.
Incorrect Position Detection in Digital Circuits:
- Cause: Switch bouncing.
- Solution: Implement software or hardware debouncing techniques.
Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the voltage or current rating.
- Solution: Verify the ratings and replace the switch with a higher-rated model if needed.
FAQs
Q: Can the selector switch handle both AC and DC currents?
A: Yes, most selector switches are designed to handle both AC and DC currents, but always check the voltage and current ratings for your specific model.Q: How do I know which position the switch is in?
A: The position can be determined by the physical marking on the switch or by measuring the continuity between the common terminal and the output terminals.Q: Can I use a selector switch for high-frequency signals?
A: Selector switches are generally not suitable for high-frequency signals due to potential signal degradation. Use a specialized RF switch for such applications.Q: Is the selector switch waterproof?
A: Standard selector switches are not waterproof. If you need a waterproof switch, look for models with an IP65 or higher rating.