
How to Use Arduino Nano ESP32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
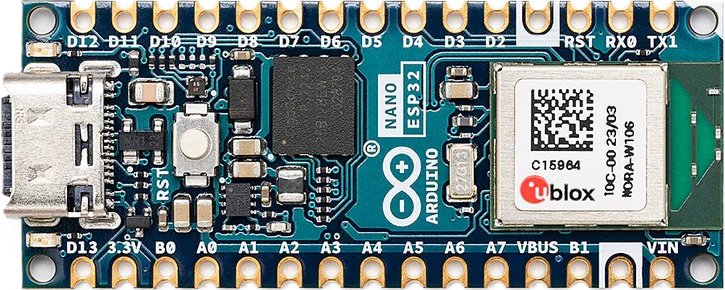
 Design with Arduino Nano ESP32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Arduino Nano ESP32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Arduino Nano ESP32 (Manufacturer Part ID: Nano-ESP32) is a compact microcontroller board developed by Arduino. It combines the familiar form factor of the Arduino Nano with the powerful ESP32 chip, enabling advanced features such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity. This board is designed for IoT (Internet of Things) applications, making it an excellent choice for projects requiring wireless communication, remote monitoring, or smart device integration.
Explore Projects Built with Arduino Nano ESP32
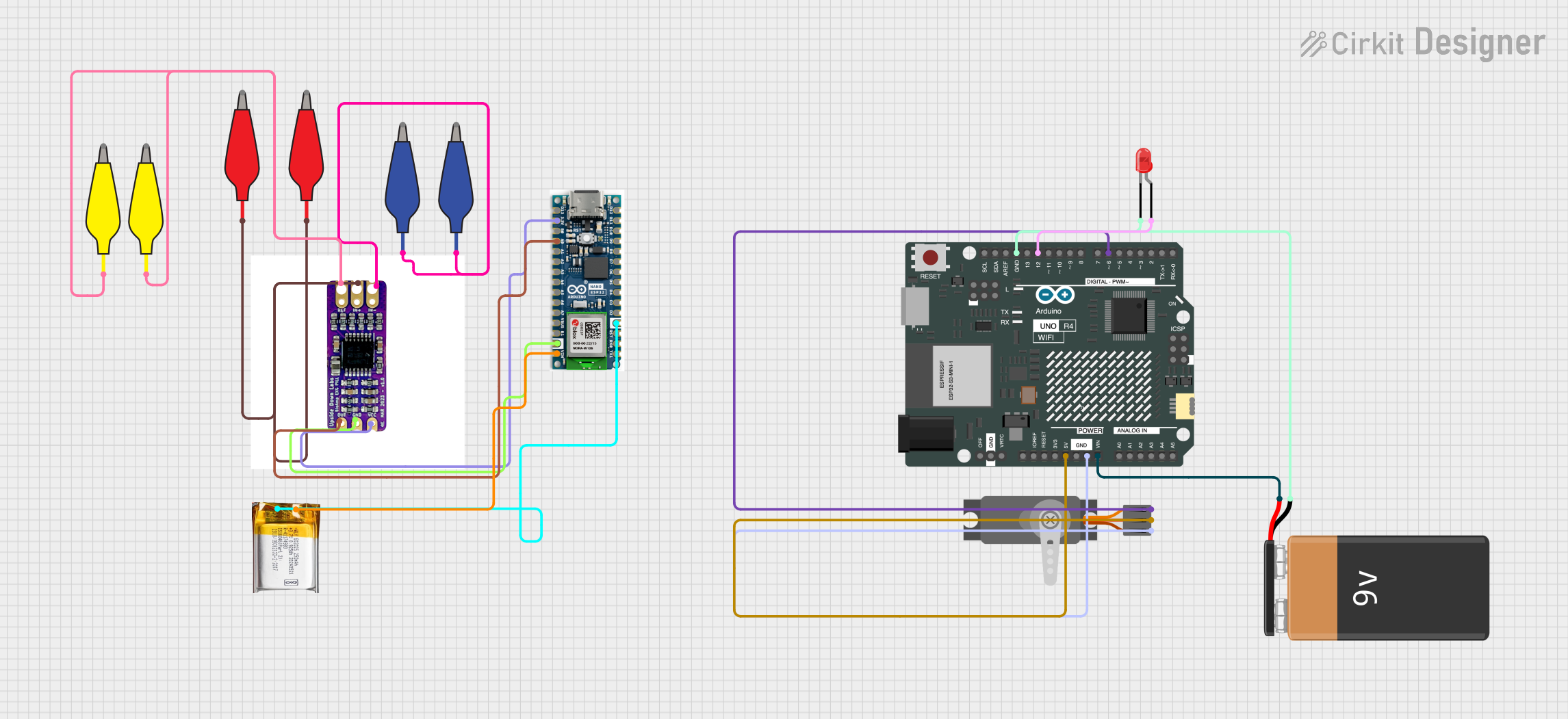
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer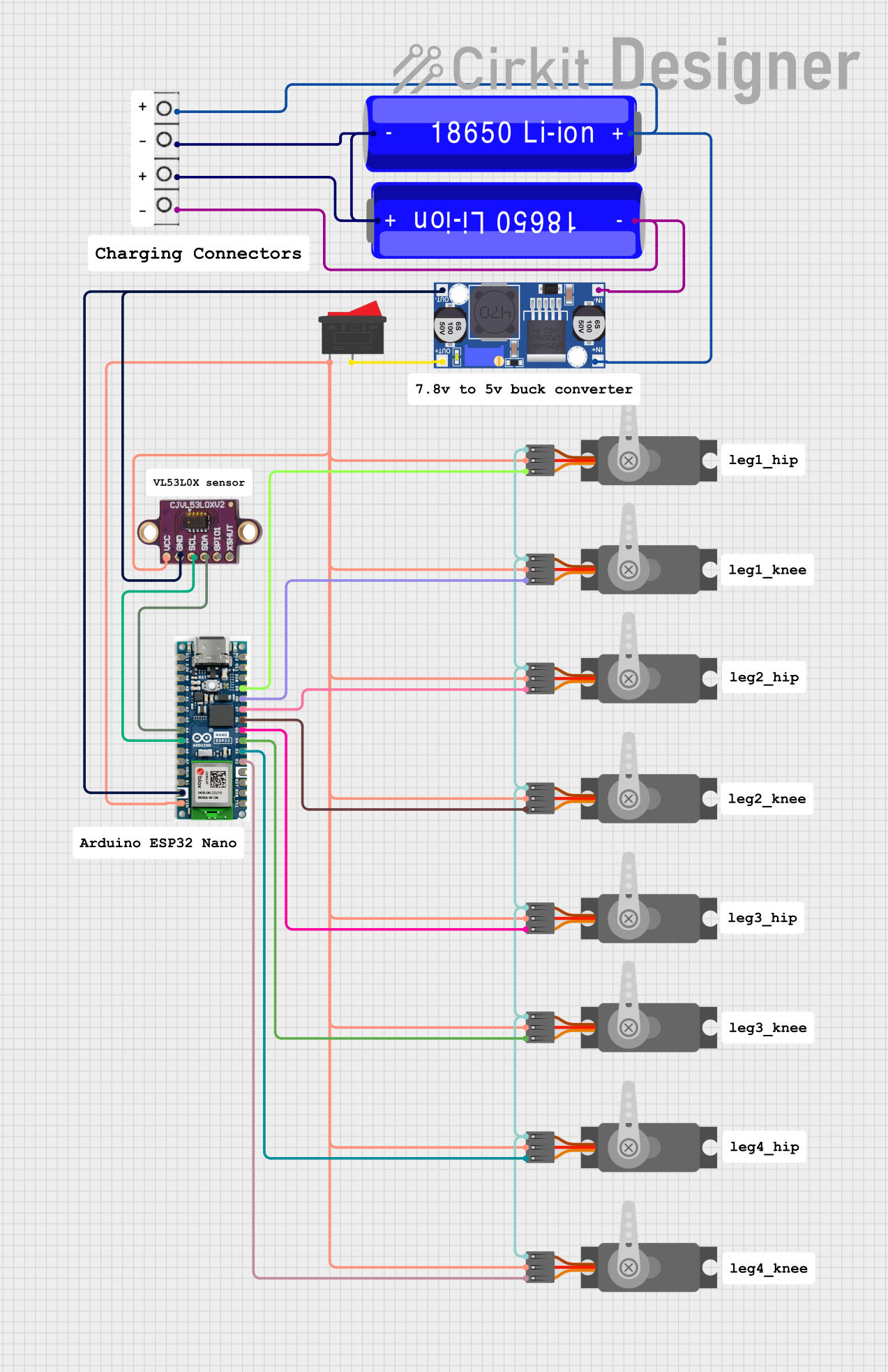
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer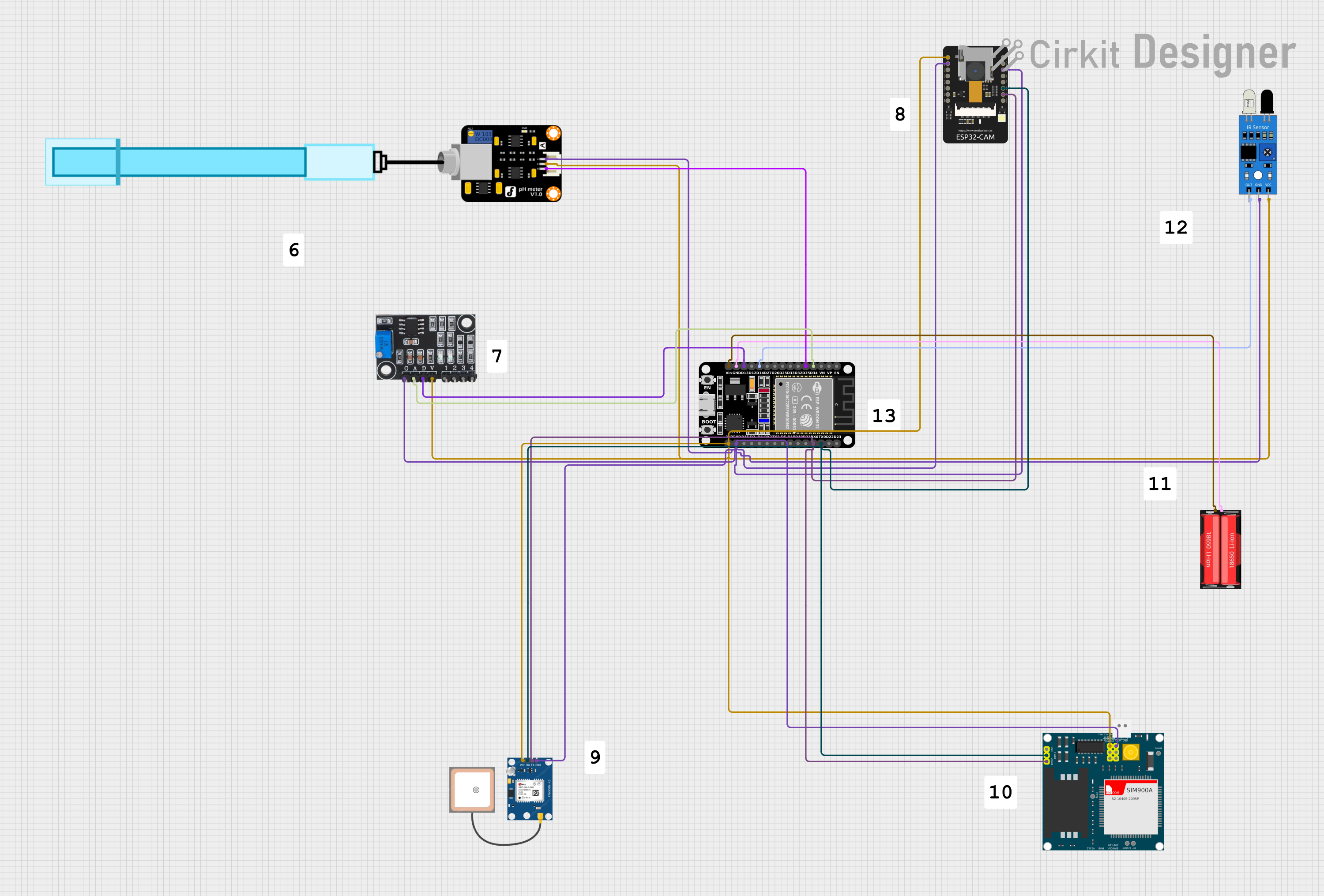
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer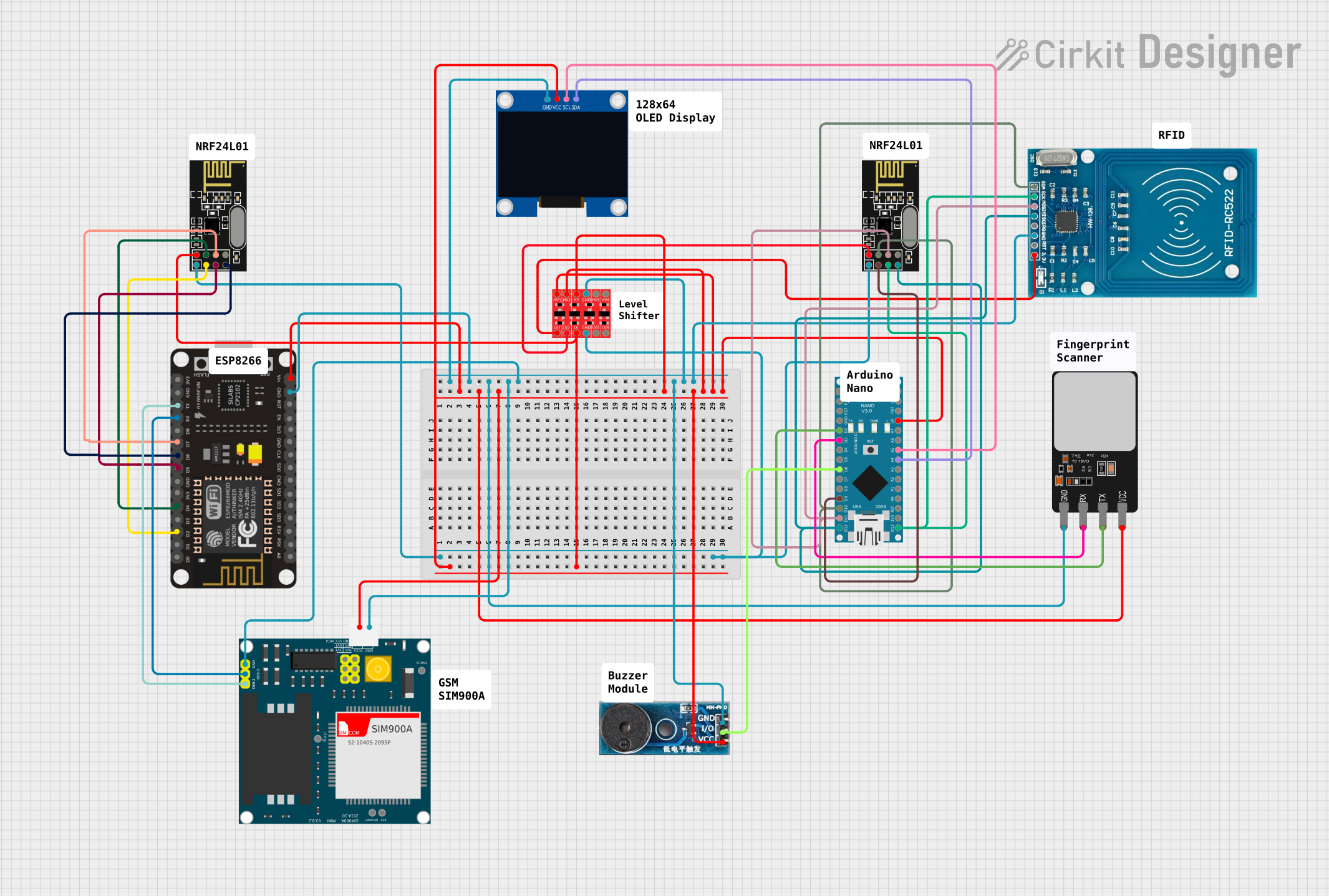
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Arduino Nano ESP32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wireless sensor networks
- Remote data logging and monitoring
- Bluetooth-enabled devices
- Robotics and automation systems
- Prototyping for connected devices
Technical Specifications
The Arduino Nano ESP32 is packed with features that make it versatile and powerful for a wide range of applications. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-S3 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Input Voltage (VIN) | 5V (via USB or VIN pin) |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 |
| Analog Input Pins | 8 |
| PWM Pins | 14 |
| Flash Memory | 8MB (external) |
| SRAM | 512KB |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 5.0 |
| USB Interface | USB-C |
| Dimensions | 45mm x 18mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Arduino Nano ESP32 features a pinout similar to the classic Arduino Nano, with additional functionality provided by the ESP32 chip. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage (5V) for powering the board. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V output from the onboard regulator. |
| 4-11 | D0-D7 | Digital I/O pins (can also be used for PWM). |
| 12-13 | RX, TX | UART communication pins. |
| 14-21 | A0-A7 | Analog input pins (can also be used as digital I/O). |
| 22 | RST | Reset pin to restart the microcontroller. |
| 23 | SDA | I2C data line. |
| 24 | SCL | I2C clock line. |
| 25 | EN | Enable pin for the ESP32 chip. |
| 26 | BOOT | Boot mode selection pin (used for flashing firmware). |
Usage Instructions
The Arduino Nano ESP32 is easy to use and program, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced developers. Below are the steps and best practices for using the board in a circuit.
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Use the USB-C port to power the board and upload code.
- Alternatively, supply 5V to the VIN pin for external power.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the digital and analog pins to connect sensors, actuators, and other peripherals.
- For I2C devices, connect to the SDA and SCL pins.
Programming the Board:
- Install the Arduino IDE and add the ESP32 board package.
- Select "Arduino Nano ESP32" as the board in the Tools menu.
- Write and upload your code via the USB-C connection.
Using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth:
- Leverage the ESP32's built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities for wireless communication.
- Use libraries such as
WiFi.handBluetoothSerial.hfor easy implementation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed 5V to avoid damaging the board.
- Use level shifters when interfacing with 5V logic devices, as the board operates at 3.3V.
- Avoid placing the board near sources of electromagnetic interference to maintain reliable wireless communication.
- Use proper decoupling capacitors when connecting external components to reduce noise.
Example Code for Arduino Nano ESP32 with Wi-Fi
Below is an example of how to connect the Arduino Nano ESP32 to a Wi-Fi network and print the IP address:
#include <WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
Serial.println("Connecting to Wi-Fi...");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Start Wi-Fi connection
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000); // Wait for connection
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the IP address
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The board is not detected by the Arduino IDE:
- Ensure the correct USB driver is installed for the ESP32.
- Check that the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
Wi-Fi connection fails:
- Double-check the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and not overloaded.
The board overheats:
- Avoid overloading the GPIO pins with excessive current.
- Ensure proper ventilation around the board.
Code upload fails:
- Press and hold the BOOT button while uploading the code.
- Verify that the correct board and port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Arduino Nano ESP32 with 5V sensors?
A: Yes, but you will need level shifters to convert the 5V logic to 3.3V.
Q: Does the board support OTA (Over-The-Air) updates?
A: Yes, the ESP32 supports OTA updates, which can be implemented using the Arduino IDE or other tools.
Q: Can I use the board with the Arduino Nano shields?
A: The pinout is similar, but compatibility depends on the shield's voltage requirements and functionality.
Q: How do I reset the board?
A: Press the RST button or toggle the EN pin to reset the board.
This concludes the documentation for the Arduino Nano ESP32. For further assistance, refer to the official Arduino documentation or community forums.