
How to Use RFM210LCF: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with RFM210LCF in Cirkit Designer
Design with RFM210LCF in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The RFM210LCF is a low-power, long-range RF transceiver module manufactured by Hope Microelectronics. Designed for wireless communication, it operates in the 433 MHz frequency band and is ideal for applications requiring reliable and efficient data transmission. Its compact design and ease of integration make it a popular choice for developers working on remote control systems, telemetry, and sensor networks.
Explore Projects Built with RFM210LCF
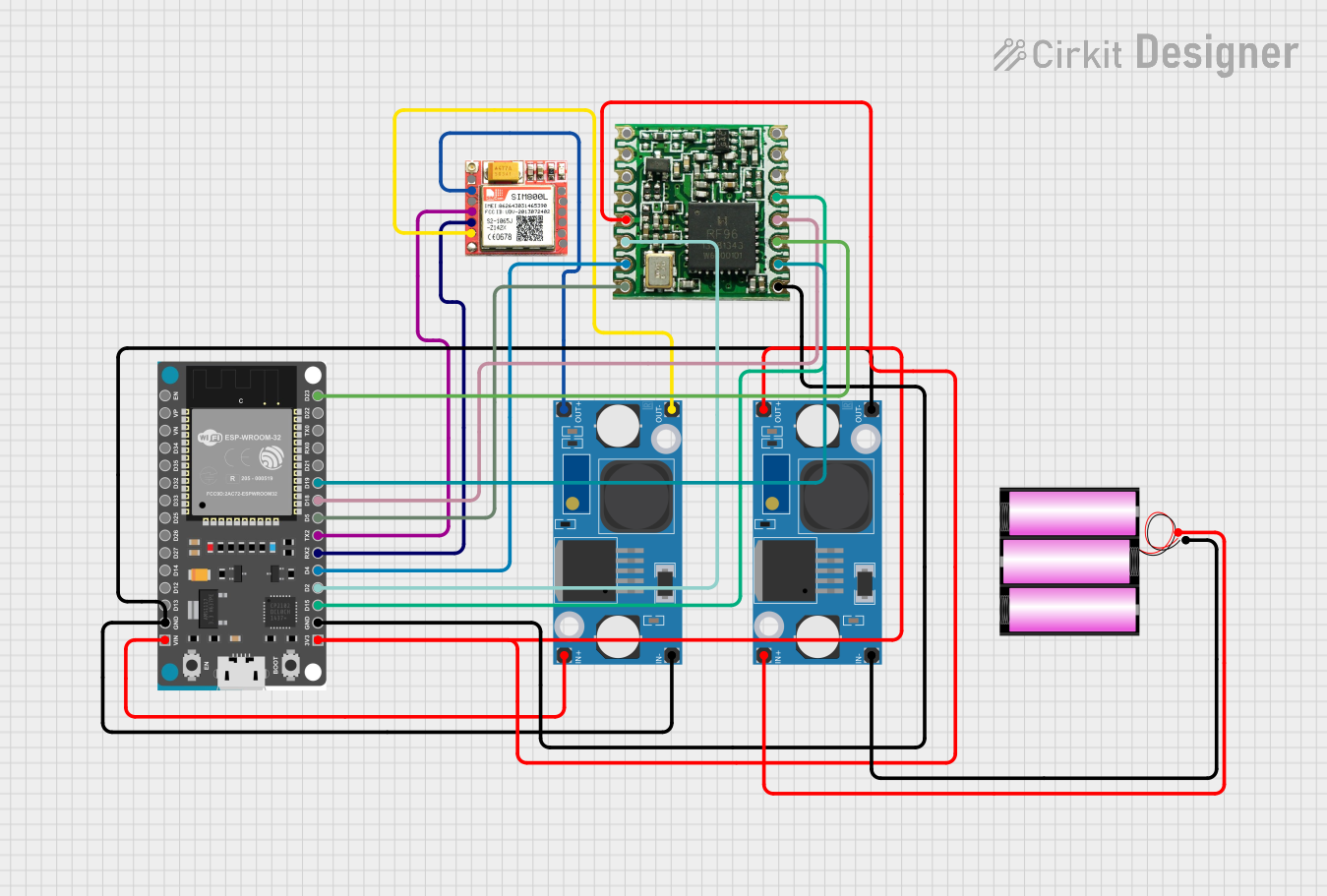
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer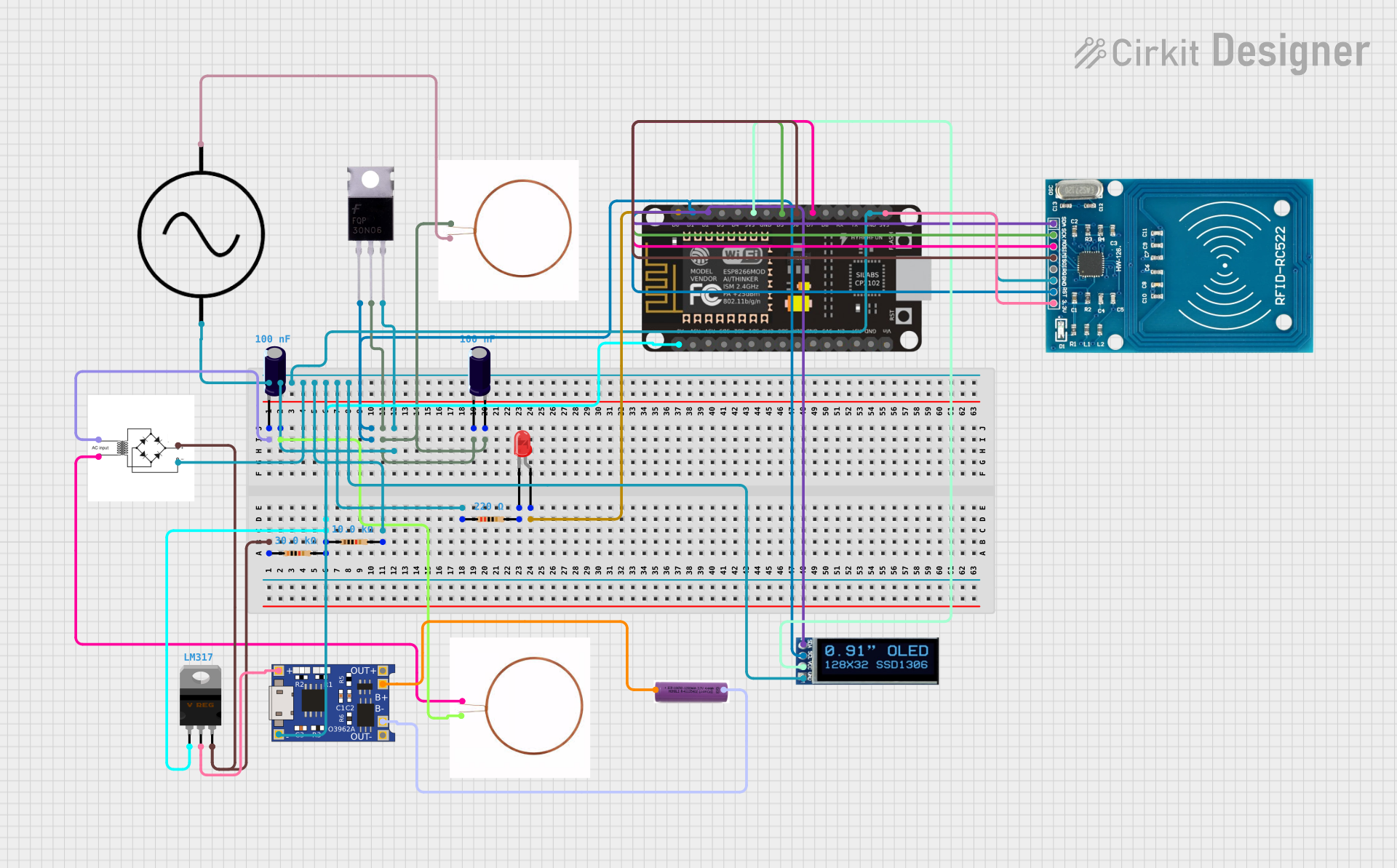
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer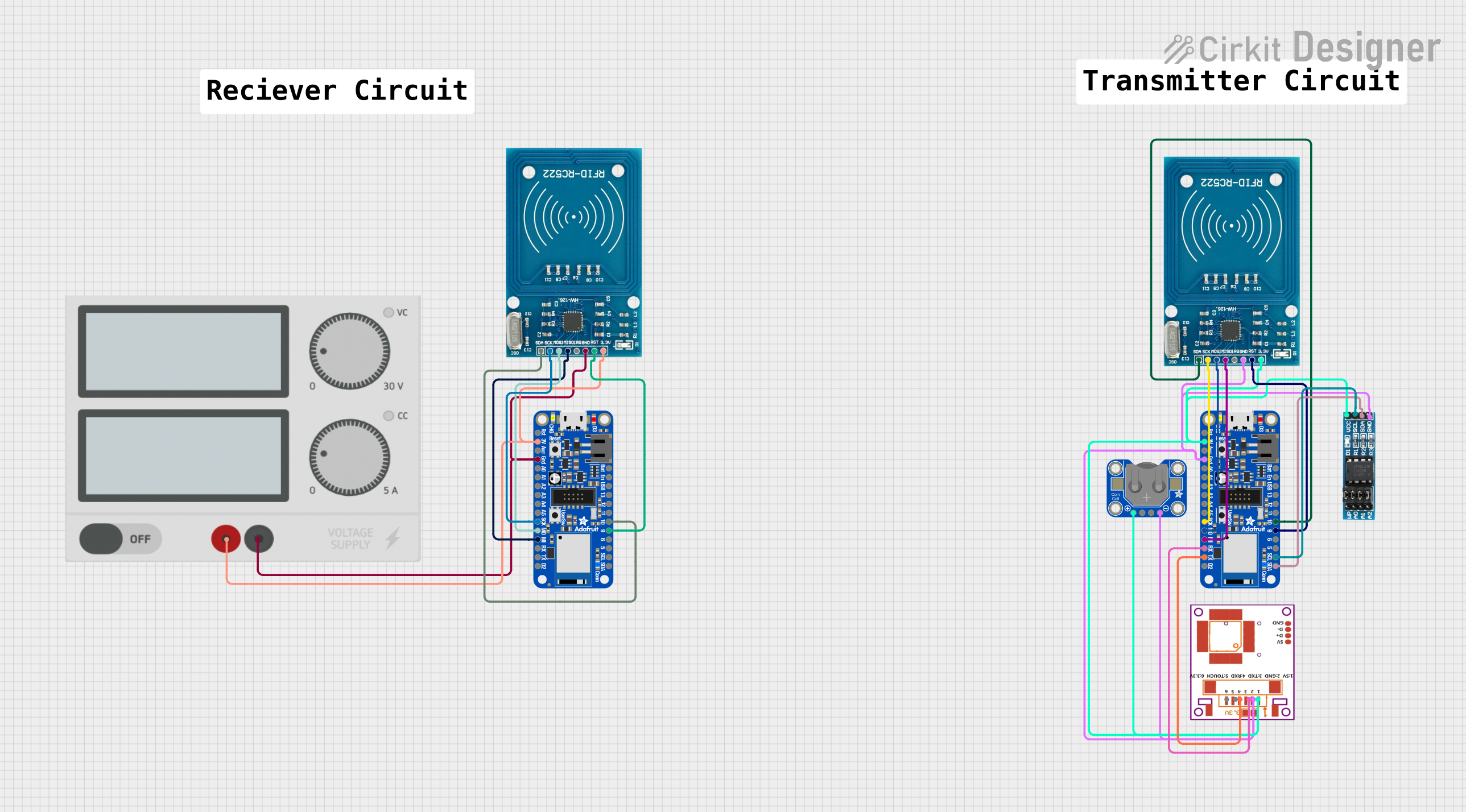
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RFM210LCF

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Remote control systems (e.g., garage doors, home automation)
- Wireless sensor networks
- Telemetry and data acquisition
- Industrial monitoring and control
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the RFM210LCF module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 433 MHz |
| Modulation Type | FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) |
| Supply Voltage | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Current Consumption | 9.5 mA (transmit mode, typical) |
| Sensitivity | -110 dBm (at 2.4 kbps) |
| Output Power | Up to +10 dBm |
| Data Rate | 1.2 kbps to 256 kbps |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 16 mm x 16 mm x 2 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The RFM210LCF module has a simple pinout for easy integration. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (1.8V to 3.6V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | ANT | Antenna connection for RF signal |
| 4 | SDI | Serial Data Input (SPI interface) |
| 5 | SDO | Serial Data Output (SPI interface) |
| 6 | SCK | Serial Clock Input (SPI interface) |
| 7 | CS | Chip Select (active low) |
| 8 | IRQ | Interrupt Request Output (indicates events) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the RFM210LCF in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a regulated power source (1.8V to 3.6V) and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Antenna: Attach a 50-ohm antenna to the ANT pin for optimal RF performance.
- SPI Communication: Use the SDI, SDO, SCK, and CS pins to interface with a microcontroller via the SPI protocol.
- Interrupt Handling: Connect the IRQ pin to a GPIO pin on your microcontroller to handle events such as data reception or transmission completion.
Important Considerations
- Antenna Design: Ensure the antenna is properly matched to the 433 MHz frequency band for maximum range and efficiency.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) close to the VCC pin to reduce noise and improve stability.
- SPI Configuration: Configure the SPI interface on your microcontroller to match the RFM210LCF's requirements (e.g., clock polarity and phase).
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure your application complies with local RF regulations for the 433 MHz band.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the RFM210LCF to an Arduino UNO and send data:
Wiring Diagram
| RFM210LCF Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| SDI | D11 (MOSI) |
| SDO | D12 (MISO) |
| SCK | D13 (SCK) |
| CS | D10 |
| IRQ | D2 |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SPI.h>
// Define RFM210LCF pins
#define CS_PIN 10
#define IRQ_PIN 2
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize SPI
SPI.begin();
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Set CS high to deselect the module
// Configure IRQ pin
pinMode(IRQ_PIN, INPUT);
Serial.println("RFM210LCF Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Example: Send a command to the RFM210LCF
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Select the module
SPI.transfer(0x01); // Send a dummy command (replace with actual command)
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deselect the module
// Check for IRQ events
if (digitalRead(IRQ_PIN) == LOW) {
Serial.println("IRQ Event Detected");
// Handle the event (e.g., read received data)
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No RF Signal Detected
- Solution: Verify the antenna connection and ensure it is tuned for the 433 MHz band.
- Solution: Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range (1.8V to 3.6V).
SPI Communication Fails
- Solution: Ensure the SPI pins are correctly connected and configured on the microcontroller.
- Solution: Verify the SPI clock settings (e.g., polarity and phase) match the RFM210LCF's requirements.
Short Range or Poor Signal Quality
- Solution: Use a high-quality 50-ohm antenna and minimize obstructions between the transmitter and receiver.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor near the VCC pin to reduce noise.
IRQ Pin Not Triggering
- Solution: Ensure the IRQ pin is connected to a GPIO pin configured as an input.
- Solution: Check the RFM210LCF's configuration to ensure interrupts are enabled.
FAQs
Q: Can the RFM210LCF operate at frequencies other than 433 MHz?
A: No, the RFM210LCF is specifically designed for the 433 MHz frequency band.
Q: What is the maximum data rate supported by the RFM210LCF?
A: The module supports data rates up to 256 kbps.
Q: Is the RFM210LCF suitable for battery-powered applications?
A: Yes, its low power consumption makes it ideal for battery-powered devices.
Q: Does the RFM210LCF support encryption?
A: No, the module does not have built-in encryption. You can implement encryption at the software level on your microcontroller.