
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use Step-Down Converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Step-Down Converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with Step-Down Converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Step-Down Converter, commonly referred to as a Buck Converter, is an essential electronic component used in power management applications. It is a type of DC-DC converter that efficiently reduces an input voltage to a lower output voltage while allowing control over the output current. This component is widely used in battery-operated devices, power supplies, and portable electronics to extend battery life and optimize power consumption.
Explore Projects Built with Step-Down Converter
Battery-Powered UPS with Step-Down Buck Converter and BMS

This circuit is a power management system that steps down a 240V AC input to a lower DC voltage using a buck converter, which then powers a 40W UPS. The UPS is controlled by a rocker switch and is backed up by a battery management system (BMS) connected to three 3.7V batteries in series, ensuring continuous power supply.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino Mega 2560-Based Robotic System with Stepper Motors and IR Sensors
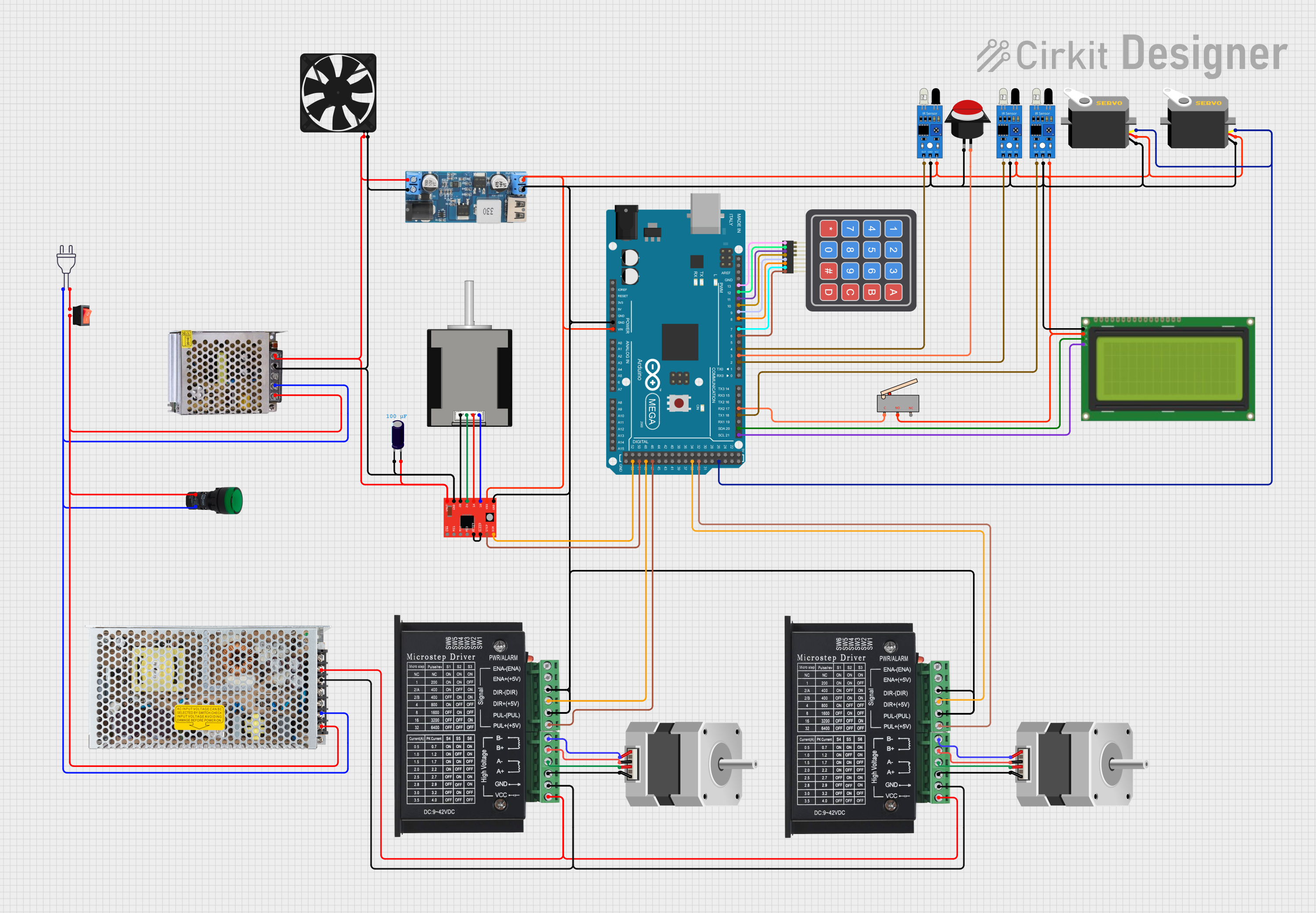
This circuit is a control system powered by a 12V to 5V step-down converter, featuring an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller that interfaces with various sensors (IR sensors, limit switch), actuators (servos, stepper motors), and a 20x4 LCD display. The system is designed to monitor inputs from sensors and control outputs to motors and display information, suitable for applications like automation or robotics.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerBattery-Powered DC Generator with XL4015 Buck Converter

This circuit consists of a 12V battery connected to a rocker switch, which controls the input to an XL4015 DC Buck Step-down converter. The converter steps down the voltage to power a DC generator, with the generator's output connected back to the converter to form a feedback loop.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerUSB Power Supply with Overcurrent Protection

This circuit is designed to step down voltage from a 12V battery to a lower voltage suitable for USB devices. It includes a buck converter connected to the battery through a fuse and fuse holder for overcurrent protection. The output of the buck converter is connected to a USB female port, providing a regulated power supply for USB-powered devices.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Step-Down Converter

Battery-Powered UPS with Step-Down Buck Converter and BMS
This circuit is a power management system that steps down a 240V AC input to a lower DC voltage using a buck converter, which then powers a 40W UPS. The UPS is controlled by a rocker switch and is backed up by a battery management system (BMS) connected to three 3.7V batteries in series, ensuring continuous power supply.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino Mega 2560-Based Robotic System with Stepper Motors and IR Sensors
This circuit is a control system powered by a 12V to 5V step-down converter, featuring an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller that interfaces with various sensors (IR sensors, limit switch), actuators (servos, stepper motors), and a 20x4 LCD display. The system is designed to monitor inputs from sensors and control outputs to motors and display information, suitable for applications like automation or robotics.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Battery-Powered DC Generator with XL4015 Buck Converter
This circuit consists of a 12V battery connected to a rocker switch, which controls the input to an XL4015 DC Buck Step-down converter. The converter steps down the voltage to power a DC generator, with the generator's output connected back to the converter to form a feedback loop.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
USB Power Supply with Overcurrent Protection
This circuit is designed to step down voltage from a 12V battery to a lower voltage suitable for USB devices. It includes a buck converter connected to the battery through a fuse and fuse holder for overcurrent protection. The output of the buck converter is connected to a USB female port, providing a regulated power supply for USB-powered devices.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voltage regulation for low-power devices
- Powering LEDs with constant current
- Battery charging circuits
- Embedded systems and microcontroller power supplies
- Automotive electronics to step down battery voltage
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: Typically ranges from a few volts above the desired output to tens of volts.
- Output Voltage Range: Usually adjustable via external components.
- Maximum Output Current: Determined by the converter design and cooling.
- Efficiency: Varies with load, but typically between 80% to 95%.
- Switching Frequency: Can range from tens of kHz to several MHz.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage supply pin. Connect to the source voltage. |
| 2 | GND | Ground reference for the converter. |
| 3 | VOUT | Regulated output voltage pin. |
| 4 | EN | Enable pin for turning the converter on or off. |
| 5 | FB | Feedback pin for output voltage regulation. |
| 6 | SW | Switch node, connected to the internal switching element. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Input Supply: Connect a voltage source to the VIN pin, ensuring it is within the specified input range.
- Output Load: Connect your load to the VOUT pin.
- Grounding: Connect the GND pin to the system ground.
- Enable Pin: Apply a high logic level to the EN pin to turn on the converter.
- Feedback Network: Set up the feedback network using resistors to adjust the output voltage as required.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Management: Ensure adequate cooling for the converter, especially at high output currents.
- Input Capacitor: Place a high-quality capacitor close to the VIN pin to stabilize input supply.
- Output Capacitor: Use a low ESR capacitor at the output to minimize voltage ripple.
- Switching Noise: Keep the layout compact to reduce EMI and switching noise.
- Feedback Path: Keep the feedback path short and away from noisy traces.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Output Voltage Too High/Low: Check the feedback network and ensure correct resistor values.
- Converter Not Starting: Verify the EN pin voltage and input voltage range.
- Excessive Heat: Check for overloading or insufficient cooling.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- No Output: Ensure that the EN pin is correctly driven and that the input voltage is within specifications.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Strengthen input and output filtering with appropriate capacitors.
- Noise Issues: Review the PCB layout for proper grounding and minimize the loop areas.
FAQs
- Q: Can I use a step-down converter without an external inductor?
- A: No, buck converters require an external inductor for energy storage and proper operation.
- Q: What is the purpose of the feedback pin?
- A: The feedback pin is used to regulate the output voltage by comparing it with a reference voltage.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example code to control a Step-Down Converter with an Arduino UNO
// This example assumes the converter has a digital enable pin
const int enablePin = 3; // Connect the EN pin of the converter to digital pin 3
void setup() {
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT); // Set the enable pin as an output
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW); // Start with the converter disabled
}
void loop() {
// Enable the converter
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the converter on for 5 seconds
// Disable the converter
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the converter off for 5 seconds
}
Note: The above code is a simple example to illustrate enabling and disabling the step-down converter using an Arduino UNO. The actual implementation may require additional considerations based on the specific converter model and application requirements.