
How to Use Terminal Block (Connector): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Terminal Block (Connector) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Terminal Block (Connector) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A terminal block is a modular, insulated block designed to secure two or more wires together. It provides a convenient and reliable way to connect and disconnect electrical circuits without the need for soldering. Terminal blocks are widely used in electrical and electronic systems for organizing wiring and ensuring safe, durable connections.
Explore Projects Built with Terminal Block (Connector)
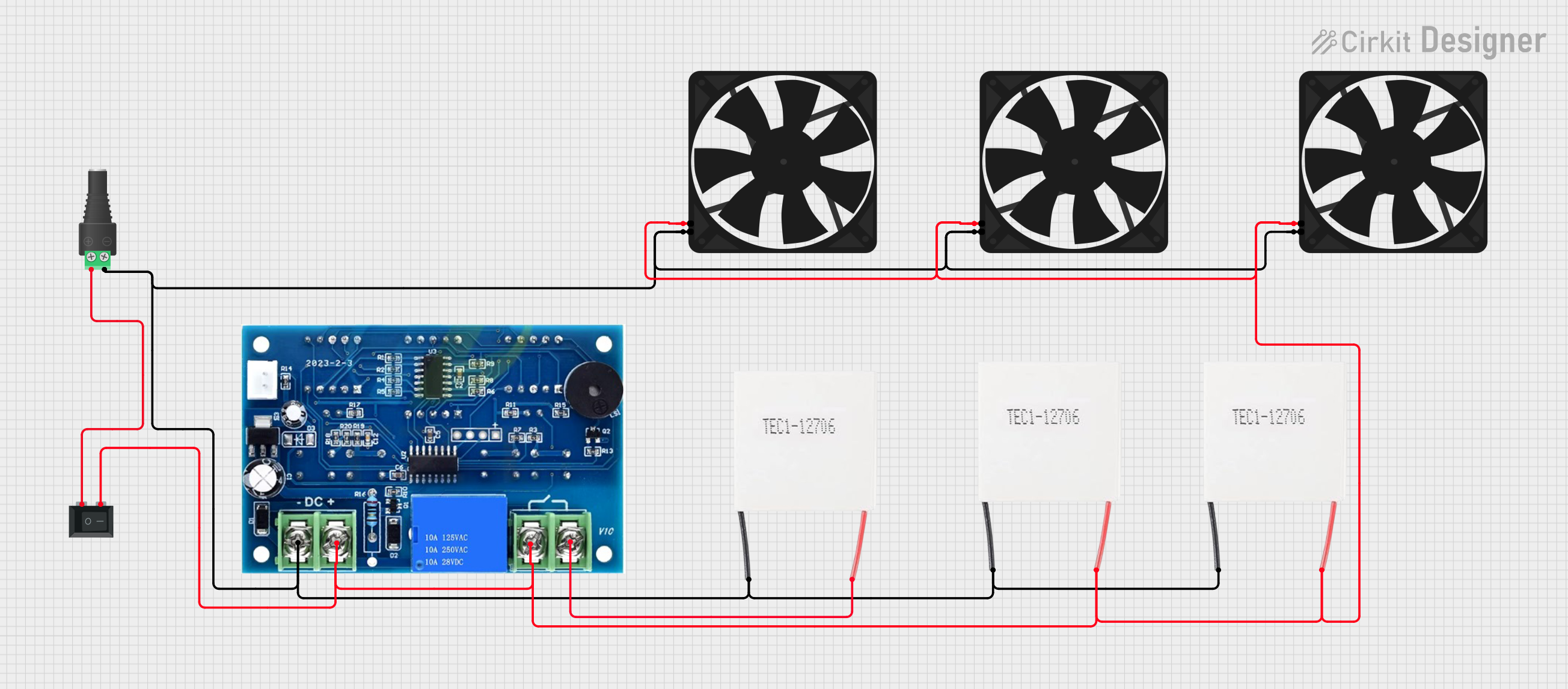
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer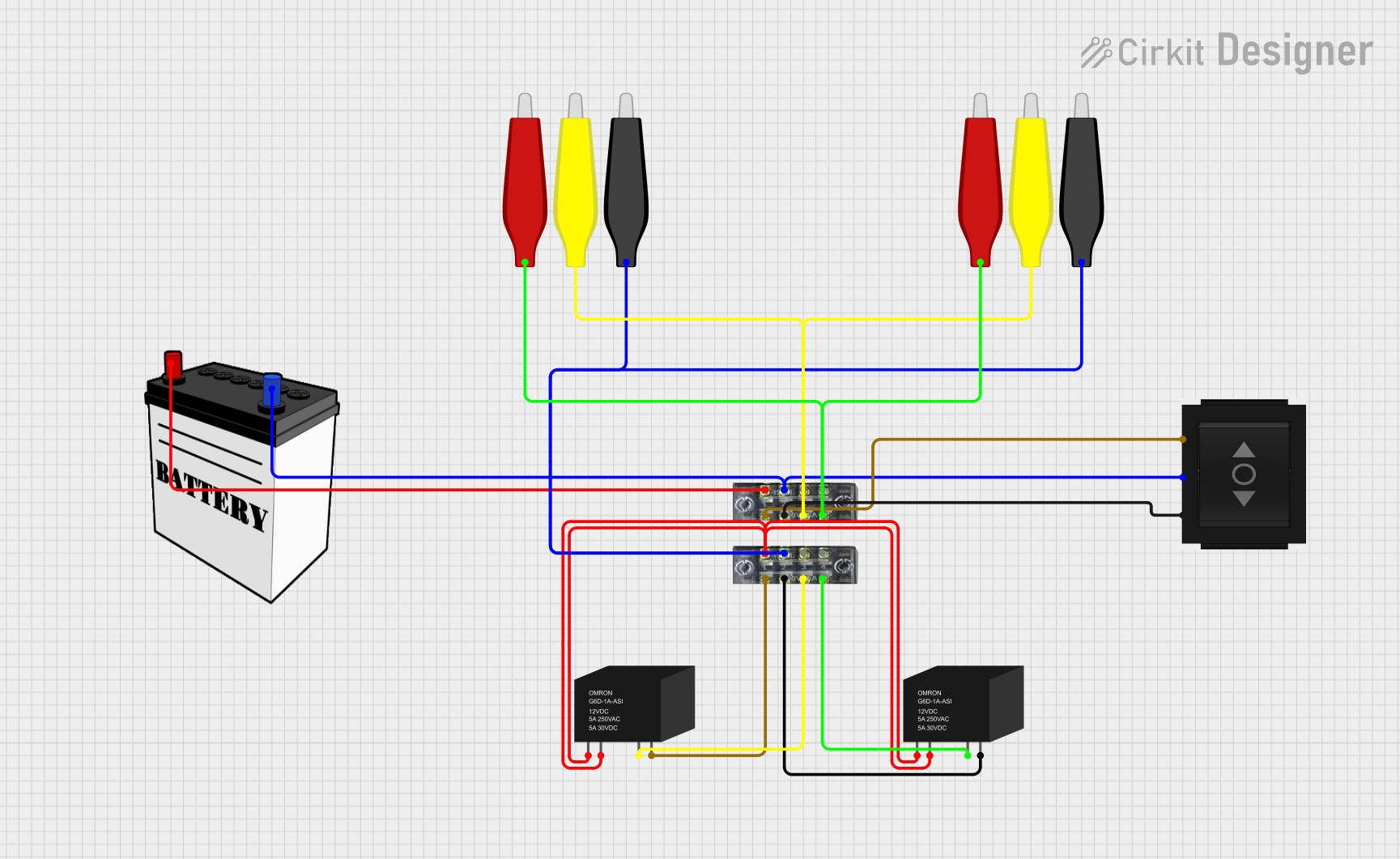
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer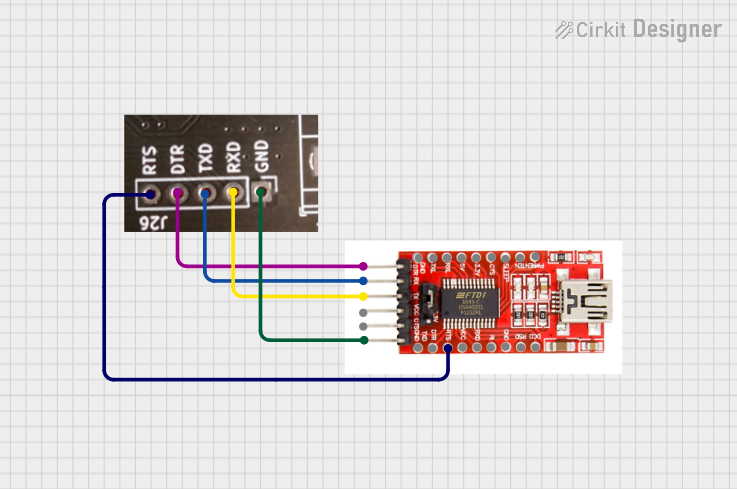
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Terminal Block (Connector)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial control panels and automation systems
- Power distribution and electrical wiring
- Circuit testing and prototyping
- Audio and speaker connections
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panel wiring)
- Home and building electrical installations
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Rating: Typically ranges from 12V to 600V, depending on the model.
- Current Rating: Commonly supports 5A to 150A, depending on the size and type.
- Wire Gauge Compatibility: Supports wire sizes from 22 AWG to 2 AWG.
- Insulation Material: Commonly made of polyamide (PA66) or other flame-retardant materials.
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +105°C (varies by model).
- Mounting Options: DIN rail, PCB mount, or panel mount.
- Connection Type: Screw terminals, spring clamps, or push-in connections.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Terminal blocks do not have "pins" in the traditional sense but instead feature connection points for wires. Below is a table describing the key parts of a typical screw-type terminal block:
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal Screw | Secures the wire in place by tightening it against the conductive metal contact. |
| Wire Entry Hole | The opening where the stripped wire is inserted. |
| Metal Contact Plate | Conductive material that ensures electrical connection between wires. |
| Insulation Housing | Non-conductive material that provides electrical insulation and mechanical support. |
| Mounting Mechanism | Allows the terminal block to be attached to a DIN rail, PCB, or panel. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Terminal Block in a Circuit
Prepare the Wires:
- Strip the insulation from the ends of the wires to expose about 5-10mm of the conductor.
- Ensure the exposed wire is clean and free of damage.
Insert the Wires:
- Loosen the terminal screw (if using a screw-type terminal block).
- Insert the stripped end of the wire into the wire entry hole.
Secure the Connection:
- Tighten the terminal screw to clamp the wire securely against the metal contact plate.
- Avoid overtightening, as this may damage the wire or the terminal block.
Verify the Connection:
- Gently tug on the wire to ensure it is firmly secured.
- Check for any exposed conductor that could cause a short circuit.
Mount the Terminal Block:
- Attach the terminal block to the desired surface (e.g., DIN rail, PCB, or panel).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Wire Compatibility: Always use wires within the supported gauge range of the terminal block.
- Tightening Torque: Follow the manufacturer's recommended torque specifications to avoid damaging the terminal.
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the current and voltage do not exceed the terminal block's ratings.
- Environmental Conditions: Use terminal blocks rated for the operating temperature and environmental conditions of your application.
- Periodic Maintenance: Inspect connections periodically for signs of corrosion, loosening, or wear.
Example: Connecting a Terminal Block to an Arduino UNO
While terminal blocks are not directly connected to an Arduino UNO, they can be used to organize and distribute power or signals in a circuit. Below is an example of using a terminal block to distribute power to multiple components in an Arduino project:
// Example: Distributing power using a terminal block in an Arduino project
// Connect the 5V and GND pins of the Arduino to the terminal block
// Use the terminal block to power multiple sensors or modules
void setup() {
// No specific code is required for the terminal block itself
// Ensure proper wiring and secure connections
}
void loop() {
// Example: Reading a sensor powered via the terminal block
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // Read sensor connected to A0
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
}
Note: Ensure that the terminal block is rated for the voltage and current of your Arduino project.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Wire slips out of the terminal block | Ensure the terminal screw is tightened properly. Check that the wire is stripped correctly. |
| Loose or intermittent connections | Inspect the wire and terminal for corrosion or damage. Retighten the screw. |
| Overheating of the terminal block | Verify that the current does not exceed the terminal block's rating. |
| Short circuits | Ensure no exposed conductor is touching adjacent terminals or metal surfaces. |
| Difficulty inserting wires | Check that the wire gauge is compatible with the terminal block. |
FAQs
Can I use a terminal block for high-frequency signals?
- Terminal blocks are generally suitable for low-frequency signals. For high-frequency applications, consider using specialized connectors to minimize signal loss.
What is the difference between screw-type and spring-clamp terminal blocks?
- Screw-type terminal blocks use screws to secure wires, while spring-clamp terminal blocks use a spring mechanism for faster and tool-free connections.
Can terminal blocks be reused?
- Yes, terminal blocks can be reused as long as they are not damaged. Ensure the screws and contacts are in good condition before reusing.
Are terminal blocks waterproof?
- Standard terminal blocks are not waterproof. For outdoor or wet environments, use terminal blocks with an IP-rated enclosure.
How do I choose the right terminal block for my application?
- Consider the voltage, current, wire gauge, mounting type, and environmental conditions when selecting a terminal block.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use terminal blocks to create safe and organized electrical connections in your projects.