
How to Use KY-040: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
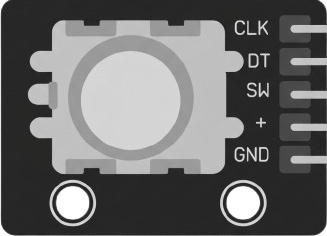
 Design with KY-040 in Cirkit Designer
Design with KY-040 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The KY-040 is a rotary encoder module that allows for precise control of position and rotation. Unlike a potentiometer, which provides an absolute position, the KY-040 outputs incremental signals, making it ideal for applications requiring relative position tracking. It features a built-in push button and provides two output signals (A and B) that can be used to determine the direction and amount of rotation.
Explore Projects Built with KY-040
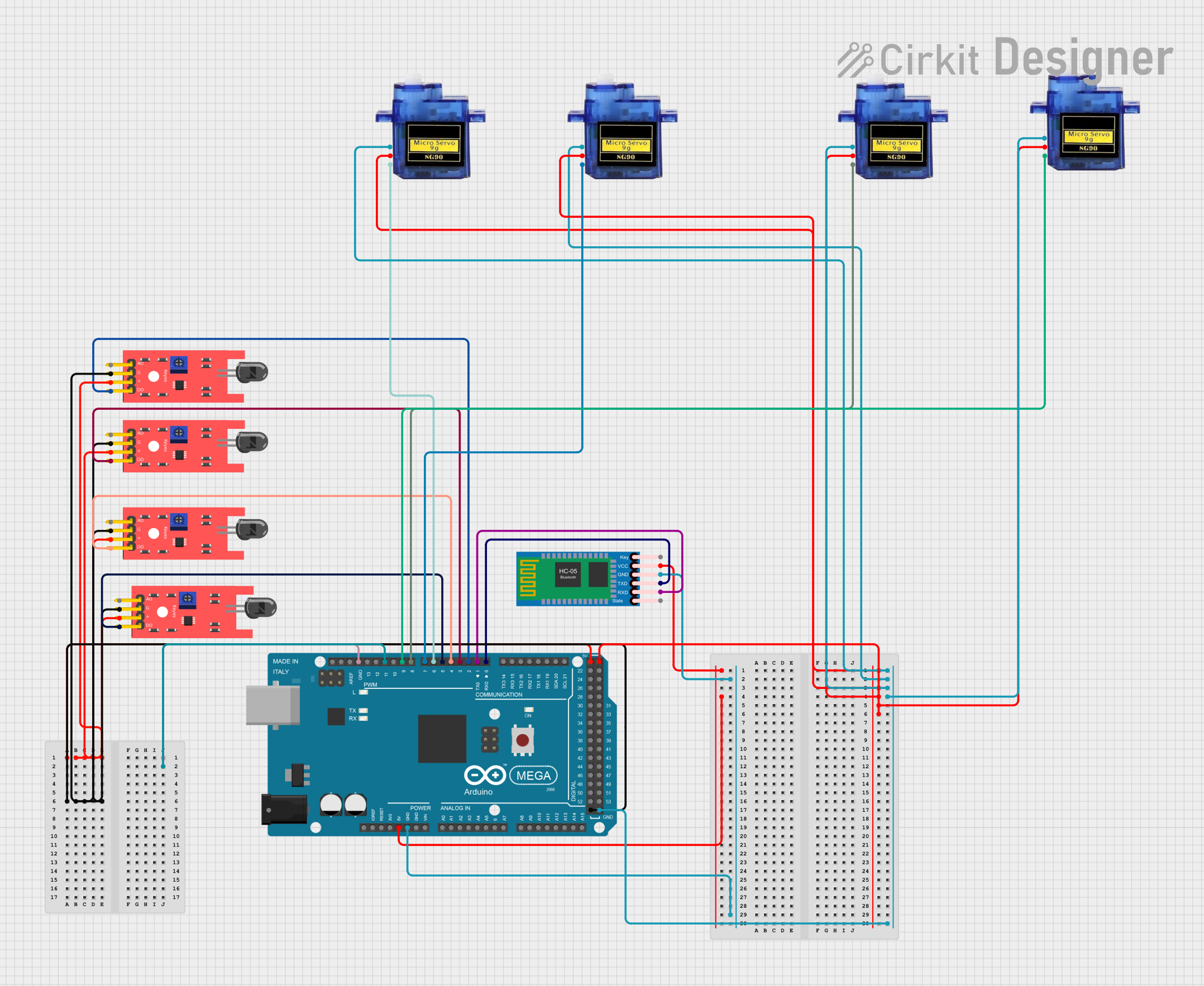
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer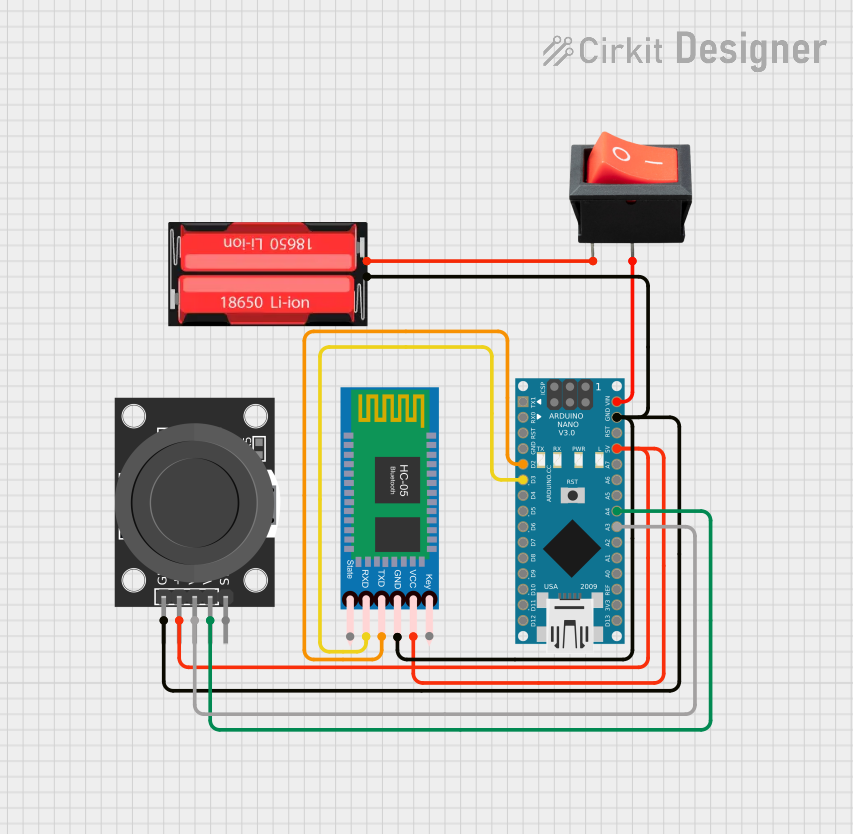
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer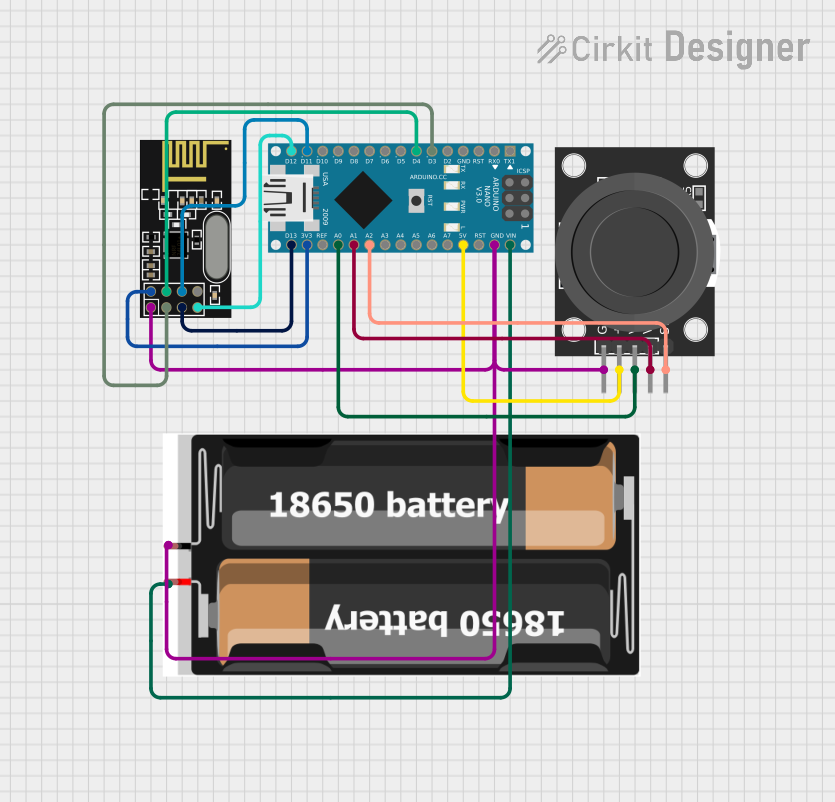
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer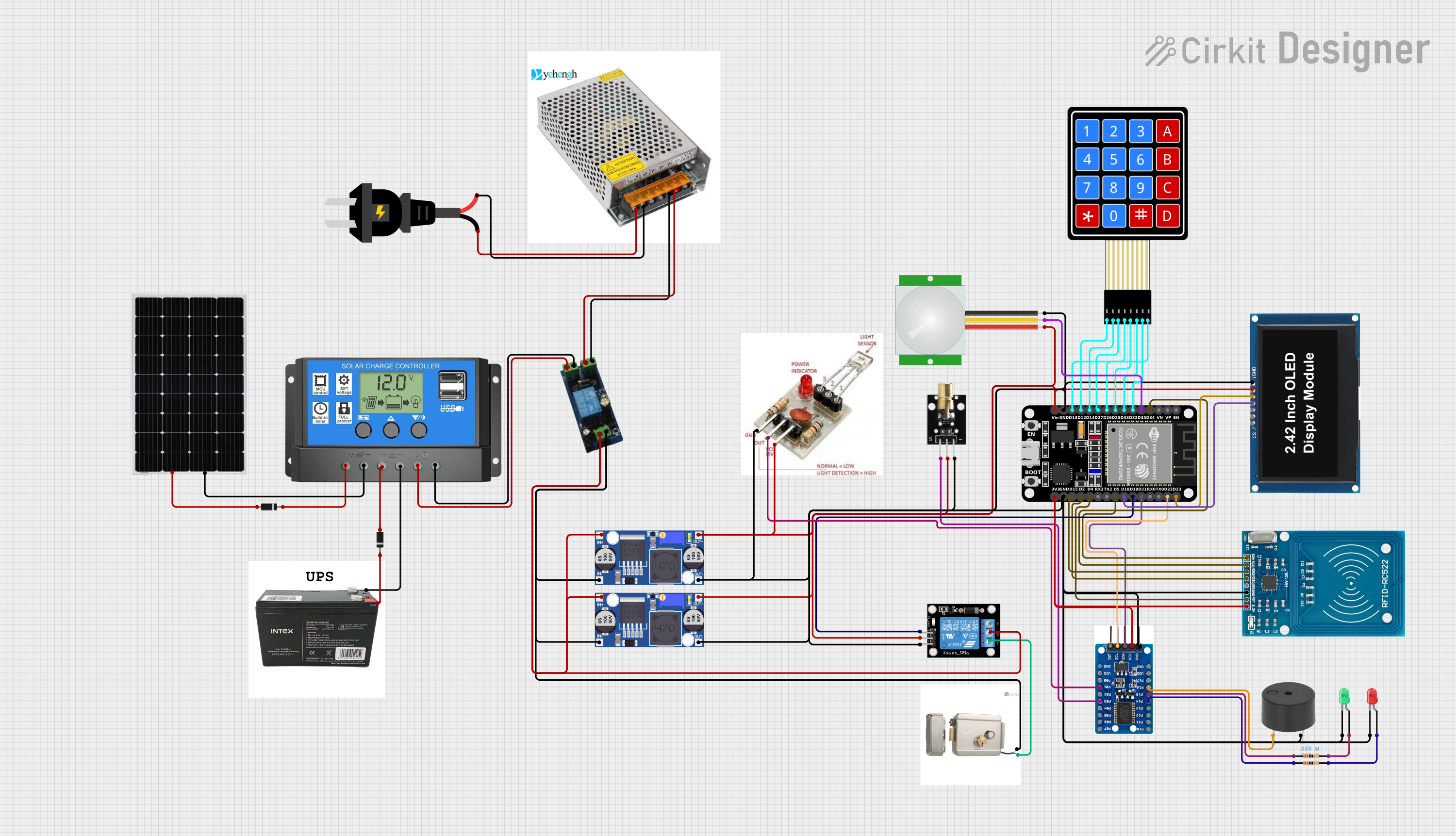
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with KY-040

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Volume control in audio devices
- Menu navigation in embedded systems
- Motor speed and position control
- Robotics and automation systems
- User input for microcontroller-based projects
Technical Specifications
The KY-040 rotary encoder module has the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Type | Digital (Incremental) |
| Number of Pins | 5 |
| Push Button | Built-in |
| Rotational Steps | 20 steps per full rotation |
| Dimensions | 32mm x 19mm x 30mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The KY-040 module has five pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | + | Power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 3 | SW | Push button output (active LOW) |
| 4 | DT | Data signal (Channel B) |
| 5 | CLK | Clock signal (Channel A) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the KY-040 in a Circuit
- Connect the Power Supply: Connect the
+pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - Connect the Output Pins:
- Connect the
CLK(Channel A) andDT(Channel B) pins to digital input pins on your microcontroller. - Optionally, connect the
SWpin to a digital input pin if you want to use the push button.
- Connect the
- Read the Signals:
- Monitor the
CLKandDTsignals to determine the direction and amount of rotation. - The
SWpin can be used to detect button presses.
- Monitor the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: The KY-040 outputs may produce noise or "bouncing" signals. Use software debouncing or external capacitors to ensure clean signal readings.
- Pull-up Resistors: If the
SWpin is not functioning as expected, ensure that a pull-up resistor is enabled in your microcontroller or added externally. - Power Supply: Ensure the module is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5V) to avoid damage.
Example: Using KY-040 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to read the KY-040 rotary encoder and detect rotation direction and button presses:
// Define KY-040 pins
#define CLK 2 // Clock pin (Channel A)
#define DT 3 // Data pin (Channel B)
#define SW 4 // Push button pin
int lastStateCLK; // To store the previous state of the CLK pin
int currentStateCLK; // To store the current state of the CLK pin
int counter = 0; // Counter to track rotation
bool buttonPressed = false; // Flag for button press
void setup() {
pinMode(CLK, INPUT);
pinMode(DT, INPUT);
pinMode(SW, INPUT_PULLUP); // Enable internal pull-up resistor for SW pin
// Read the initial state of the CLK pin
lastStateCLK = digitalRead(CLK);
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the current state of the CLK pin
currentStateCLK = digitalRead(CLK);
// If the state of CLK has changed, a rotation has occurred
if (currentStateCLK != lastStateCLK) {
// Check the direction of rotation
if (digitalRead(DT) != currentStateCLK) {
counter++; // Clockwise rotation
} else {
counter--; // Counterclockwise rotation
}
// Print the counter value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
// Update the last state of CLK
lastStateCLK = currentStateCLK;
// Check if the button is pressed
if (digitalRead(SW) == LOW) {
if (!buttonPressed) {
Serial.println("Button Pressed!");
buttonPressed = true; // Set the flag to avoid multiple prints
}
} else {
buttonPressed = false; // Reset the flag when the button is released
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Response from the Encoder:
- Ensure the power supply is connected correctly and within the specified voltage range.
- Verify that the
CLKandDTpins are connected to the correct microcontroller pins.
Incorrect Rotation Readings:
- Check for loose or faulty connections.
- Implement software debouncing to filter out noise from the encoder signals.
Push Button Not Working:
- Ensure the
SWpin is connected to a digital input pin with a pull-up resistor enabled. - Verify that the button is being pressed fully.
- Ensure the
Erratic or Unstable Readings:
- Add a small capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between the
CLKandGNDpins, and between theDTandGNDpins, to reduce noise.
- Add a small capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between the
FAQs
Q: Can the KY-040 be used with 3.3V microcontrollers like the ESP32?
A: Yes, the KY-040 is compatible with 3.3V systems. Ensure the power supply and signal levels match the microcontroller's requirements.
Q: How do I increase the resolution of the encoder?
A: The KY-040 has a fixed resolution of 20 steps per rotation. For higher resolution, consider using a different encoder with more steps.
Q: Can I use the KY-040 for absolute position tracking?
A: No, the KY-040 is an incremental encoder and does not provide absolute position information. It is best suited for relative position tracking.