
How to Use 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB in Cirkit Designer
Design with 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB (Manufacturer Part ID: 3706) is a compact, high-performance gearmotor designed by Pololu. It features a 20 mm diameter and 44 mm length, making it ideal for applications requiring high torque and low speed. This gearmotor operates at 6V and is well-suited for robotics, automation systems, and other precision motion control projects.
Explore Projects Built with 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB
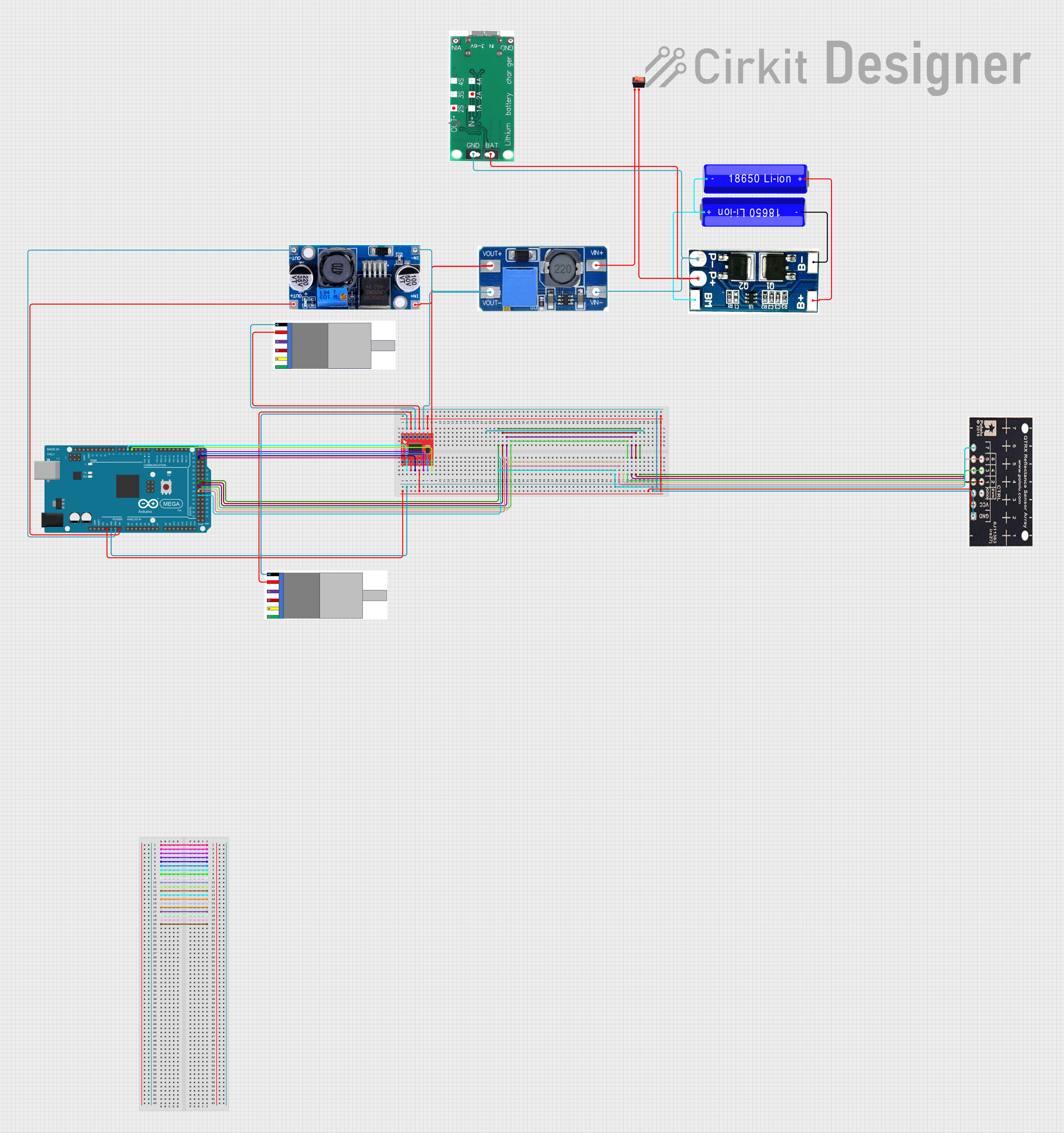
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer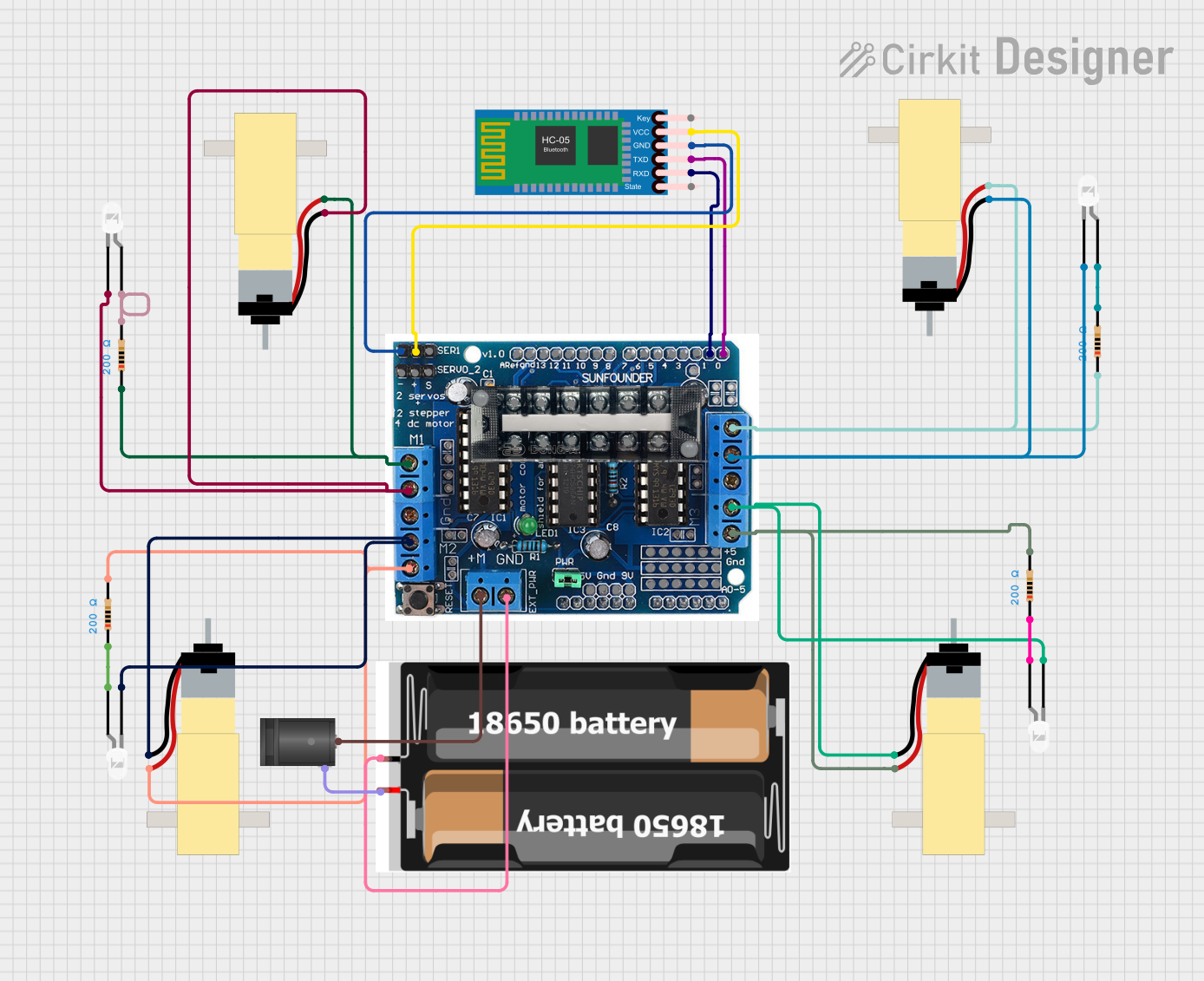
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer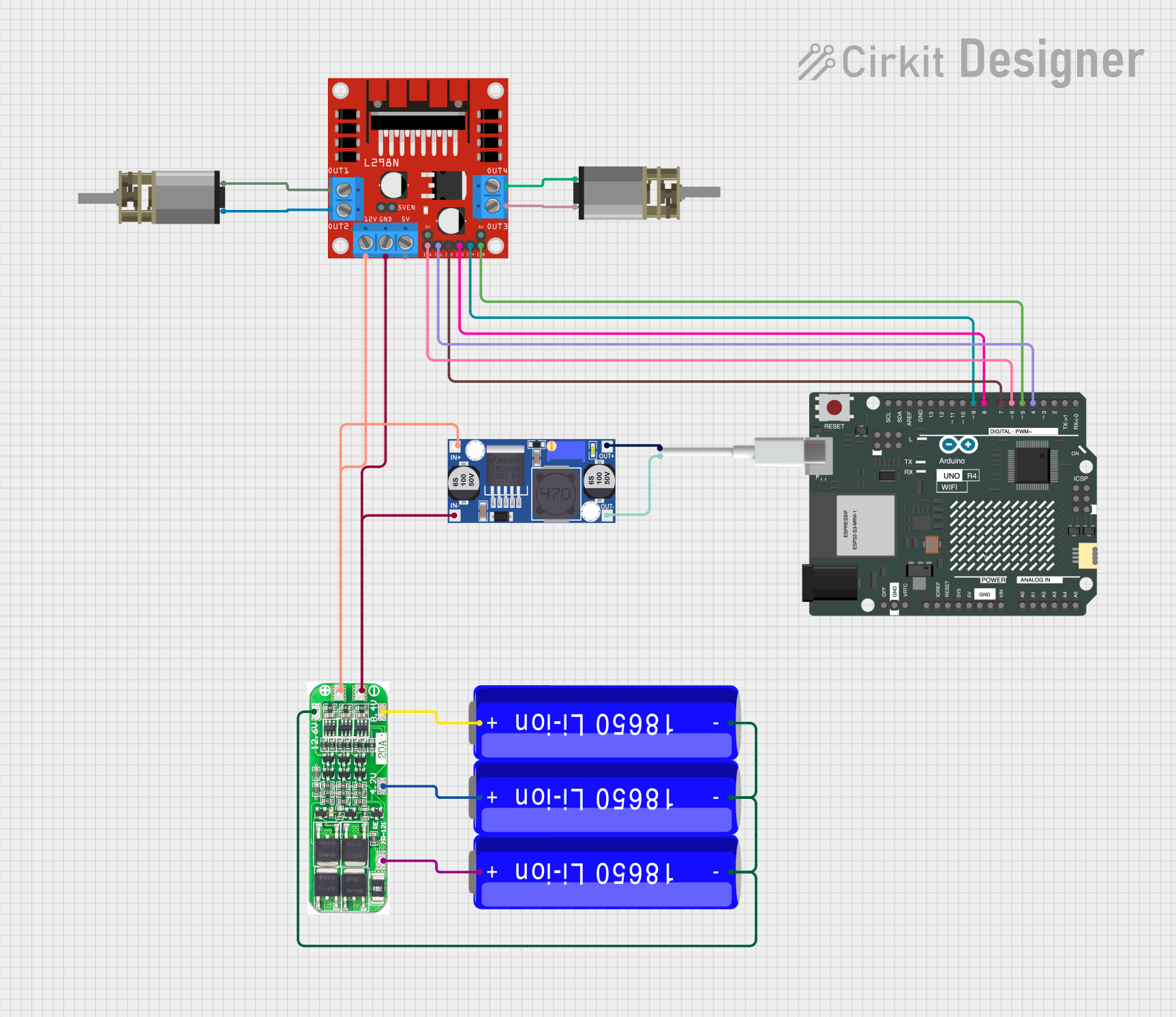
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 156:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L mm 6V CB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Robotics (e.g., driving wheels or actuators)
- Automated systems (e.g., conveyor belts, small lifts)
- Precision motion control in hobbyist and industrial projects
- Educational projects involving motorized mechanisms
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 156:1 Metal Gearmotor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Gear Ratio | 156:1 |
| Operating Voltage | 6V |
| No-Load Speed (at 6V) | 100 RPM |
| Stall Torque (at 6V) | 2.5 kg·cm (0.245 N·m) |
| Stall Current (at 6V) | 1.6 A |
| No-Load Current (at 6V) | 0.13 A |
| Shaft Diameter | 4 mm |
| Shaft Length | 18 mm |
| Motor Dimensions | 20 mm (diameter) x 44 mm (length) |
| Weight | 50 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The motor has two terminals for electrical connections. These terminals are used to control the motor's direction and speed.
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Motor power input (connect to positive voltage) |
| Terminal 2 | Motor power input (connect to ground or negative voltage) |
Note: Reversing the polarity of the terminals will reverse the motor's rotation direction.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the motor to a 6V DC power source. Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current (at least 1.6 A for stall conditions).
- Motor Driver: Use a motor driver or H-bridge circuit to control the motor's speed and direction. Directly connecting the motor to a microcontroller is not recommended due to high current requirements.
- Polarity Control: To change the motor's rotation direction, reverse the polarity of the voltage applied to the terminals.
- PWM Control: For speed control, use a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal from a motor driver or microcontroller.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Handling: Ensure your motor driver or power supply can handle the stall current (1.6 A) to avoid damage.
- Heat Dissipation: Prolonged operation at high loads may cause the motor to heat up. Allow for adequate cooling or limit continuous operation under heavy loads.
- Mounting: Secure the motor using the mounting holes provided on the gearbox. Avoid applying excessive force to the shaft.
- Decoupling Capacitors: To reduce electrical noise, consider adding a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor across the motor terminals.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the motor using an Arduino UNO and an L298N motor driver.
Circuit Connections
- Connect Terminal 1 and Terminal 2 of the motor to the output pins of the L298N motor driver (e.g., OUT1 and OUT2).
- Connect the L298N's input pins (e.g., IN1 and IN2) to Arduino digital pins (e.g., D9 and D10).
- Connect the L298N's power input to a 6V power supply.
Arduino Code
// Define motor control pins
const int motorPin1 = 9; // IN1 on L298N
const int motorPin2 = 10; // IN2 on L298N
void setup() {
// Set motor pins as outputs
pinMode(motorPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorPin2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, HIGH);
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Motor Does Not Spin
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify that the power supply provides 6V and sufficient current. Check all connections.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction
- Cause: Incorrect polarity of the motor terminals.
- Solution: Reverse the connections to the motor terminals.
Motor Overheats
- Cause: Prolonged operation under high load or stall conditions.
- Solution: Reduce the load or limit the motor's runtime. Allow the motor to cool between uses.
Electrical Noise Interference
- Cause: Motor generates electrical noise during operation.
- Solution: Add a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor across the motor terminals to suppress noise.
FAQs
Q: Can I operate the motor at a voltage higher than 6V?
A: Operating the motor above 6V is not recommended as it may damage the motor or reduce its lifespan.
Q: How do I calculate the torque required for my application?
A: Determine the load's weight and the radius of the wheel or arm. Use the formula:
Torque (N·m) = Force (N) × Radius (m).
Ensure the motor's stall torque exceeds this value.
Q: Can I use this motor without a motor driver?
A: While possible, it is not recommended. A motor driver allows for better control of speed and direction while protecting the motor and power source.
Q: What is the lifespan of this motor?
A: The lifespan depends on operating conditions, such as load, voltage, and runtime. Proper usage and maintenance can significantly extend its life.