
How to Use Diode (Output Rectifier): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
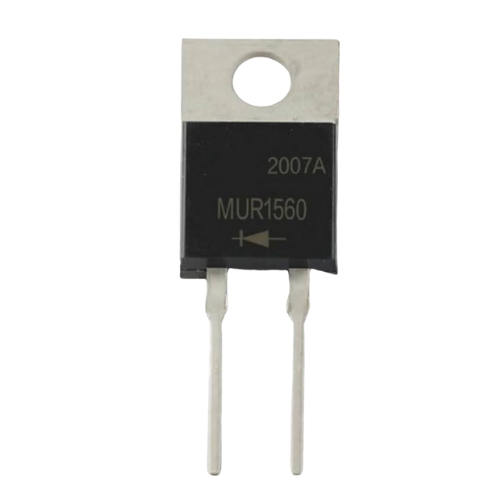

 Design with Diode (Output Rectifier) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Diode (Output Rectifier) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Diode (Output Rectifier), manufactured by John, is a semiconductor device designed to allow current to flow in one direction only. This component is primarily used in power supply circuits to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). Its rectification properties make it an essential component in various electronic applications, including power adapters, battery chargers, and DC power supplies.
Explore Projects Built with Diode (Output Rectifier)
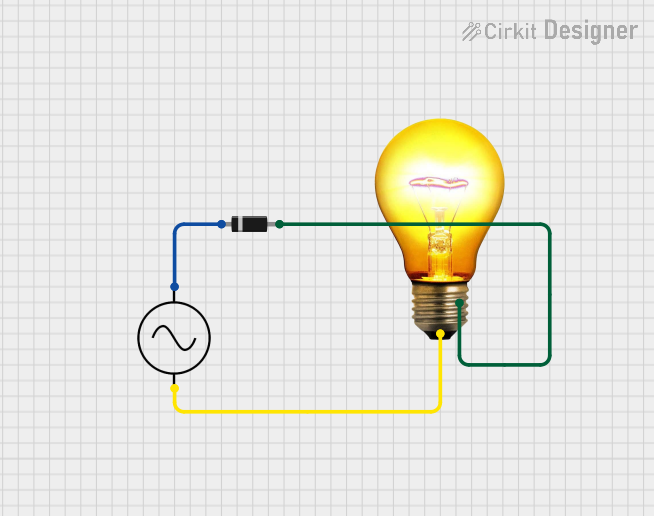
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer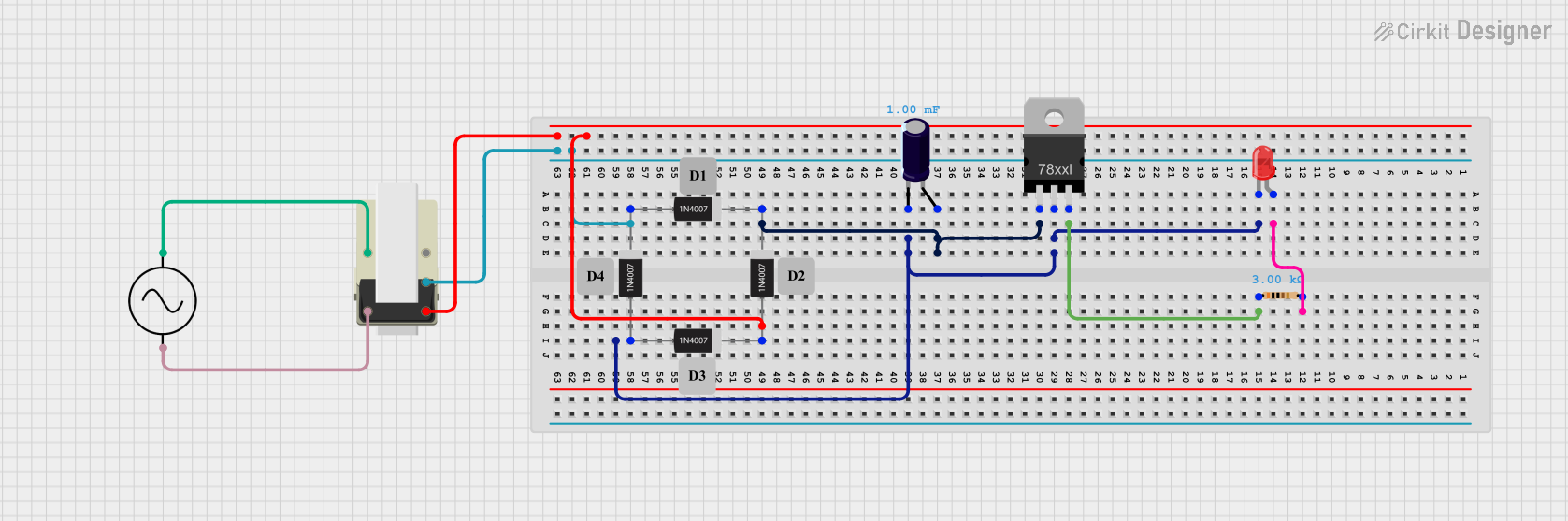
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer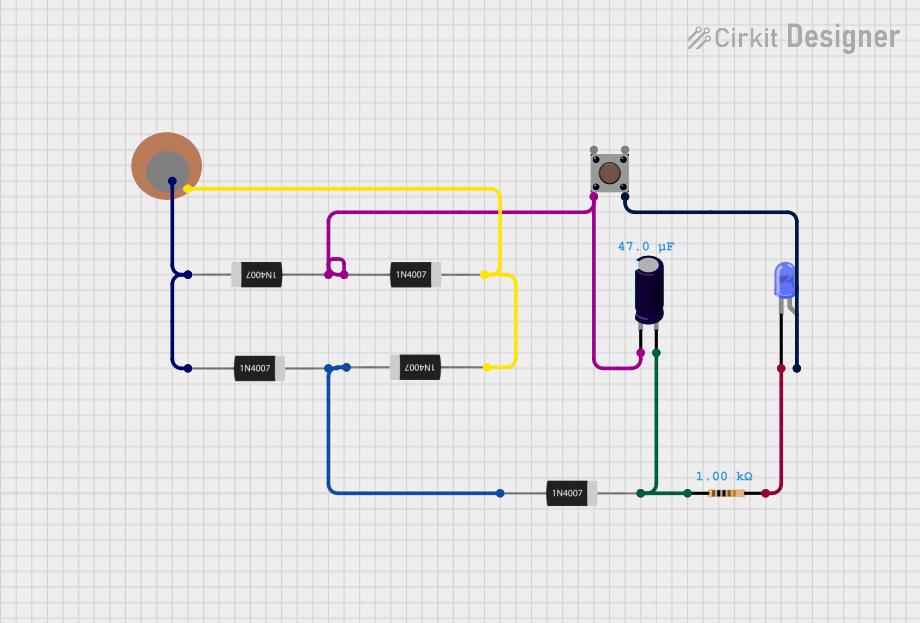
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer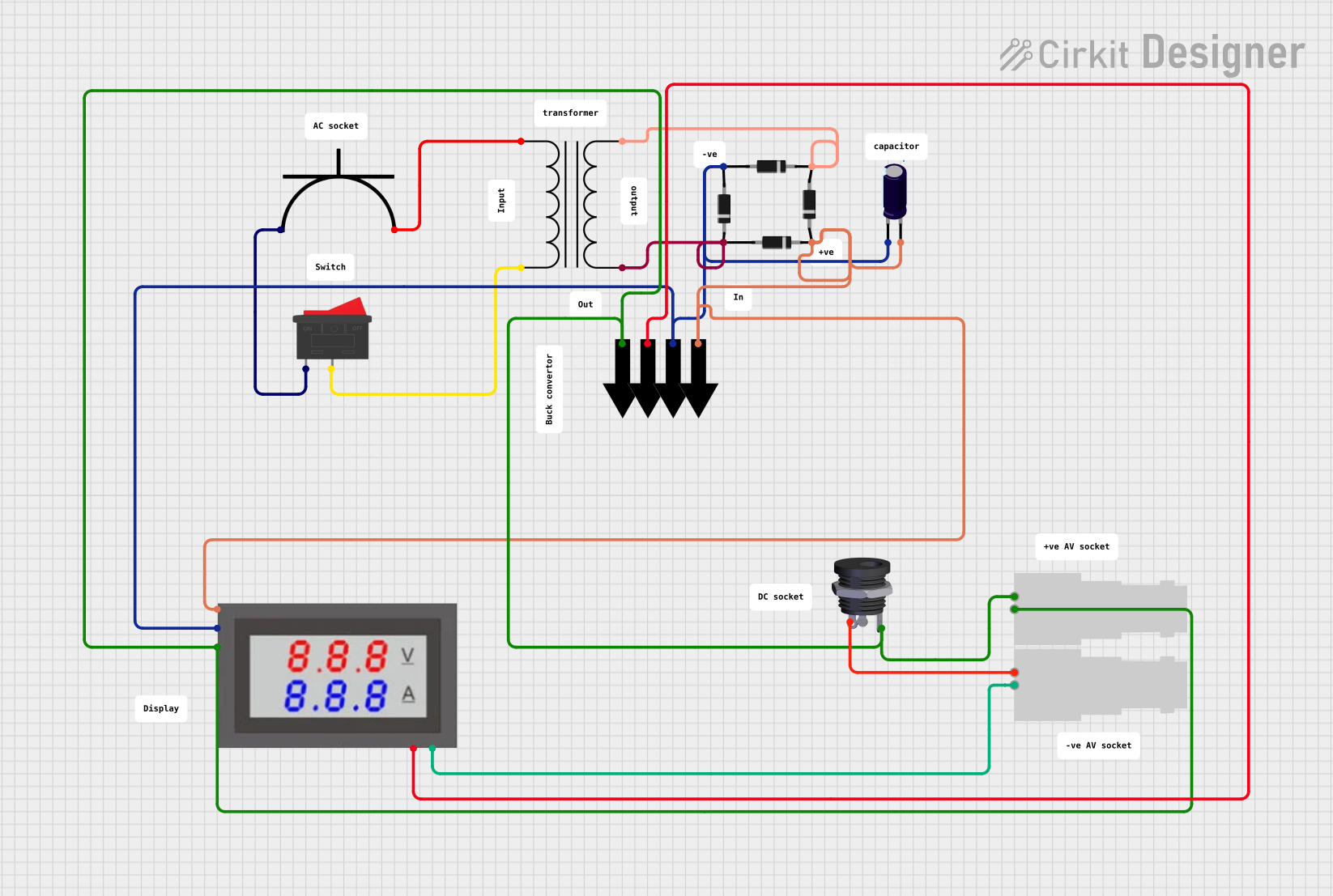
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Diode (Output Rectifier)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- AC to DC conversion in power supply circuits
- Voltage regulation and protection
- Signal demodulation in communication systems
- Freewheeling diodes in motor control circuits
- Reverse polarity protection in electronic devices
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the John Diode (Output Rectifier):
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Reverse Voltage (VR) | 100V - 1000V (varies by model) |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | 0.7V (Silicon) / 0.3V (Schottky) |
| Maximum Forward Current (IF) | 1A - 10A (varies by model) |
| Peak Surge Current (IFSM) | 30A - 150A (varies by model) |
| Reverse Recovery Time (trr) | 50ns - 200ns (varies by model) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +150°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The diode has two terminals: Anode and Cathode. The following table describes the pin configuration:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Anode | Positive terminal where current enters the diode. |
| Cathode | Negative terminal where current exits the diode. |
The cathode is typically marked with a band or stripe on the diode body for easy identification.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Diode in a Circuit
- Identify the Anode and Cathode: Locate the cathode stripe on the diode body to ensure proper orientation.
- Connect the Diode:
- For rectification, connect the anode to the AC source and the cathode to the DC load.
- Ensure the diode is oriented correctly to allow current flow in the desired direction.
- Add Supporting Components:
- Use a capacitor in parallel with the load to smooth the rectified DC output.
- For bridge rectifier configurations, use four diodes arranged in a bridge topology.
- Verify Ratings:
- Ensure the diode's voltage and current ratings exceed the circuit's requirements to prevent damage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: High current flow can generate heat. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation if necessary.
- Reverse Voltage Protection: Avoid exceeding the maximum reverse voltage rating to prevent breakdown.
- Surge Current: Protect the diode from high inrush currents by using a series resistor or inrush current limiter.
- Testing: Use a multimeter in diode mode to verify the diode's functionality before installation.
Example: Using a Diode with an Arduino UNO
The diode can be used to protect an Arduino UNO from reverse polarity. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Description
- Place the diode in series with the Arduino's power input (VIN pin).
- Connect the anode to the power source and the cathode to the Arduino's VIN pin.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code to blink an LED connected to pin 13
// Ensure the diode protects the Arduino from reverse polarity
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Diode Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current or insufficient heat dissipation.
- Solution: Use a diode with a higher current rating or add a heatsink.
No Current Flow:
- Cause: Incorrect orientation of the diode.
- Solution: Verify the anode and cathode connections.
Voltage Drop Too High:
- Cause: Using a silicon diode instead of a Schottky diode.
- Solution: Replace with a Schottky diode for lower forward voltage drop.
Diode Failure:
- Cause: Exceeding reverse voltage or forward current ratings.
- Solution: Use a diode with appropriate ratings for the application.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this diode for high-frequency applications?
A: Yes, but ensure the reverse recovery time (trr) is suitable for the operating frequency. Schottky diodes are recommended for high-frequency circuits.
Q: How do I test if a diode is working?
A: Use a multimeter in diode mode. A functional diode will show a low voltage drop (e.g., 0.7V for silicon) in the forward direction and no conduction in the reverse direction.
Q: Can this diode protect my circuit from reverse polarity?
A: Yes, place the diode in series with the power supply to block reverse current flow.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the John Diode (Output Rectifier) in your electronic projects.