
How to Use Relay 4 channel: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Relay 4 channel in Cirkit Designer
Design with Relay 4 channel in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Relay 4 Channel module is an electronic component designed to control four independent circuits using low voltage signals. It acts as an electrically operated switch, allowing you to control high-power devices such as lights, fans, or appliances with a microcontroller or other low-power control systems. This module is widely used in home automation, industrial control systems, and IoT projects.
Explore Projects Built with Relay 4 channel
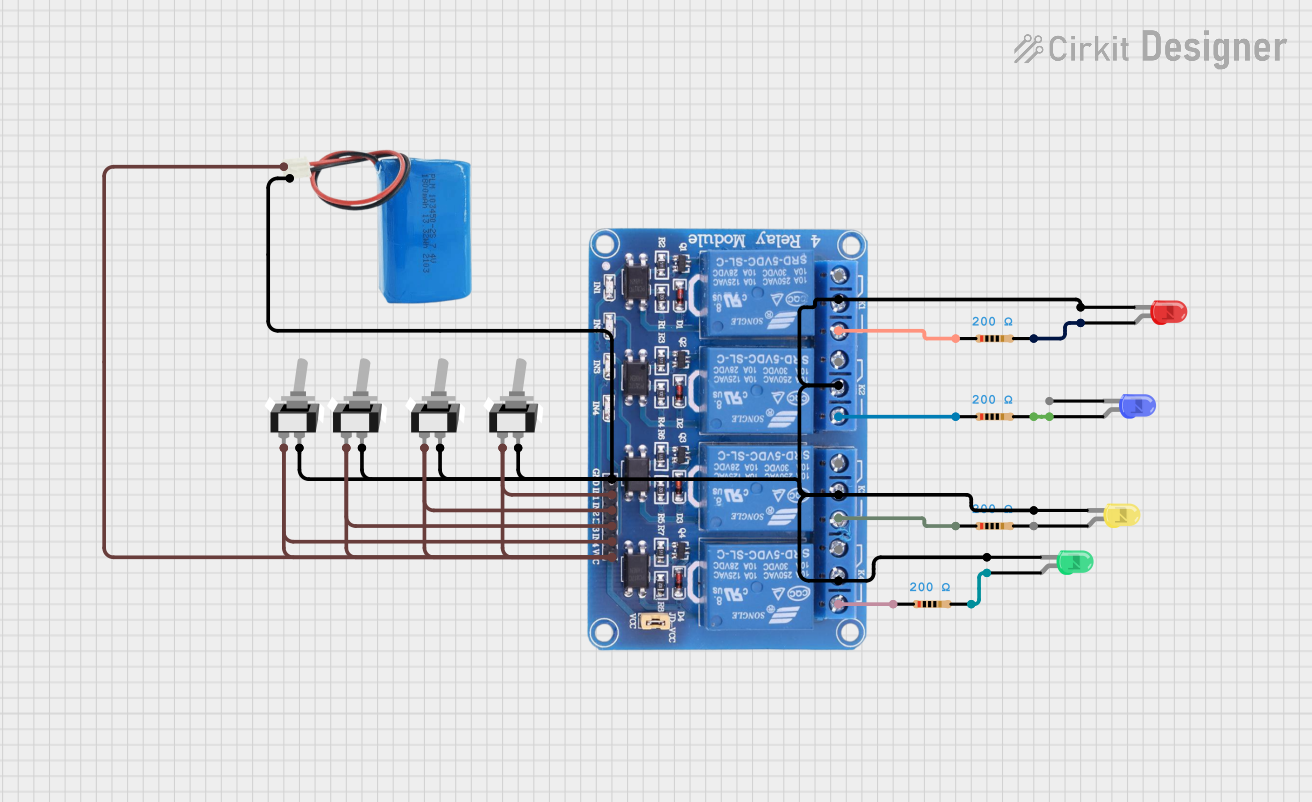
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer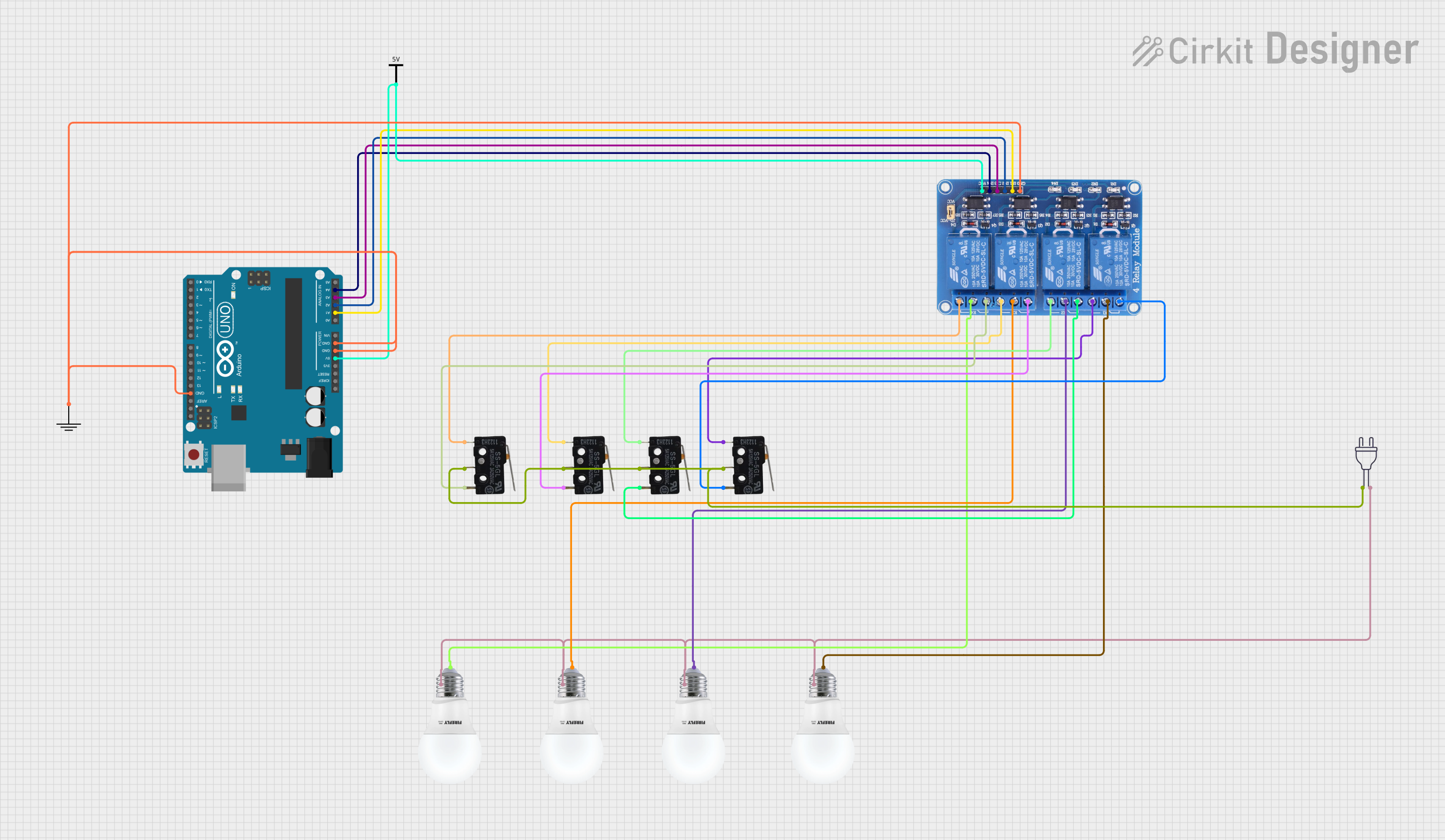
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer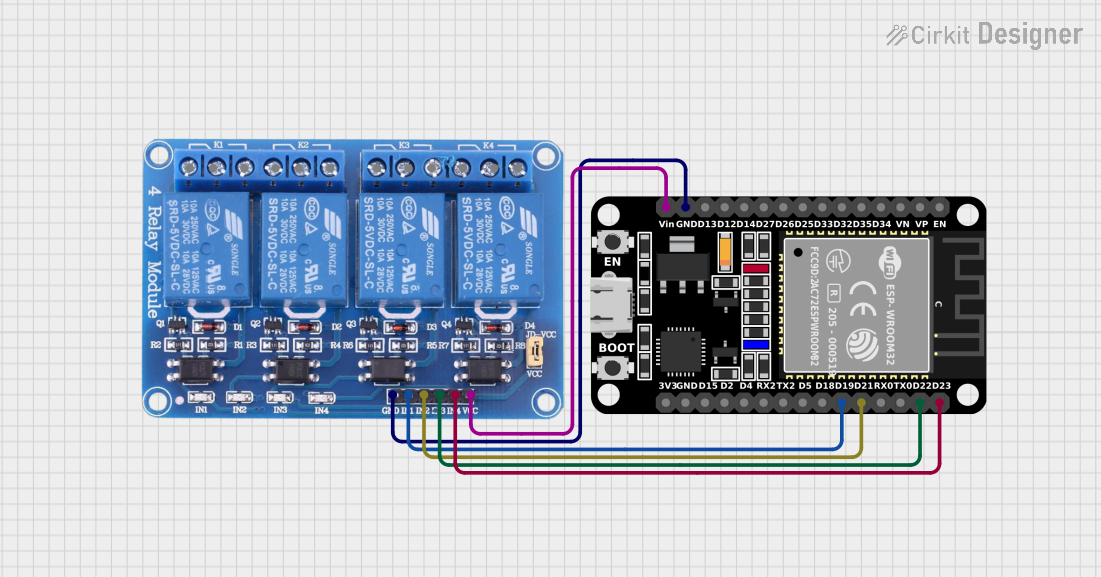
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer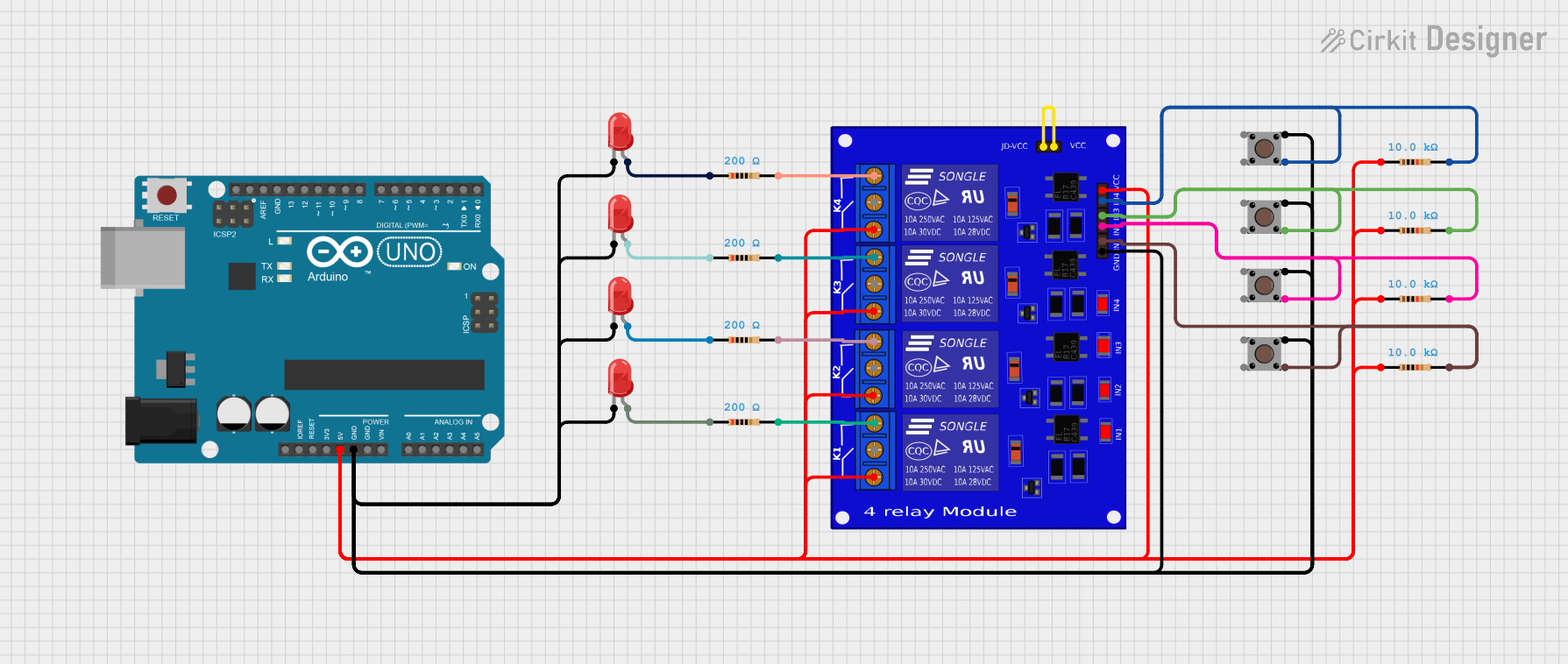
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Relay 4 channel

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation (e.g., controlling lights, fans, or appliances)
- Industrial equipment control
- IoT projects for remote device management
- Robotics and automation systems
- Smart energy management systems
Technical Specifications
The Relay 4 Channel module is designed to interface with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other control systems. Below are its key specifications:
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 5V DC
- Trigger Voltage: 3.3V to 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- Relay Type: Electromechanical
- Maximum Load (per channel):
- AC: 250V at 10A
- DC: 30V at 10A
- Isolation: Optocoupler isolation for signal protection
- Dimensions: Varies by manufacturer, typically ~75mm x 55mm x 20mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The module has two main sections: the input control pins and the relay output terminals.
Input Control Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Connect to the 5V power supply of the microcontroller. |
| GND | Connect to the ground of the microcontroller. |
| IN1 | Control signal for Relay 1 (active LOW). |
| IN2 | Control signal for Relay 2 (active LOW). |
| IN3 | Control signal for Relay 3 (active LOW). |
| IN4 | Control signal for Relay 4 (active LOW). |
Relay Output Terminals
Each relay has three output terminals: COM (Common), NO (Normally Open), and NC (Normally Closed).
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| COM | Common terminal for the relay. Connect to the power source or load. |
| NO | Normally Open terminal. Circuit is open when the relay is inactive. |
| NC | Normally Closed terminal. Circuit is closed when the relay is inactive. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Relay 4 Channel Module in a Circuit
- Power the Module:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power supply and the GND pin to the ground of your microcontroller.
- Connect Control Signals:
- Connect the IN1, IN2, IN3, and IN4 pins to the digital output pins of your microcontroller.
- Ensure the control signals are active LOW (sending a LOW signal activates the relay).
- Connect the Load:
- For each relay, connect the load to the COM and NO/NC terminals based on your requirements:
- Use NO if you want the circuit to be OFF by default and ON when the relay is activated.
- Use NC if you want the circuit to be ON by default and OFF when the relay is activated.
- For each relay, connect the load to the COM and NO/NC terminals based on your requirements:
- Write Control Code:
- Use your microcontroller to send LOW signals to the IN pins to activate the relays.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the module is powered with a stable 5V DC supply. Avoid exceeding the voltage rating.
- Isolation: The module uses optocouplers for isolation, but ensure proper grounding to avoid electrical noise.
- Load Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum load ratings (10A for AC or DC) to prevent damage to the relays.
- Inductive Loads: When controlling inductive loads (e.g., motors), use a flyback diode across the load to suppress voltage spikes.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to control the Relay 4 Channel module using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the relay control pins
#define RELAY1 2 // Pin connected to IN1
#define RELAY2 3 // Pin connected to IN2
#define RELAY3 4 // Pin connected to IN3
#define RELAY4 5 // Pin connected to IN4
void setup() {
// Set relay pins as outputs
pinMode(RELAY1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RELAY2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RELAY3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RELAY4, OUTPUT);
// Initialize all relays to OFF (HIGH state)
digitalWrite(RELAY1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RELAY2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RELAY3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RELAY4, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Turn relays ON and OFF with a delay
digitalWrite(RELAY1, LOW); // Activate Relay 1
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY1, HIGH); // Deactivate Relay 1
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY2, LOW); // Activate Relay 2
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY2, HIGH); // Deactivate Relay 2
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY3, LOW); // Activate Relay 3
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY3, HIGH); // Deactivate Relay 3
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY4, LOW); // Activate Relay 4
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(RELAY4, HIGH); // Deactivate Relay 4
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relays Not Activating:
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Ensure the module is powered with a stable 5V DC supply and check all connections.
Microcontroller Resetting:
- Cause: High current draw from the relays causing voltage drops.
- Solution: Use a separate power supply for the relay module and connect the grounds.
Load Not Switching:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of the load to the relay terminals.
- Solution: Verify the load is connected to the correct COM and NO/NC terminals.
Relay Clicking Noise:
- Cause: Rapid switching or unstable control signals.
- Solution: Check the control code and ensure proper signal timing.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the Relay 4 Channel module with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A1: Yes, the module is compatible with 3.3V control signals, but ensure the VCC pin is powered with 5V.
Q2: Can I control DC motors with this module?
A2: Yes, but for inductive loads like motors, use a flyback diode to protect the relay from voltage spikes.
Q3: How do I know if a relay is active?
A3: Most modules have an LED indicator for each relay that lights up when the relay is active.
Q4: Can I use this module to control 220V AC appliances?
A4: Yes, but ensure the load does not exceed 250V AC at 10A, and follow proper safety precautions.