
How to Use Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC, 8S / 33.6V with 5 AMP BEC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
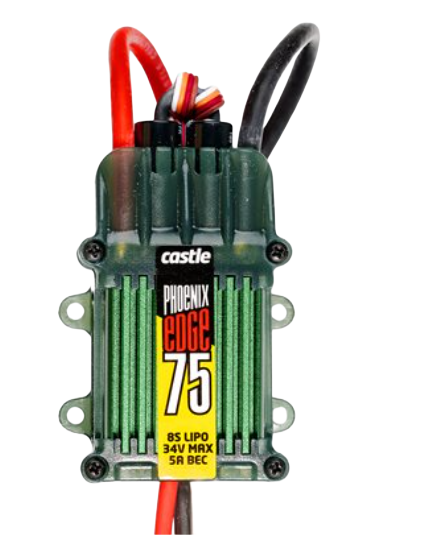

 Design with Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC, 8S / 33.6V with 5 AMP BEC in Cirkit Designer
Design with Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC, 8S / 33.6V with 5 AMP BEC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC is a high-performance electronic speed controller (ESC) designed for demanding applications in RC vehicles, drones, and other motor-driven systems. Manufactured by Phoenix, this ESC is capable of handling up to 75 amps of continuous current and supports 8S lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries, providing a maximum input voltage of 33.6V. It also features an integrated 5 amp battery eliminator circuit (BEC), which can power servos, receivers, and other auxiliary devices without requiring a separate power source.
Explore Projects Built with Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC, 8S / 33.6V with 5 AMP BEC
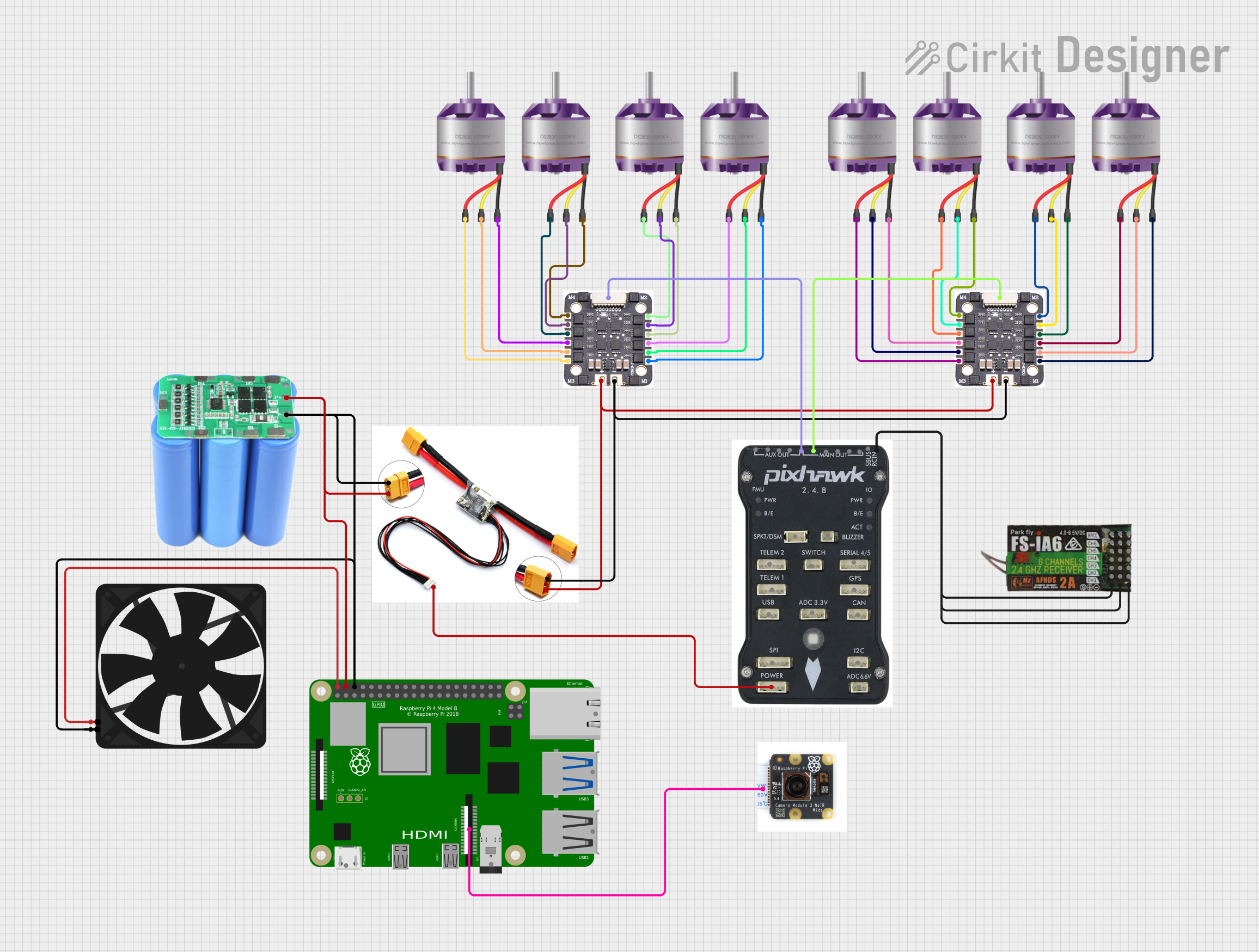
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer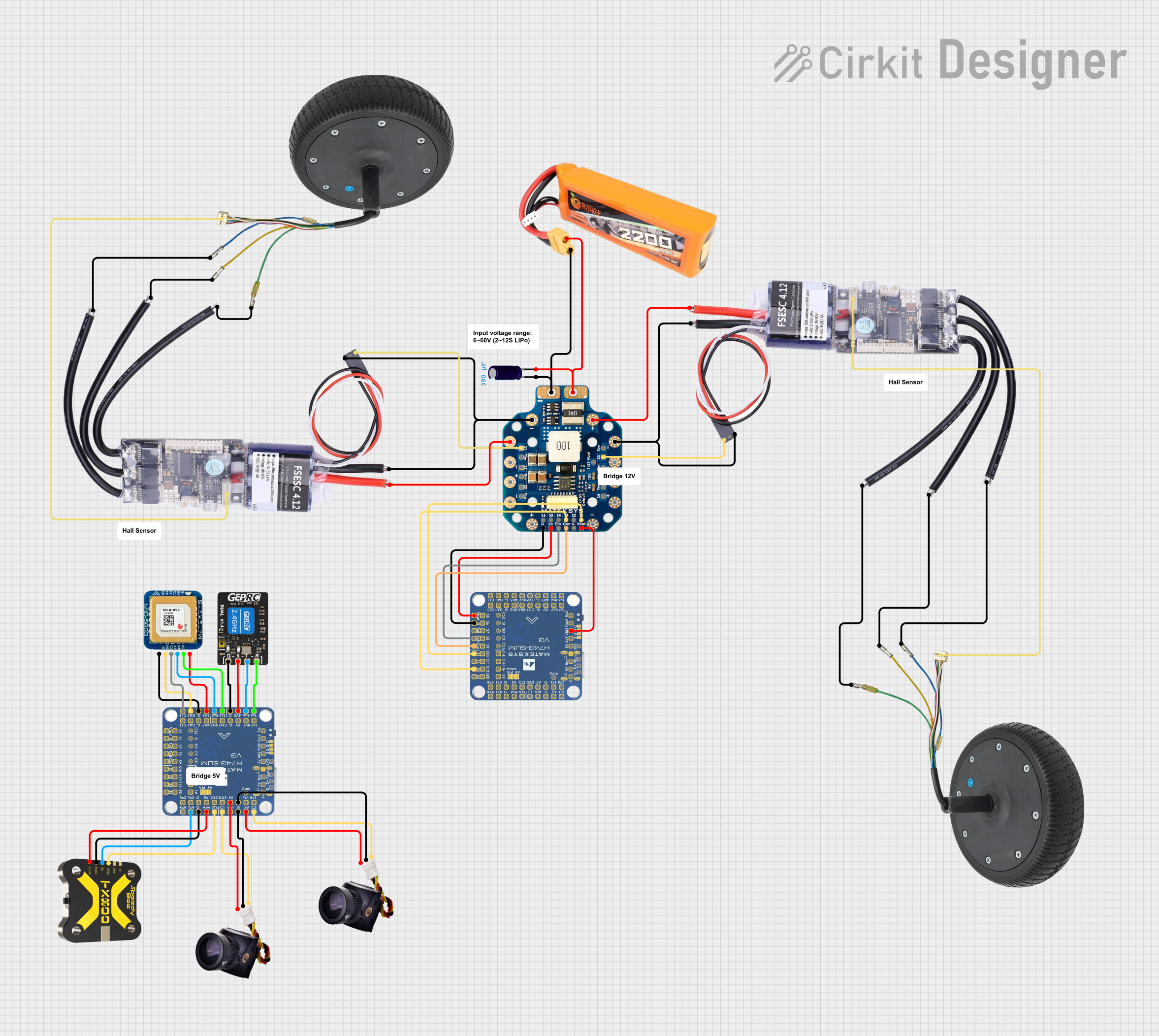
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer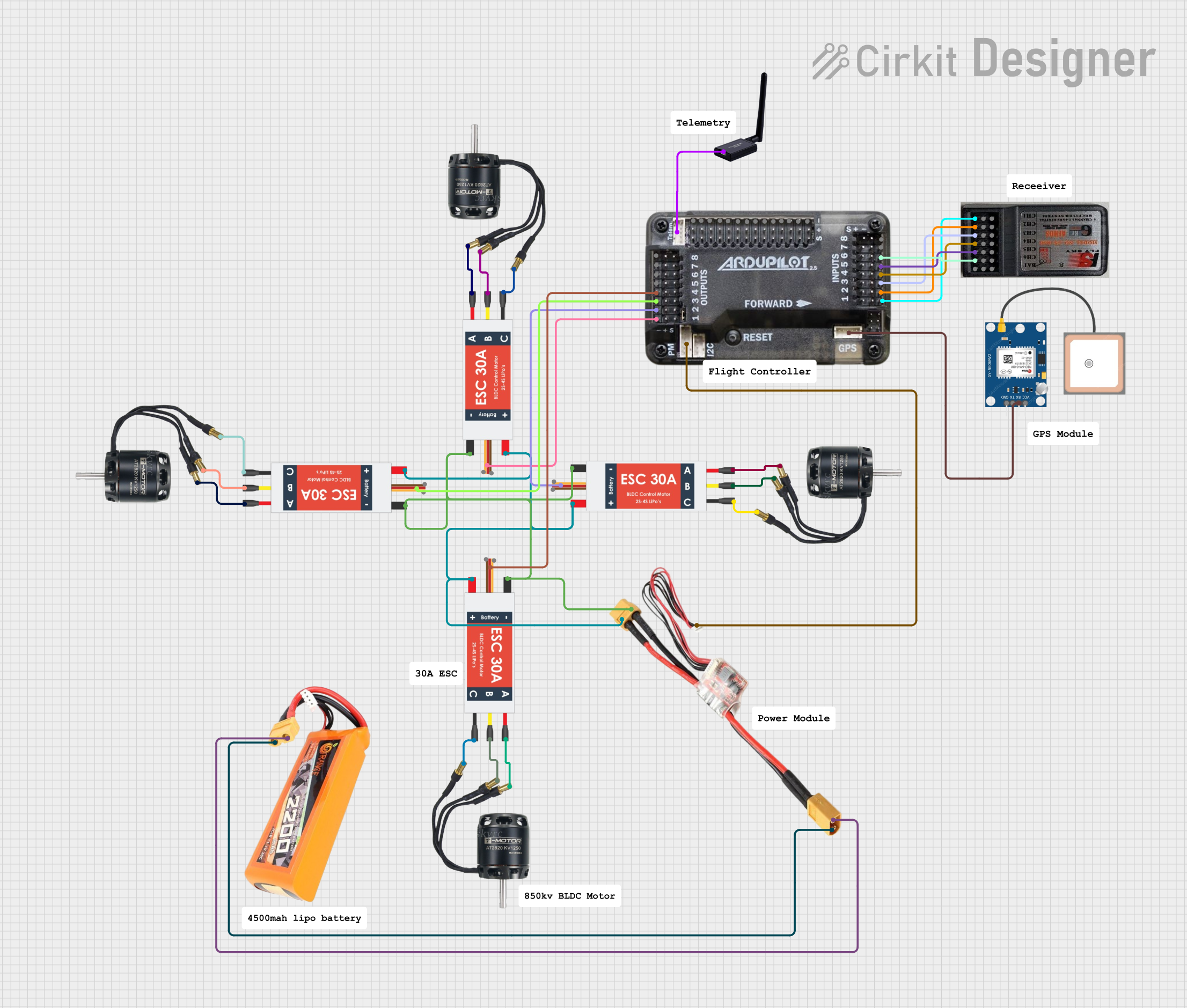
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC, 8S / 33.6V with 5 AMP BEC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- RC airplanes, helicopters, and drones
- High-performance RC cars and boats
- Robotics and automation systems
- Custom motor control projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Phoenix |
| Part ID | ESC RC |
| Continuous Current Rating | 75 Amps |
| Input Voltage Range | 2S to 8S LiPo (7.4V to 33.6V) |
| BEC Output | 5 Amps @ 5.0V (linear regulator) |
| Dimensions | 2.1 x 1.0 x 0.6 inches (53 x 25 x 15 mm) |
| Weight | 1.5 oz (42.5 grams) |
| Motor Compatibility | Brushless motors |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20°C to 85°C |
| Safety Features | Overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, low-voltage cutoff |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery Input | Connects to the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the LiPo battery. |
| Motor Output | Three wires (A, B, C) for connecting to the brushless motor. |
| Signal Input | Standard 3-pin servo connector for receiving throttle signals from the receiver. |
| BEC Output | Provides 5V power to the receiver and servos via the signal input connector. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Battery: Attach the LiPo battery to the ESC's battery input terminals, ensuring correct polarity.
- Connect the Motor: Connect the three motor wires (A, B, C) to the brushless motor. If the motor spins in the wrong direction, swap any two wires.
- Connect the Receiver: Plug the ESC's signal input connector into the throttle channel of your RC receiver.
- Power On: Turn on the transmitter first, then connect the battery to the ESC. The ESC will initialize and emit a series of beeps to indicate readiness.
- Calibrate Throttle: Follow the ESC's user manual to calibrate the throttle range for optimal performance.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Selection: Use only 2S to 8S LiPo batteries within the specified voltage range.
- Cooling: Ensure adequate airflow around the ESC to prevent overheating during operation.
- Wiring: Use appropriately rated wires and connectors to handle the high current.
- Programming: Use the Phoenix programming interface (if available) to customize settings such as throttle response, braking, and timing.
Arduino UNO Example Code
The Phoenix Edge ESC can be controlled using a PWM signal from an Arduino UNO. Below is an example code snippet to control the ESC:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library for PWM control
Servo esc; // Create a Servo object to control the ESC
void setup() {
esc.attach(9); // Attach the ESC signal wire to pin 9 on the Arduino
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Send minimum throttle signal (1000 µs)
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds to allow the ESC to initialize
}
void loop() {
esc.writeMicroseconds(1500); // Send a mid-throttle signal (1500 µs)
delay(5000); // Run the motor at mid-throttle for 5 seconds
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Send minimum throttle signal to stop the motor
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before repeating
}
Note: Ensure the ESC is properly calibrated before using it with an Arduino. Refer to the ESC's user manual for calibration instructions.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or throttle signal not detected.
- Solution: Verify motor connections (A, B, C) and ensure the ESC is receiving a valid PWM signal from the receiver or Arduino.
ESC Overheating
- Cause: Insufficient cooling or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Improve airflow around the ESC and ensure the motor and propeller are not overloading the system.
Beeping Sounds
- Cause: Low battery voltage or throttle signal not detected.
- Solution: Check the battery voltage and ensure the transmitter is powered on and bound to the receiver.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction
- Cause: Incorrect motor wiring.
- Solution: Swap any two of the three motor wires (A, B, C) to reverse the direction.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this ESC with a brushed motor?
A: No, the Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC is designed specifically for brushless motors.Q: How do I program the ESC?
A: Use the Phoenix programming interface or follow the manual's instructions for programming via the transmitter.Q: What happens if I exceed the 75A current limit?
A: The ESC's overcurrent protection will activate, shutting down the motor to prevent damage.Q: Can I use this ESC with a 12V lead-acid battery?
A: No, this ESC is designed for use with 2S to 8S LiPo batteries only.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the Phoenix Edge 75 AMP ESC into their projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.