
How to Use Adapter power voltage: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Adapter power voltage in Cirkit Designer
Design with Adapter power voltage in Cirkit DesignerAdapter Power Voltage Documentation
1. Introduction
The Adapter Power Voltage is a crucial electronic component designed to convert electrical power from one voltage level to another. This functionality is essential for ensuring that various electronic devices operate at their required voltage levels, thereby enhancing their performance and longevity.
Common applications of the Adapter Power Voltage include:
- Powering microcontrollers and development boards (e.g., Arduino, ESP32)
- Supplying power to sensors and actuators in robotics
- Adapting power supplies for consumer electronics
- Providing voltage regulation in renewable energy systems
2. Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 100-240V AC |
| Output Voltage | 5V, 9V, 12V DC |
| Output Current | Up to 2A |
| Power Rating | 10W to 24W |
| Efficiency | >85% |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AC Input | Connects to the AC power source |
| 2 | DC Output | Provides the converted DC voltage |
| 3 | Ground | Common ground connection |
| 4 | Voltage Select | Selects the output voltage level (if applicable) |
3. Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the AC Input: Attach the AC input pins to a suitable power source (100-240V AC).
- Set the Output Voltage: If the adapter has a voltage select pin, configure it to the desired output voltage (5V, 9V, or 12V).
- Connect the DC Output: Use the DC output pin to connect to your device, ensuring that the voltage matches the device's requirements.
- Ground Connection: Connect the ground pin to the common ground of your circuit.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Always verify that the output voltage matches the requirements of your device to prevent damage.
- Current Rating: Ensure that the current drawn by your device does not exceed the adapter's rated output current.
- Heat Management: Monitor the adapter for excessive heat during operation, as overheating can lead to failure.
- Safety Precautions: Handle the AC connections with care, and ensure that the adapter is properly insulated.
4. Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Device Not Powering On:
- Solution: Check the connections and ensure that the input voltage is correct.
Overheating:
- Solution: Ensure that the load does not exceed the adapter's current rating. Allow for proper ventilation.
Incorrect Output Voltage:
- Solution: Verify the voltage select setting (if applicable) and check for any faults in the adapter.
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Always use a multimeter to measure the output voltage and current.
- Inspect the adapter for any visible damage or wear.
- If the adapter is not functioning, consider testing it with a different load to isolate the issue.
5. Example Code for Arduino UNO
If you are using the Adapter Power Voltage to power an Arduino UNO, here is a simple code example to get you started:
// Simple LED Blink Example
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
This code will blink an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO, demonstrating that the board is powered correctly by the Adapter Power Voltage.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the Adapter Power Voltage in their projects, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Explore Projects Built with Adapter power voltage

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer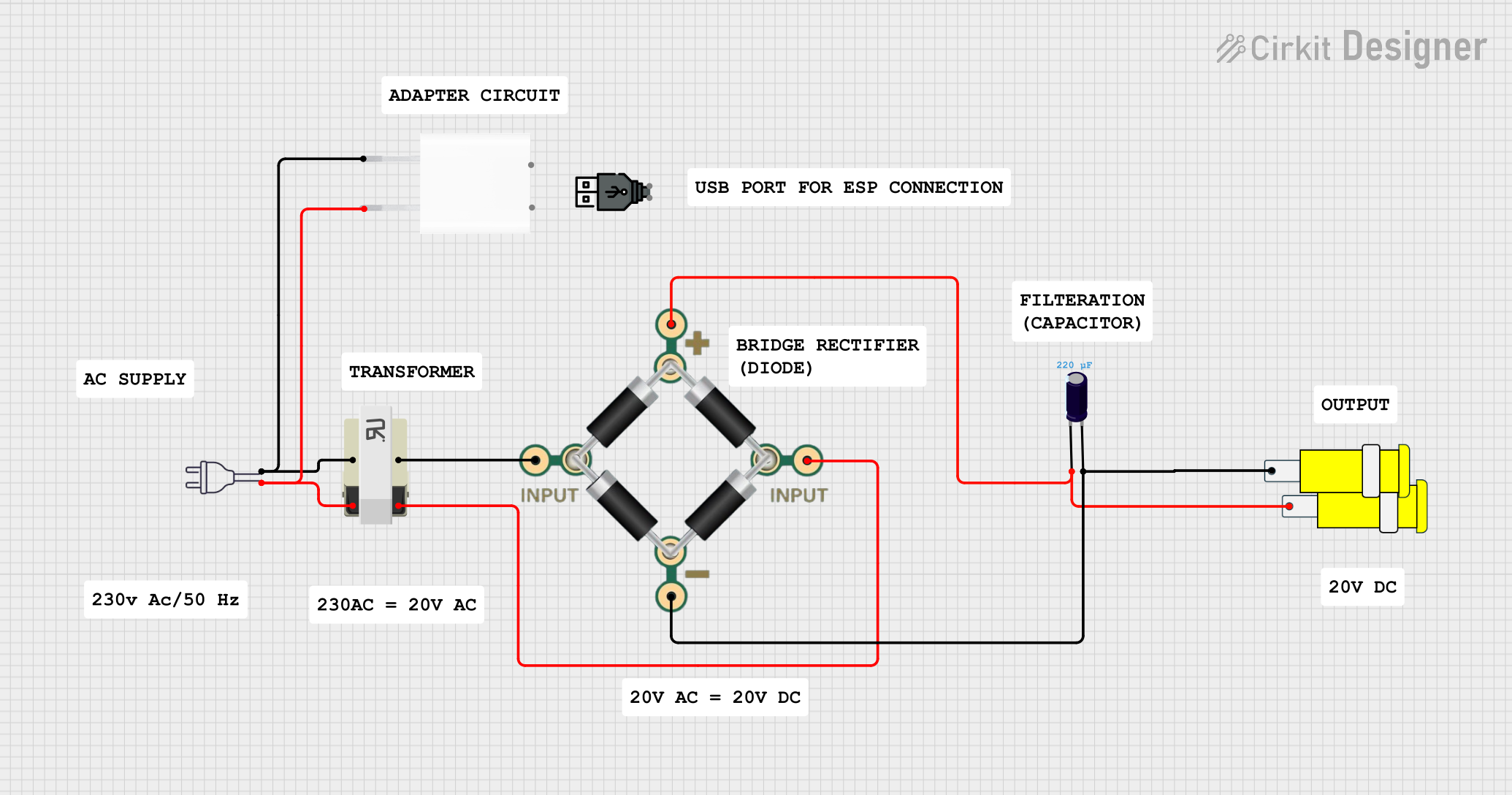
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Adapter power voltage

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer