
How to Use SENSOR PH: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
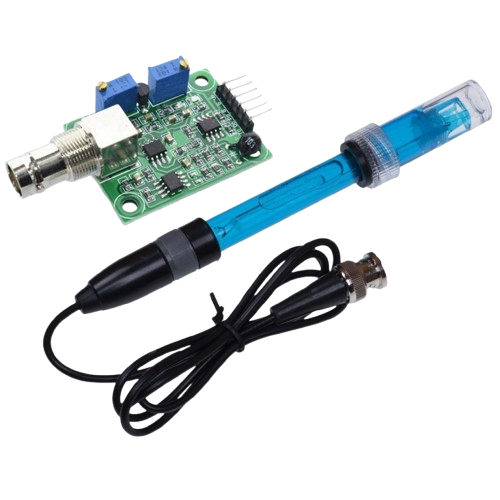
 Design with SENSOR PH in Cirkit Designer
Design with SENSOR PH in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The pH sensor is an electronic component designed to measure the pH level of a solution, which indicates its acidity or alkalinity. It works by generating an electrical signal proportional to the pH value of the solution being tested. This sensor is widely used in applications such as water quality monitoring, aquariums, hydroponics, food processing, and laboratory experiments. Its ability to provide accurate and real-time pH measurements makes it an essential tool in both industrial and hobbyist projects.
Explore Projects Built with SENSOR PH
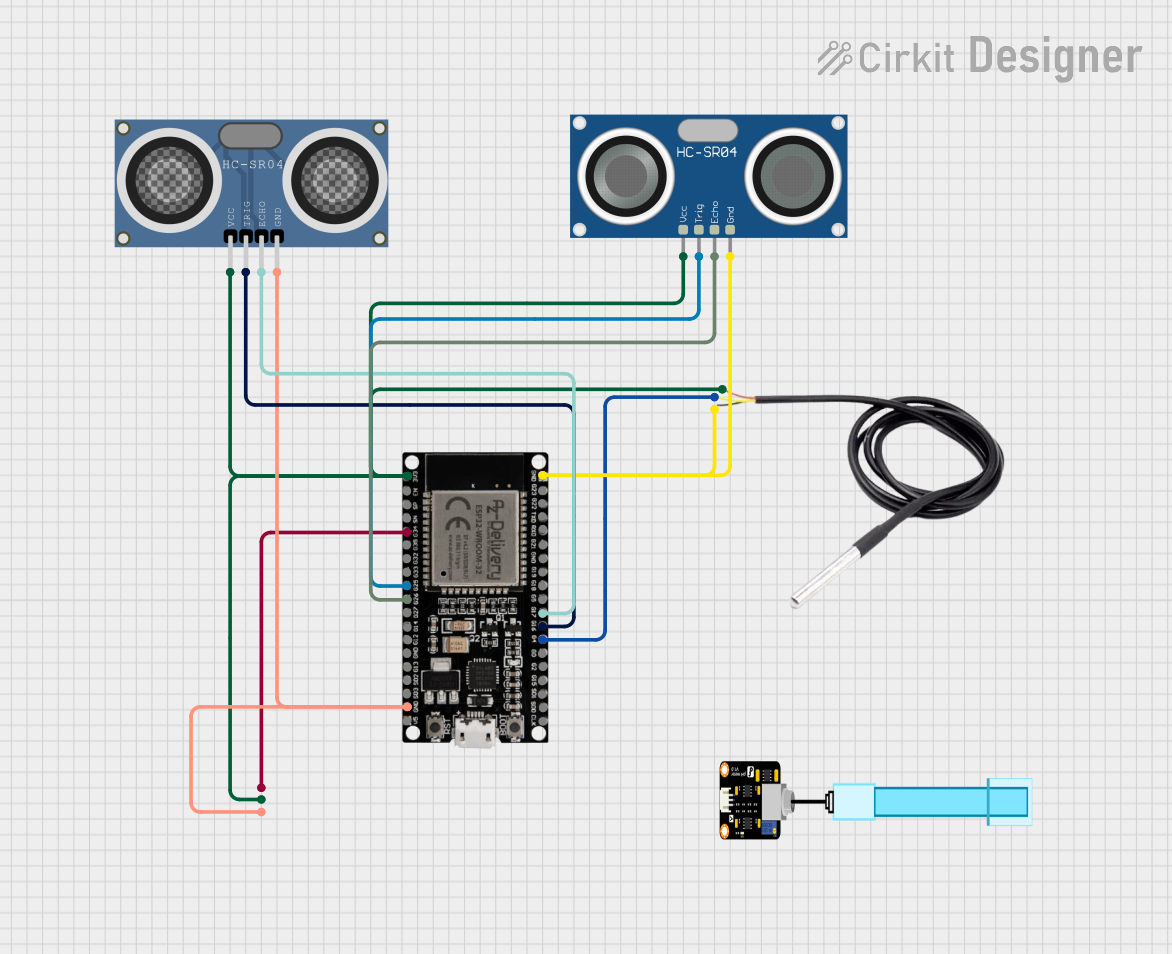
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer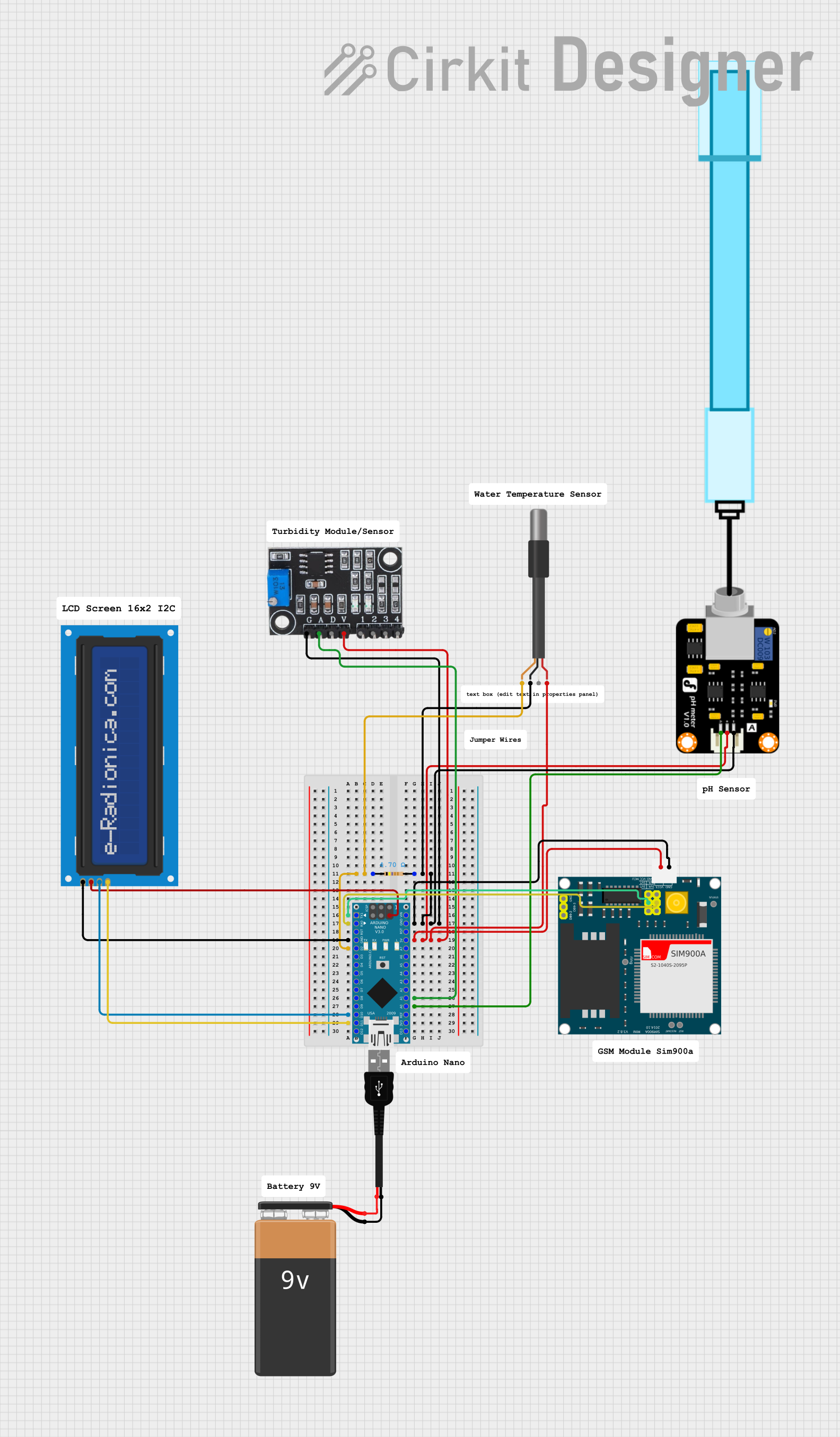
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer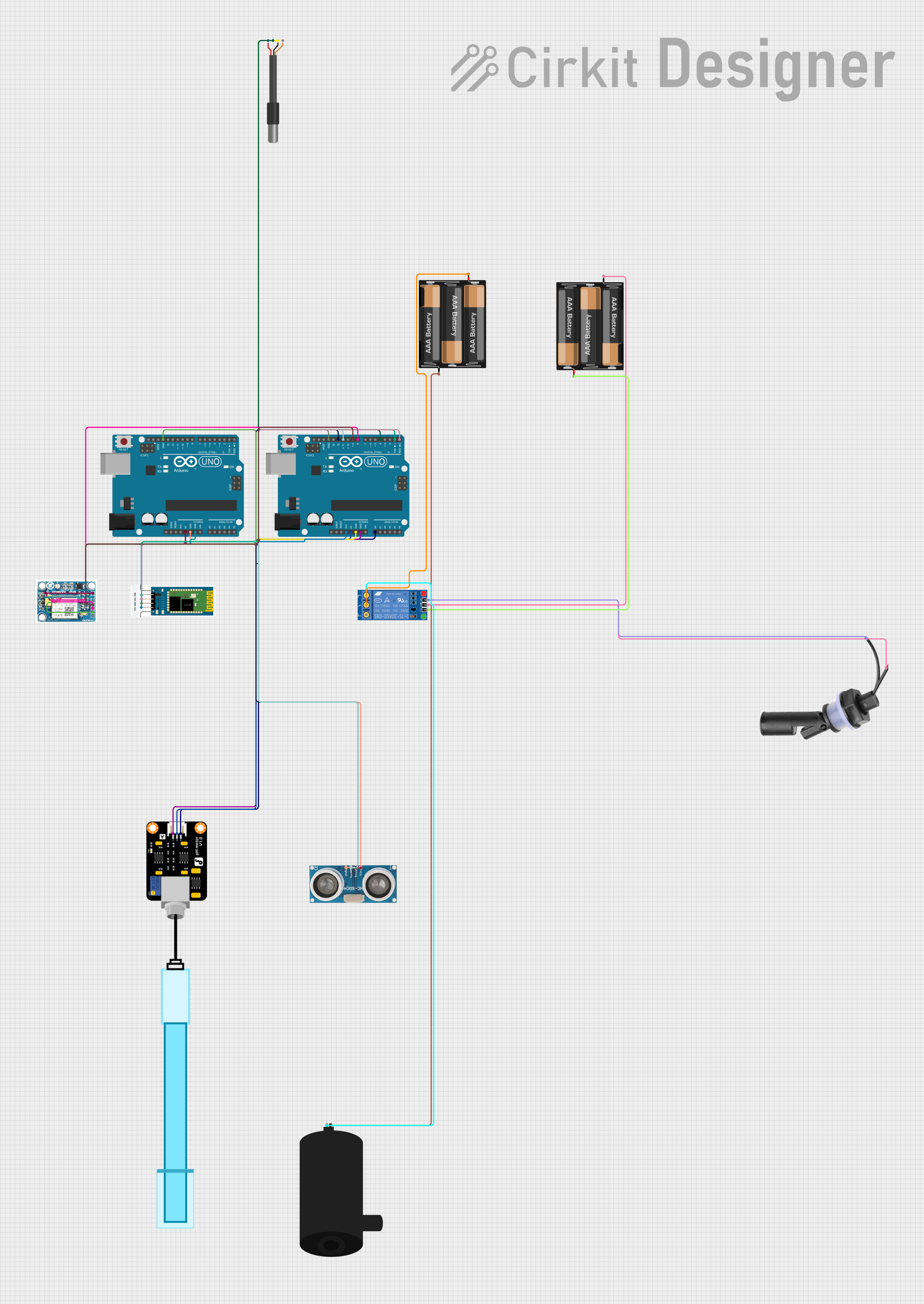
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer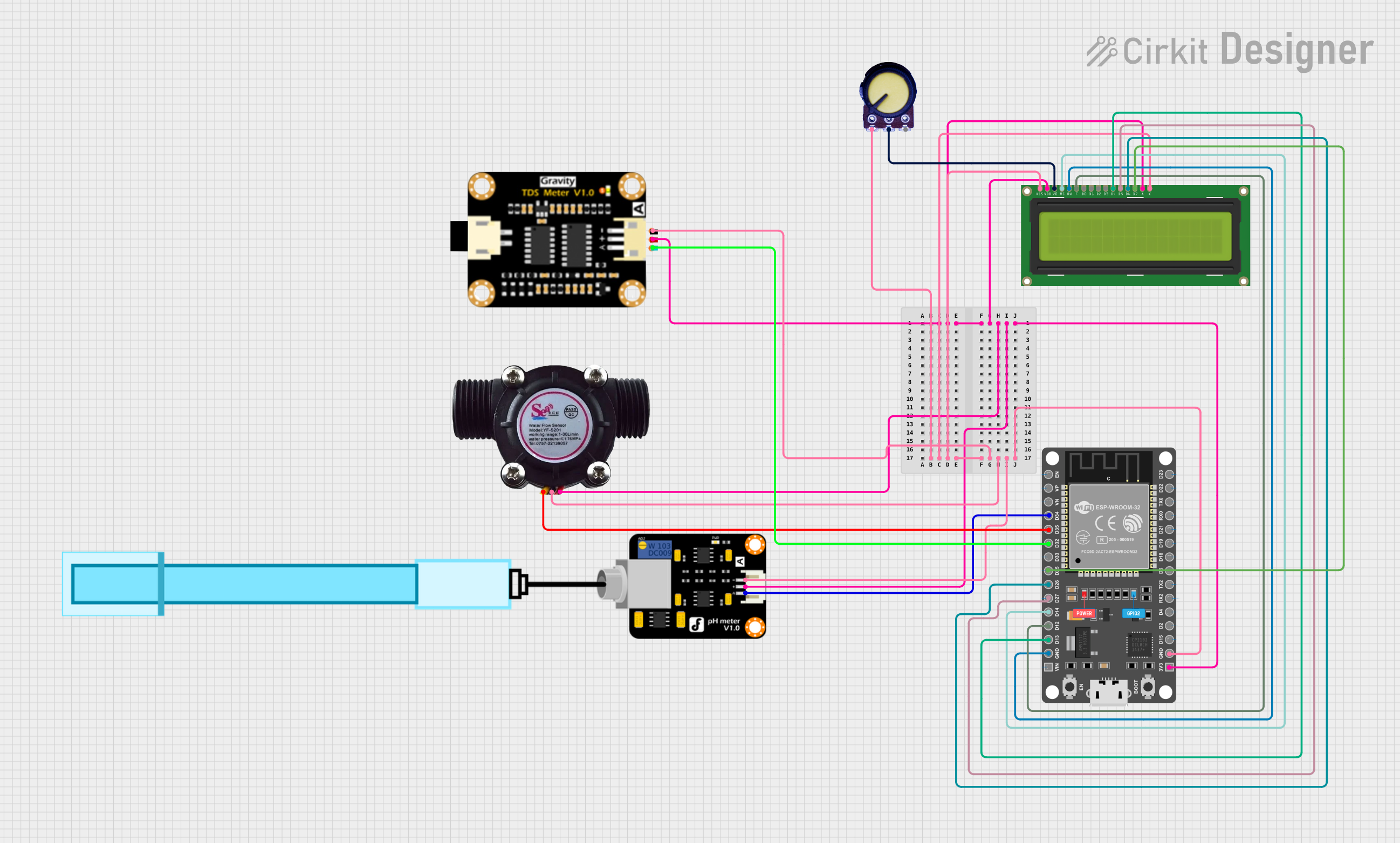
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SENSOR PH

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical pH sensor module:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (proportional to pH) |
| pH Measurement Range | 0 - 14 pH |
| Accuracy | ±0.1 pH (at 25°C) |
| Temperature Compensation | No (requires external compensation) |
| Response Time | ≤ 1 second |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C - 60°C |
| Storage Temperature | -10°C - 50°C |
Pin Configuration
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| AOUT | Analog output signal (proportional to pH value) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the pH Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor to a Microcontroller:
- Connect the
VCCpin of the sensor to the 5V pin of the microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO). - Connect the
GNDpin of the sensor to the GND pin of the microcontroller. - Connect the
AOUTpin of the sensor to an analog input pin (e.g., A0) on the microcontroller.
- Connect the
Calibrate the Sensor:
- Use standard buffer solutions (e.g., pH 4.0, pH 7.0, and pH 10.0) to calibrate the sensor.
- Adjust the potentiometer on the sensor module to fine-tune the output for accurate readings.
Write Code to Read pH Values:
- Use the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of the microcontroller to read the sensor's output.
- Convert the analog voltage to a pH value using the sensor's calibration data.
Place the Sensor in the Solution:
- Immerse the sensor's probe in the solution to be tested.
- Ensure the probe is rinsed with distilled water before and after each measurement to avoid contamination.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always calibrate the sensor before use to ensure accurate readings.
- Avoid exposing the sensor to extreme temperatures or corrosive chemicals.
- Store the sensor's probe in a pH storage solution when not in use to maintain its sensitivity.
- Use a temperature compensation mechanism if the solution's temperature varies significantly.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example code to read pH sensor values using Arduino UNO
const int pH_Pin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's AOUT pin
float voltage; // Variable to store the sensor's output voltage
float pH_Value; // Variable to store the calculated pH value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(pH_Pin, INPUT); // Set the pH sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the pH sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(pH_Pin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage (assuming 5V reference)
voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Convert the voltage to pH value (calibration required for accuracy)
// Example formula: pH = 3.5 * voltage (adjust based on calibration)
pH_Value = 3.5 * voltage;
// Print the pH value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("pH Value: ");
Serial.println(pH_Value);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Inaccurate pH Readings:
- Cause: Sensor not calibrated properly.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor using standard buffer solutions before use.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the sensor is powered correctly.
Slow Response Time:
- Cause: Probe contamination or damage.
- Solution: Clean the probe with distilled water and check for physical damage.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Use a decoupling capacitor near the sensor's power pins and ensure a stable power source.
FAQs
Q1: Can the pH sensor be used to measure the pH of hot liquids?
A1: Most pH sensors are designed for use within a temperature range of 0°C to 60°C. For hot liquids, use a sensor with built-in temperature compensation or cool the liquid before measurement.
Q2: How often should the sensor be calibrated?
A2: Calibration frequency depends on usage. For critical applications, calibrate before each use. For general use, calibrate weekly or monthly.
Q3: Can the sensor be submerged completely in water?
A3: No, only the probe should be submerged. The electronic module must remain dry to avoid damage.
Q4: Why is temperature compensation important?
A4: pH readings can vary with temperature. Temperature compensation ensures accurate measurements in solutions with varying temperatures.