
How to Use optocoupler: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with optocoupler in Cirkit Designer
Design with optocoupler in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An optocoupler, also known as an optoisolator, is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits using light waves. It typically consists of a light-emitting diode (LED) and a photodetector (such as a phototransistor, photodiode, or photothyristor) housed in a single package. The LED converts the electrical input signal into light, which is then detected by the photodetector to produce an output signal. This design ensures electrical isolation between the input and output, protecting sensitive components and preventing high-voltage spikes from damaging low-voltage circuits.
Explore Projects Built with optocoupler
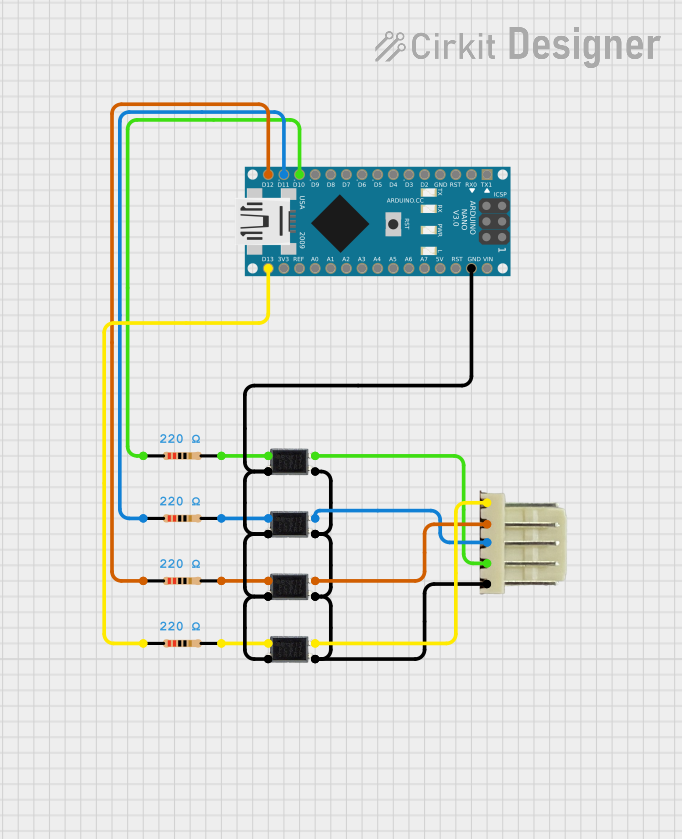
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer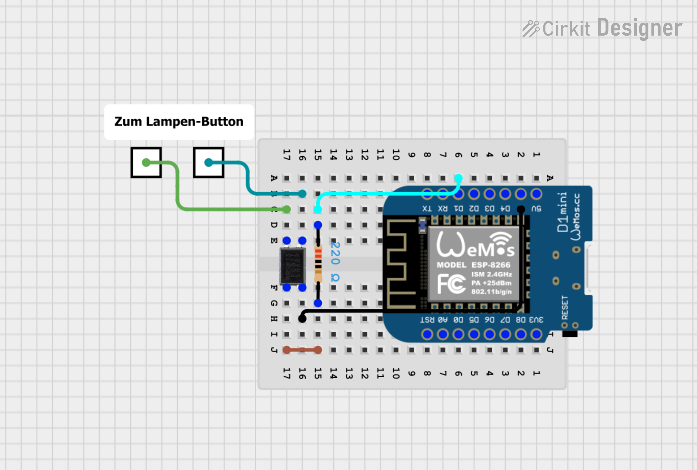
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer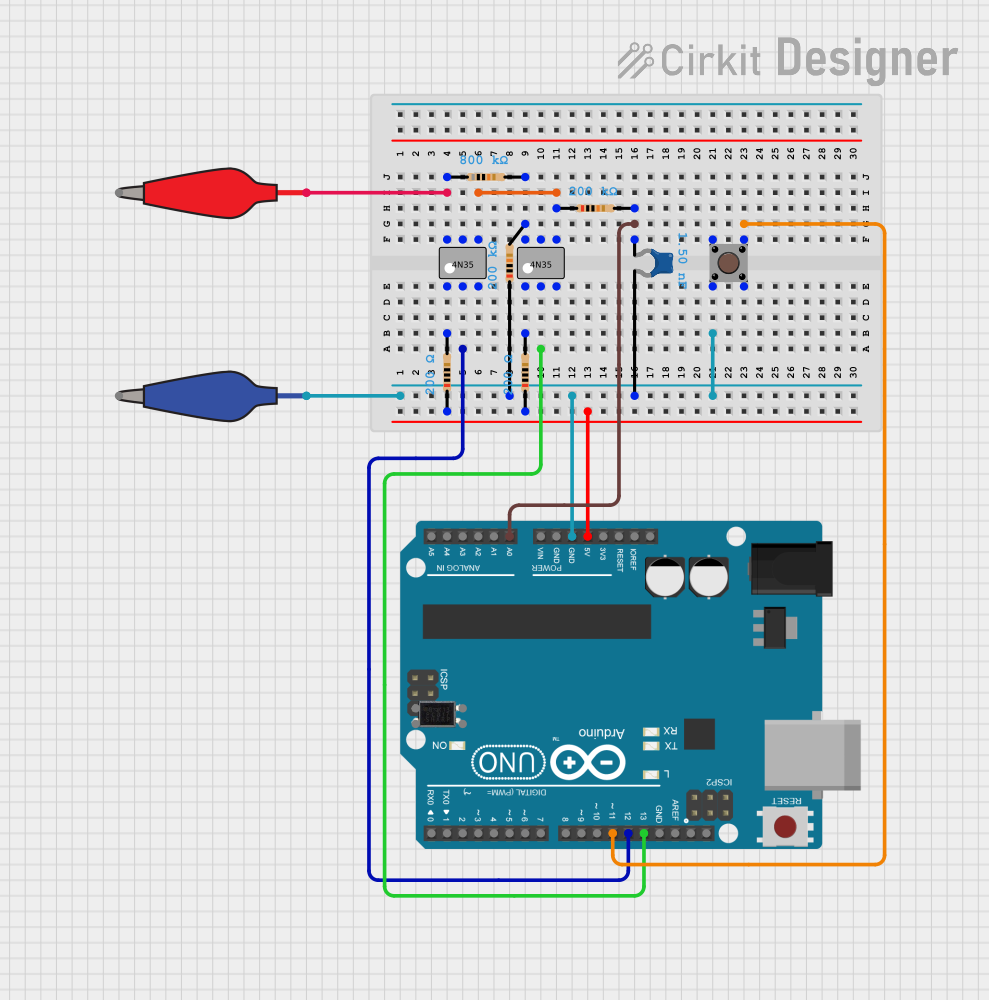
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer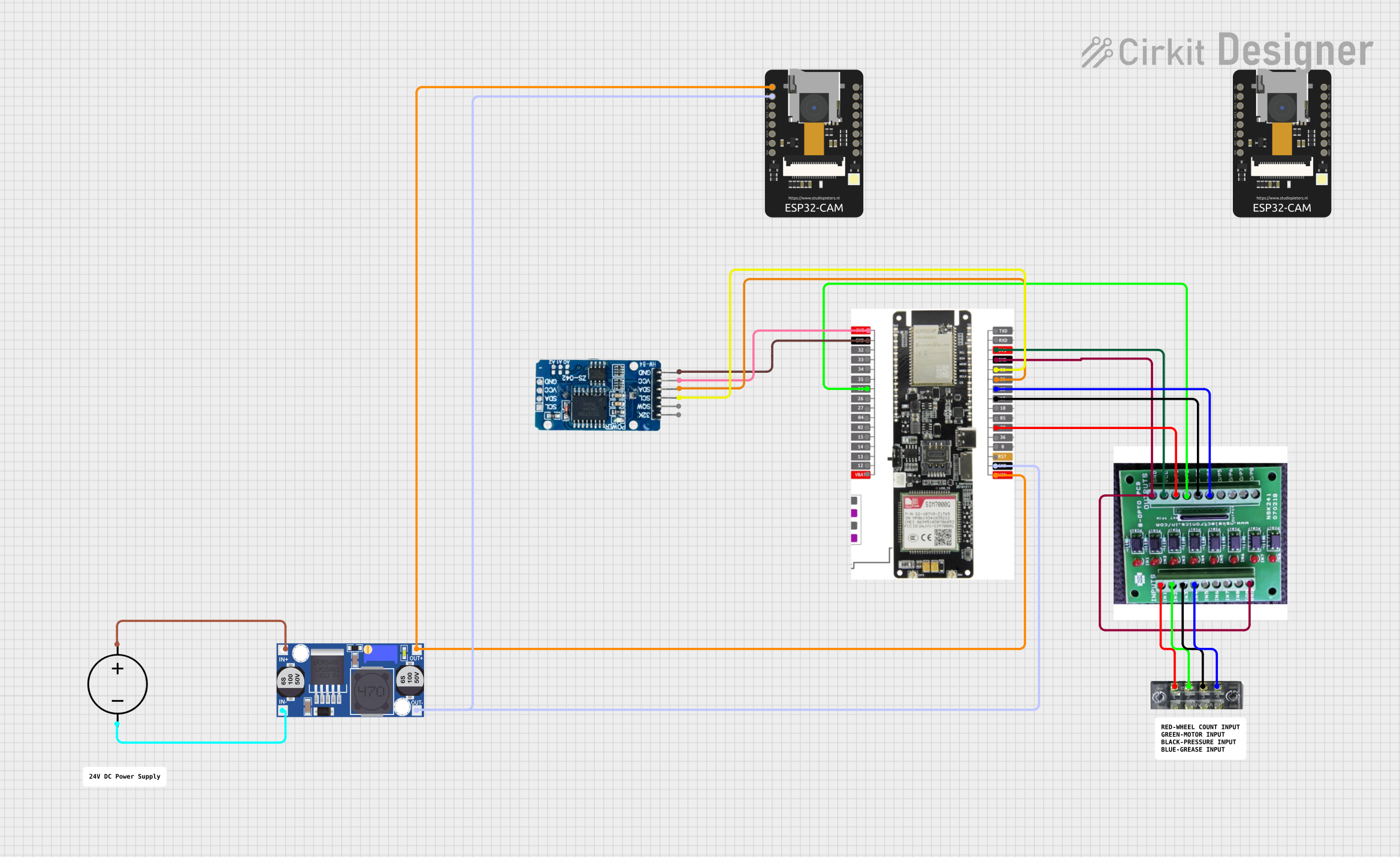
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with optocoupler

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Signal Isolation: Protecting low-voltage control circuits from high-voltage power circuits.
- Switching Applications: Used in solid-state relays and motor control systems.
- Noise Reduction: Eliminating electrical noise in communication systems.
- Microcontroller Interfacing: Safely interfacing microcontrollers with high-power devices.
- Industrial Automation: Used in PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and industrial sensors.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a Panasonic optocoupler. Always refer to the specific datasheet for the exact model you are using.
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage (LED Forward Voltage): 1.2V to 1.4V (typical)
- Input Current (LED Forward Current): 10mA to 20mA (typical)
- Output Voltage (Collector-Emitter Voltage): Up to 35V
- Output Current (Collector Current): Up to 50mA
- Isolation Voltage: 5,000 Vrms (typical)
- Response Time: 2 µs to 10 µs (depending on the model)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +100°C
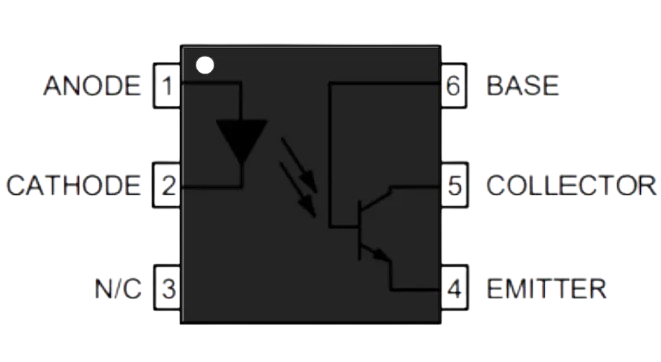
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The optocoupler typically comes in a 4-pin or 6-pin DIP (Dual Inline Package). Below is the pin configuration for a standard 4-pin optocoupler:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (LED +) | Positive terminal of the internal LED. Connect to the input signal. |
| 2 | Cathode (LED -) | Negative terminal of the internal LED. Connect to ground or the return path. |
| 3 | Emitter | Emitter terminal of the phototransistor. Connect to the output circuit ground. |
| 4 | Collector | Collector terminal of the phototransistor. Connect to the output signal path. |
For a 6-pin optocoupler, additional pins may include a base terminal for the phototransistor or NC (No Connection) pins.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Input Side (LED):
- Connect the anode (Pin 1) to the positive side of the input signal through a current-limiting resistor.
- Connect the cathode (Pin 2) to ground or the return path of the input circuit.
- Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's Law:
[ R = \frac{V_{in} - V_f}{I_f} ]
Where (V_{in}) is the input voltage, (V_f) is the forward voltage of the LED (typically 1.2V), and (I_f) is the desired forward current (e.g., 10mA).
Output Side (Phototransistor):
- Connect the collector (Pin 4) to the positive supply voltage through a pull-up resistor.
- Connect the emitter (Pin 3) to ground.
- The output signal can be read at the collector terminal. When the LED is on, the phototransistor conducts, pulling the output low.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Always use a resistor in series with the LED to prevent overcurrent damage.
- Isolation Voltage: Ensure the isolation voltage rating is sufficient for your application.
- Speed Requirements: For high-speed applications, choose an optocoupler with a fast response time.
- Temperature Range: Verify that the operating temperature range matches your environment.
- Interfacing with Microcontrollers: Use a pull-up resistor on the output side to ensure proper logic levels for microcontroller inputs.
Example: Interfacing with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a Panasonic optocoupler to interface a 5V Arduino UNO with a 12V relay.
Circuit Diagram
- Input Side: Connect the Arduino digital pin (e.g., D2) to the optocoupler anode through a 220Ω resistor. Connect the cathode to ground.
- Output Side: Connect the optocoupler collector to the 12V relay input through a 1kΩ pull-up resistor. Connect the emitter to ground.
Arduino Code
// Optocoupler Example with Arduino UNO
// This code toggles the optocoupler to control a 12V relay.
const int optoPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to optocoupler input
void setup() {
pinMode(optoPin, OUTPUT); // Set optoPin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(optoPin, HIGH); // Turn on the optocoupler (relay ON)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(optoPin, LOW); // Turn off the optocoupler (relay OFF)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect input resistor value or insufficient input current.
- Solution: Verify the resistor value and ensure the input current is within the specified range.
Output Signal Always High:
- Cause: Pull-up resistor missing or phototransistor not conducting.
- Solution: Add a pull-up resistor to the collector terminal and check the LED input.
Slow Response Time:
- Cause: Optocoupler model not suitable for high-speed applications.
- Solution: Use a high-speed optocoupler designed for fast switching.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current through the LED or phototransistor.
- Solution: Use appropriate current-limiting resistors and ensure the component is within its rated limits.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an optocoupler for AC signals?
A: Yes, but you may need a bidirectional optocoupler or additional circuitry (e.g., a bridge rectifier) to handle AC signals.Q: How do I choose the right optocoupler for my application?
A: Consider factors such as isolation voltage, response time, input/output current, and voltage ratings.Q: Can an optocoupler drive a high-power load directly?
A: No, optocouplers are typically used to control low-power signals. Use a transistor or relay to drive high-power loads.Q: What is the lifespan of an optocoupler?
A: Optocouplers have a long lifespan but may degrade over time due to LED aging. Check the datasheet for the expected operational hours.