
How to Use SN65HVD232DR : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with SN65HVD232DR in Cirkit Designer
Design with SN65HVD232DR in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SN65HVD232DR is a high-speed CAN (Controller Area Network) transceiver manufactured by Texas Instruments. It is designed to enable robust and reliable communication in automotive, industrial, and other demanding environments. This transceiver supports data rates of up to 1 Mbps, making it ideal for high-speed communication systems. Additionally, it features low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The device operates over a wide voltage range and includes built-in protection against overvoltage, electrostatic discharge (ESD), and thermal faults.
Explore Projects Built with SN65HVD232DR
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SN65HVD232DR

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive communication systems (e.g., in-vehicle networking)
- Industrial automation and control systems
- Battery-powered devices requiring CAN communication
- Building automation and HVAC systems
- Medical equipment with CAN-based communication
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 3.3 V to 5 V |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps |
| Bus Voltage Range | -2 V to +7 V |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| ESD Protection | ±16 kV (Human Body Model) |
| Low Power Mode | <370 µA (Standby mode) |
| Receiver Differential Input Resistance | 30 kΩ (typical) |
| Package Type | SOIC-8 (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
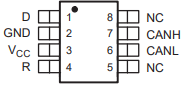
The SN65HVD232DR is an 8-pin device with the following pinout:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | D | Driver input (TXD) - Data input for the CAN bus. |
| 2 | GND | Ground - Connect to system ground. |
| 3 | Vcc | Supply voltage - Connect to 3.3 V or 5 V. |
| 4 | R | Receiver output (RXD) - Data output from the CAN bus. |
| 5 | CANL | Low-level CAN bus line. |
| 6 | CANH | High-level CAN bus line. |
| 7 | Rs | Slope control - Connect a resistor to ground to control the driver slew rate. |
| 8 | NC | No connection - Leave unconnected. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the SN65HVD232DR in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin to a 3.3 V or 5 V power supply and the GND pin to the system ground.
- CAN Bus Lines: Connect the CANH and CANL pins to the corresponding high and low lines of the CAN bus.
- Data Input/Output:
- Connect the D pin to the microcontroller's TXD (transmit data) pin.
- Connect the R pin to the microcontroller's RXD (receive data) pin.
- Slope Control: Use a resistor between the Rs pin and ground to control the driver slew rate. For high-speed operation, connect Rs directly to ground.
- Termination Resistor: Add a 120 Ω termination resistor between CANH and CANL at each end of the CAN bus for proper signal integrity.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the supply voltage (Vcc) is stable and within the specified range (3.3 V to 5 V).
- Use proper decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor) close to the Vcc pin to filter noise.
- Avoid long stubs on the CAN bus to minimize signal reflections and maintain signal integrity.
- Ensure that the CAN bus is properly terminated with 120 Ω resistors at both ends.
- For ESD protection, ensure that the device is properly grounded and consider using additional external protection diodes if needed.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The SN65HVD232DR can be used with an Arduino UNO to enable CAN communication. Below is an example of how to connect the transceiver to the Arduino and a sample code snippet for sending data.
Wiring Diagram
| SN65HVD232DR Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| D (TXD) | D2 |
| R (RXD) | D3 |
| Vcc | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| CANH | CANH (to CAN bus) |
| CANL | CANL (to CAN bus) |
| Rs | GND (for high-speed operation) |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SPI.h>
#include <mcp_can.h>
// Define the CAN bus CS pin
#define CAN_CS_PIN 10
// Initialize the CAN bus object
MCP_CAN CAN(CAN_CS_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
// Initialize the CAN bus at 500 kbps
if (CAN.begin(MCP_ANY, CAN_500KBPS, MCP_8MHZ) == CAN_OK) {
Serial.println("CAN bus initialized successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Error initializing CAN bus.");
while (1);
}
// Set the CAN bus to normal mode
CAN.setMode(MCP_NORMAL);
Serial.println("CAN bus set to normal mode.");
}
void loop() {
// Example data to send
byte data[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
// Send data on CAN bus
if (CAN.sendMsgBuf(0x100, 0, 8, data) == CAN_OK) {
Serial.println("Message sent successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Error sending message.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending the next message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication on the CAN Bus:
- Verify that the Vcc and GND pins are properly connected.
- Ensure that the CAN bus is terminated with 120 Ω resistors at both ends.
- Check the wiring between the transceiver and the microcontroller.
Data Corruption or Errors:
- Ensure that the CANH and CANL lines are not swapped.
- Verify that the slope control resistor on the Rs pin is appropriate for the desired data rate.
Device Overheating:
- Check for short circuits on the CANH and CANL lines.
- Ensure that the supply voltage does not exceed the maximum rating.
Low Power Mode Not Working:
- Verify that the Rs pin is properly configured for low power mode.
FAQs
Q: Can the SN65HVD232DR operate at 3.3 V?
A: Yes, the device supports a supply voltage range of 3.3 V to 5 V.
Q: What is the maximum data rate supported by the SN65HVD232DR?
A: The transceiver supports data rates of up to 1 Mbps.
Q: Is the SN65HVD232DR suitable for automotive applications?
A: Yes, the device is designed for robust communication in automotive environments and operates over a wide temperature range (-40°C to +125°C).
Q: How do I protect the device from ESD?
A: The SN65HVD232DR includes built-in ESD protection (±16 kV HBM). For additional protection, consider using external TVS diodes on the CANH and CANL lines.