
How to Use Motor Servo Analog Output: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
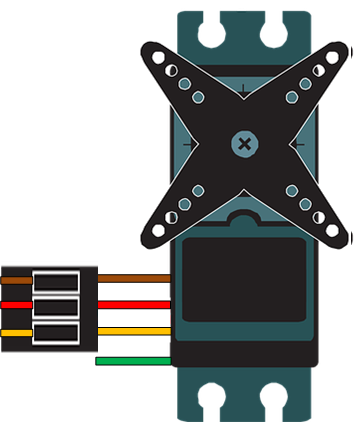
 Design with Motor Servo Analog Output in Cirkit Designer
Design with Motor Servo Analog Output in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Motor Servo Analog Output is a type of servo motor that operates using an analog signal to control its position. Unlike digital servos, which rely on pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals, analog servos respond to continuous voltage changes to adjust their position. These servos are widely used in robotics, RC vehicles, and automation systems due to their simplicity and reliability.
Explore Projects Built with Motor Servo Analog Output
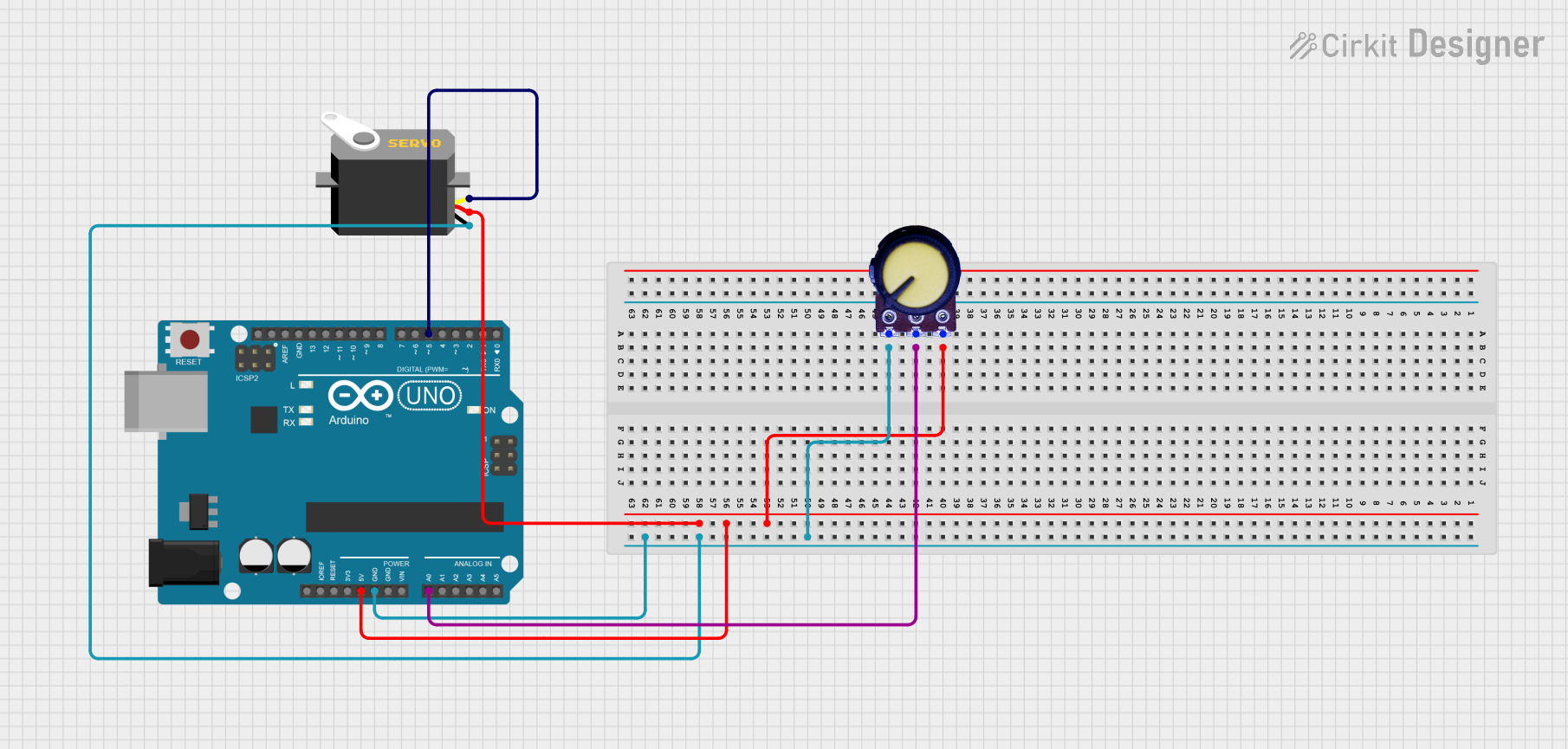
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer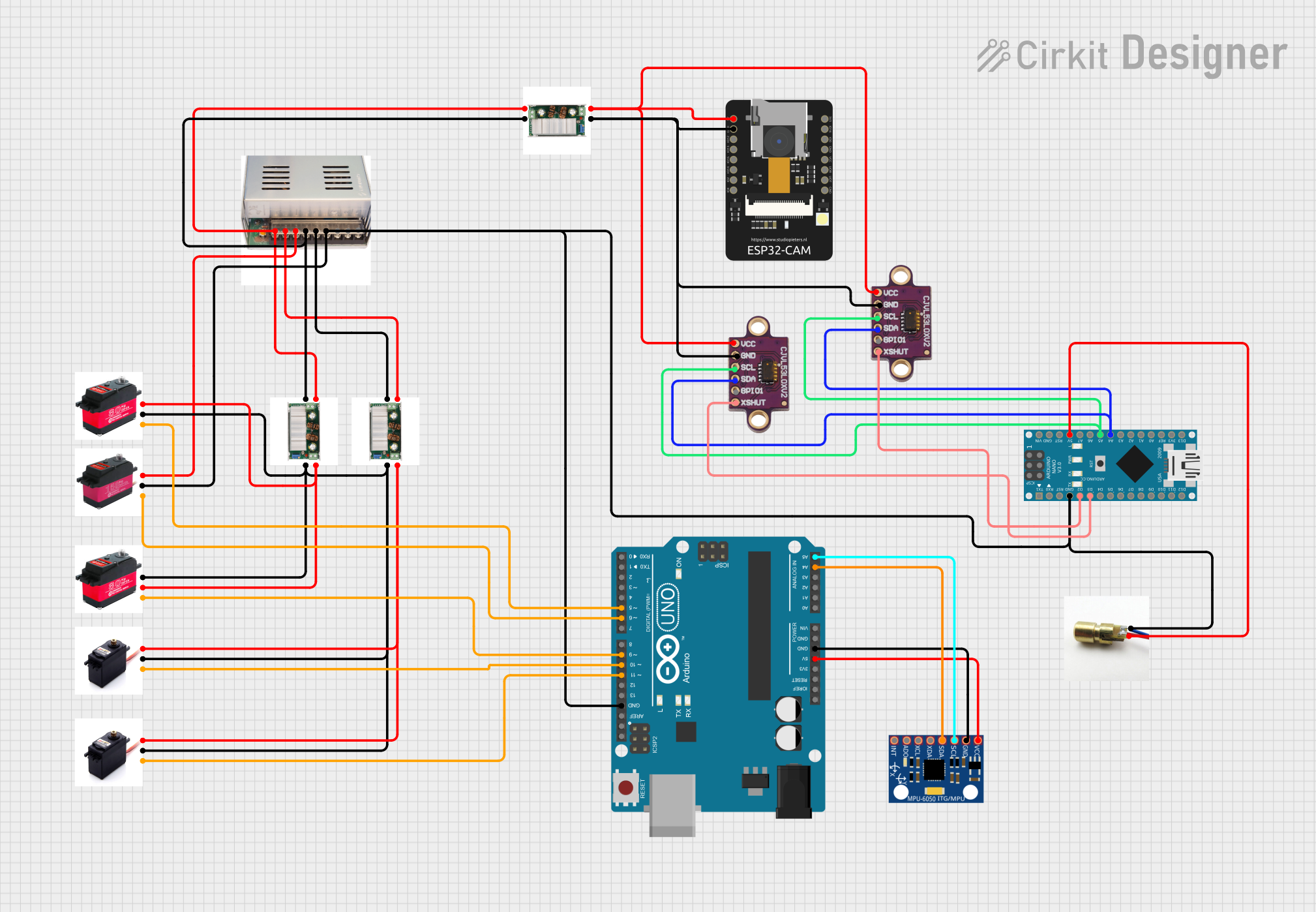
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer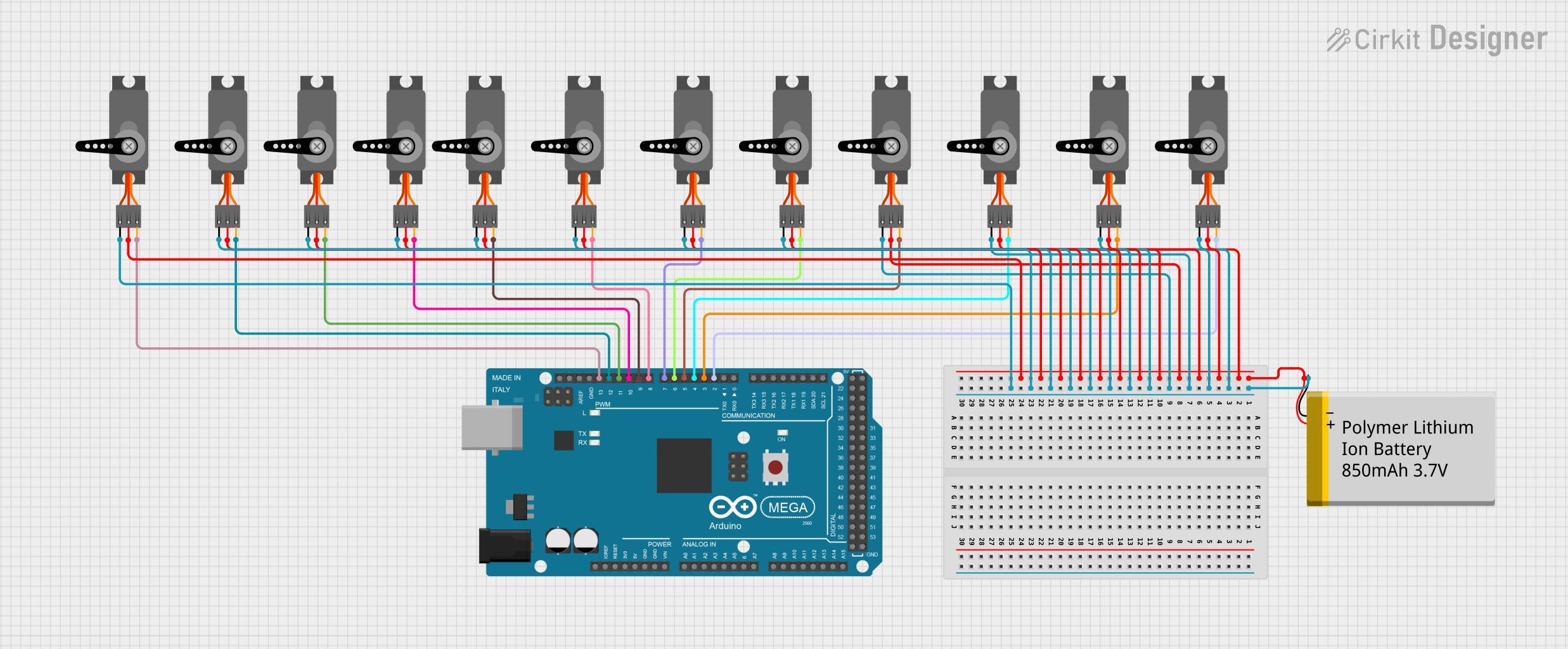
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer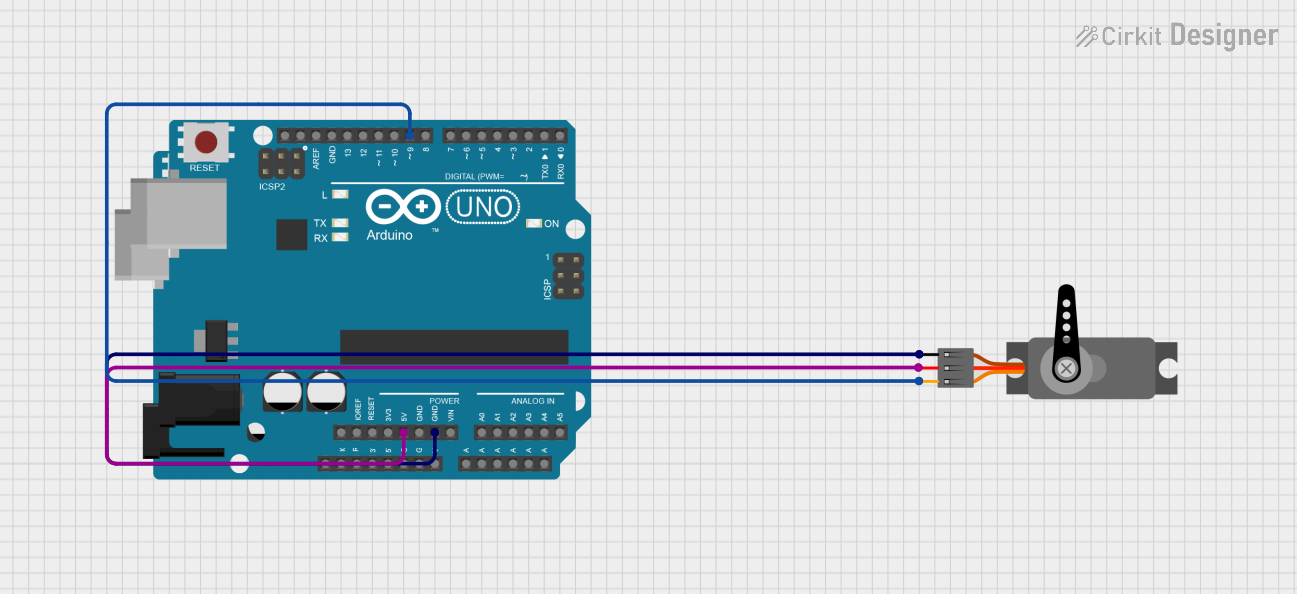
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Motor Servo Analog Output

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: For controlling arms, grippers, and joints.
- Remote-controlled vehicles: Steering and throttle control.
- Automation systems: Positioning mechanisms in industrial equipment.
- Educational projects: Demonstrating motion control concepts.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V to 6.0V
- Operating Current: 100mA to 500mA (depending on load)
- Torque: 1.5 kg·cm to 10 kg·cm (varies by model)
- Signal Type: Analog voltage (typically 0V to 5V)
- Rotation Range: 0° to 180° (standard), 360° for continuous rotation models
- Response Time: ~0.2 seconds per 60° (at 6.0V)
- Connector Type: 3-pin (Signal, VCC, GND)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description | Wire Color (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | Receives the analog control signal | Orange or White |
| VCC | Power supply (4.8V to 6.0V) | Red |
| GND | Ground connection | Black or Brown |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Servo: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Control Signal: Connect the Signal pin to an analog output pin of your microcontroller or a potentiometer for manual control.
- Load Considerations: Ensure the servo's torque rating is sufficient for the load it will move. Overloading the servo can cause overheating or failure.
- Power Supply: Use a dedicated power supply for the servo if it draws significant current, as this can prevent voltage drops in your circuit.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the torque rating of the servo to prevent damage.
- Stable Power Supply: Use capacitors near the servo to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
- Analog Signal Range: Ensure the control signal voltage matches the servo's specifications (typically 0V to 5V).
- Avoid Continuous Stalling: Prolonged stalling can overheat the motor and reduce its lifespan.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a Motor Servo Analog Output using an Arduino UNO and a potentiometer.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the servo's Signal pin to Arduino pin A0.
- Connect the servo's VCC pin to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the servo's GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Connect a potentiometer to Arduino pin A1 for manual control.
Arduino Code
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo myServo; // Create a Servo object
void setup() {
myServo.attach(A0); // Attach the servo to pin A0
}
void loop() {
int potValue = analogRead(A1); // Read the potentiometer value
int angle = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 180);
// Map the potentiometer value to a range of 0 to 180 degrees
myServo.write(angle); // Set the servo position
delay(15); // Small delay for smooth movement
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Servo Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply meets the servo's requirements.
Jittery Movement:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Add a capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the VCC and GND pins to stabilize the voltage.
Overheating:
- Cause: Continuous stalling or overloading.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the servo or use a higher-torque model.
Limited Range of Motion:
- Cause: Incorrect signal range or mechanical obstruction.
- Solution: Verify the control signal range and check for physical obstructions.
FAQs
Can I use a digital PWM signal with this servo? No, this servo is designed for analog voltage control. Using a PWM signal may result in erratic behavior.
What happens if I exceed the voltage rating? Exceeding the voltage rating can damage the servo's internal circuitry. Always stay within the specified range.
Can I control multiple servos with one microcontroller? Yes, but ensure the power supply can handle the combined current draw of all servos.
How do I know if the servo is overloaded? Signs of overloading include reduced movement speed, jittering, or overheating. Reduce the load or use a higher-torque servo.