
How to Use 220 fan: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with 220 fan in Cirkit Designer
Design with 220 fan in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 220V fan is an electric fan designed to operate on a 220-volt AC power supply. It is commonly used for cooling and ventilation purposes in a wide range of applications, including industrial equipment, home appliances, and electronic enclosures. These fans are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring the longevity of electronic components and systems.
Explore Projects Built with 220 fan
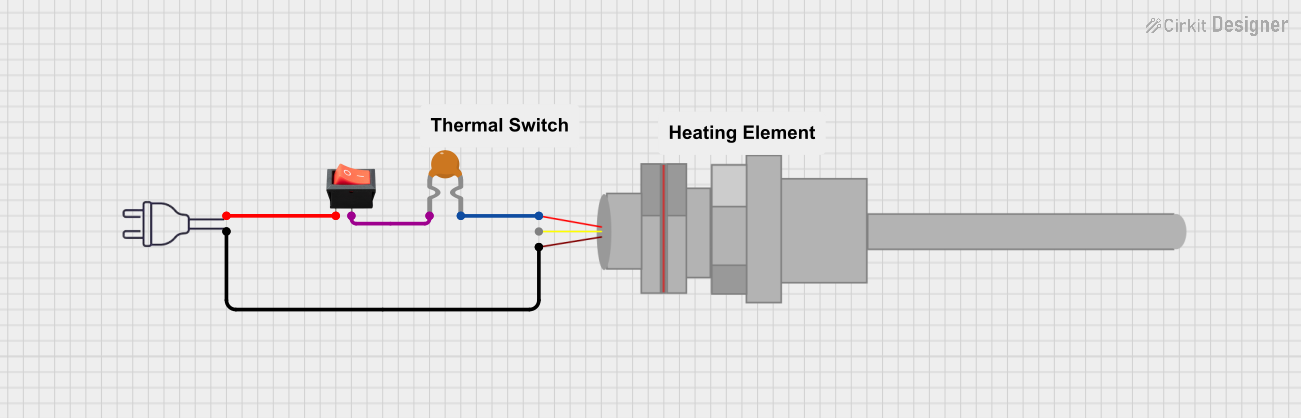
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer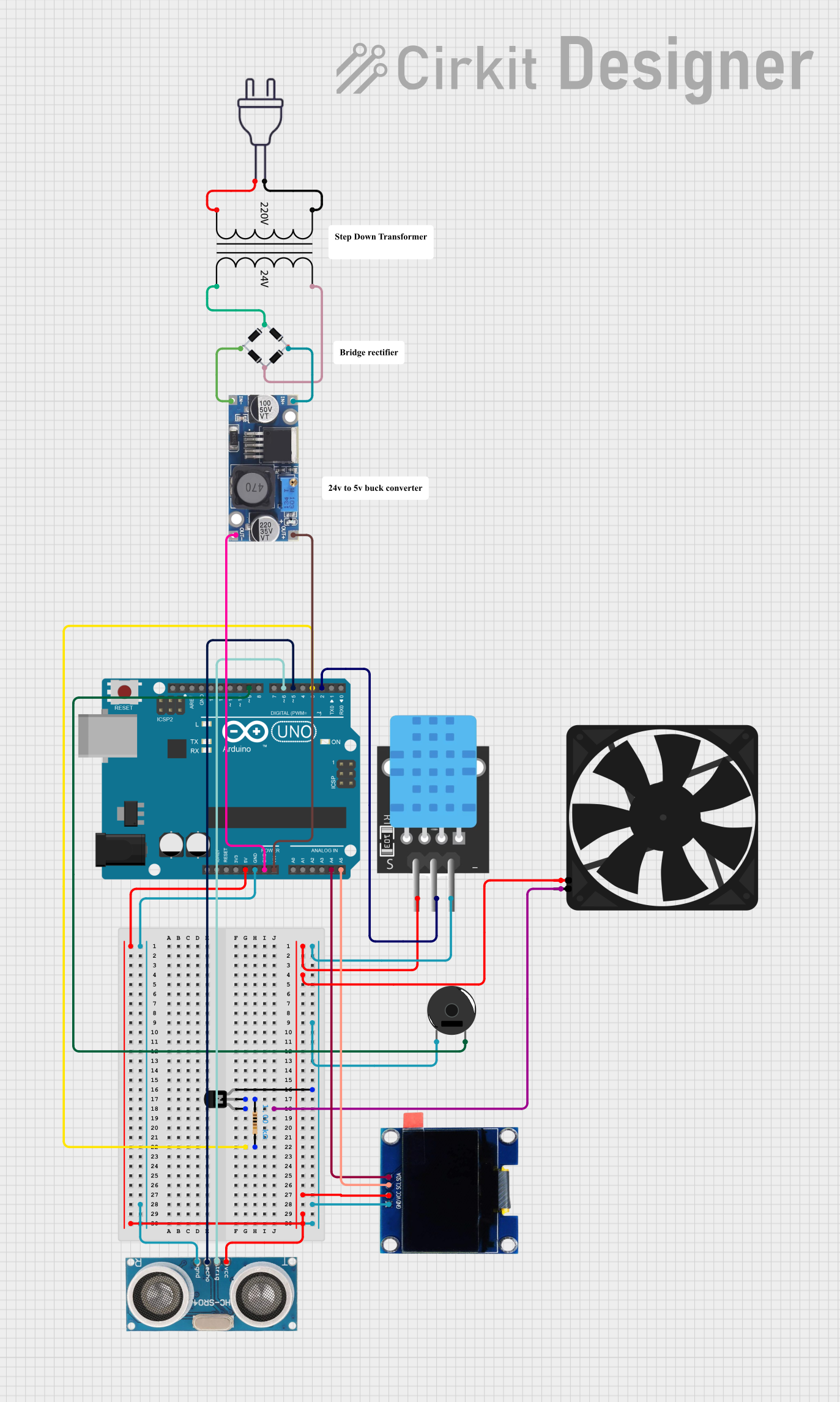
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer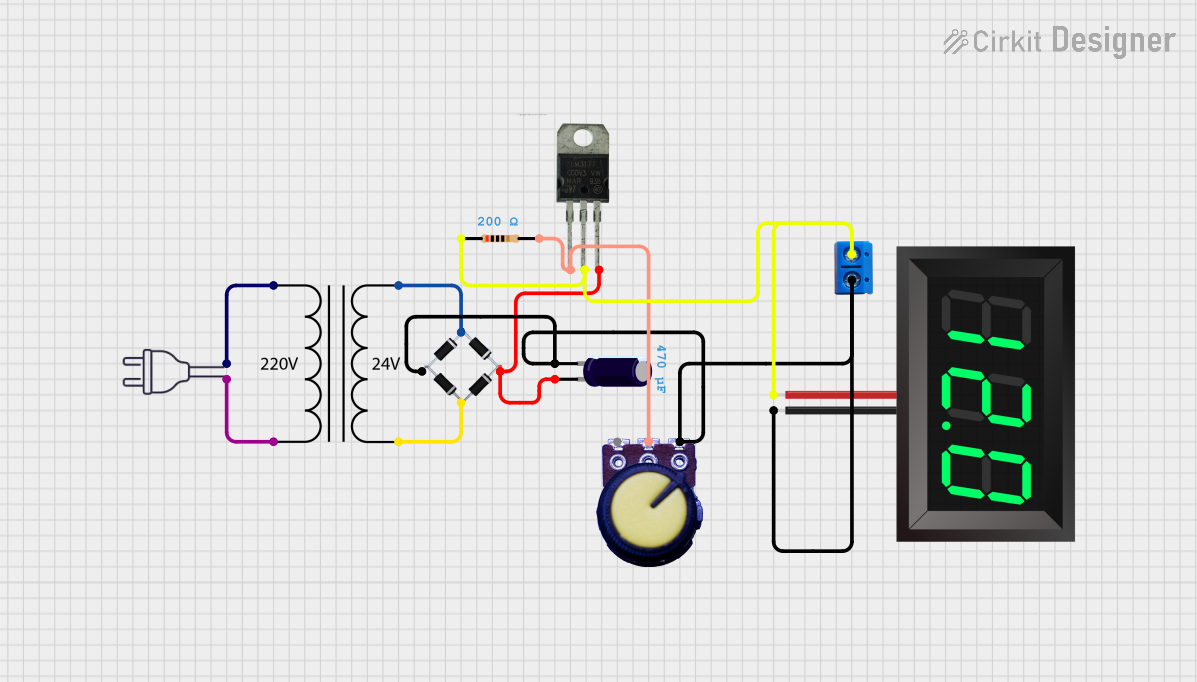
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 220 fan

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Cooling electronic devices such as power supplies, amplifiers, and computers.
- Ventilation in industrial machinery and control panels.
- Air circulation in home appliances like air purifiers and HVAC systems.
- Heat dissipation in 3D printers and other high-power equipment.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical 220V fan:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 220V AC |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Power Consumption | 10W to 50W (varies by model) |
| Airflow | 20 CFM to 200 CFM (varies by size) |
| Speed | 1500 to 3000 RPM |
| Noise Level | 25 dB to 50 dB |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 70°C |
| Dimensions | 80mm x 80mm, 120mm x 120mm, etc. |
| Connector Type | Bare wires or terminal block |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Most 220V fans have a simple two-wire configuration for AC power input. The table below describes the wiring:
| Pin/Wire | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Live (L) | Brown | Connects to the live AC line. |
| Neutral (N) | Blue | Connects to the neutral AC line. |
Note: Some models may include a third wire for grounding (green/yellow). Always refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for specific wiring details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 220V Fan in a Circuit
- Safety First: Ensure the power supply is turned off before wiring the fan. Use insulated tools and follow proper safety precautions when working with high-voltage components.
- Wiring:
- Connect the brown wire (Live) to the live terminal of the 220V AC power source.
- Connect the blue wire (Neutral) to the neutral terminal of the power source.
- If the fan includes a ground wire (green/yellow), connect it to the ground terminal for safety.
- Mounting: Secure the fan in place using screws or brackets. Ensure proper airflow direction by checking the fan's markings (usually an arrow indicating airflow direction).
- Power On: After verifying the connections, turn on the power supply to operate the fan.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the fan is rated for 220V AC. Using it with an incorrect voltage can damage the fan or pose safety risks.
- Airflow Direction: Install the fan in the correct orientation to achieve the desired airflow.
- Noise Levels: Choose a fan with an appropriate noise level for your application, especially in quiet environments.
- Maintenance: Periodically clean the fan blades and housing to prevent dust buildup, which can reduce efficiency and increase noise.
- Safety: Always use a fuse or circuit breaker to protect the fan and circuit from overcurrent.
Example: Controlling a 220V Fan with an Arduino UNO
While the Arduino UNO operates on low voltage (5V DC), you can control a 220V fan using a relay module. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Components
- Arduino UNO
- 5V relay module
- 220V fan
- External 220V AC power supply
- Jumper wires
Code Example
// This code demonstrates how to control a 220V fan using an Arduino UNO
// and a relay module. The fan will turn on for 5 seconds, then off for 5 seconds.
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off at startup
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Turn the relay (and fan) on
delay(5000); // Keep the fan on for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Turn the relay (and fan) off
delay(5000); // Keep the fan off for 5 seconds
}
Warning: Always exercise caution when working with high-voltage components. Ensure proper isolation between the Arduino and the 220V AC circuit.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fan Does Not Turn On
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring connections and ensure the power supply is active.
Fan Makes Excessive Noise
- Cause: Dust buildup or mechanical obstruction.
- Solution: Clean the fan blades and housing. Check for any loose screws or debris.
Fan Overheats
- Cause: Insufficient ventilation or prolonged operation beyond rated capacity.
- Solution: Ensure proper airflow around the fan and avoid exceeding its operating limits.
Relay Does Not Activate the Fan
- Cause: Incorrect relay wiring or insufficient power to the relay module.
- Solution: Verify the relay connections and ensure the Arduino provides sufficient current to the relay.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 220V fan with a 110V power supply?
A: No, a 220V fan is designed specifically for 220V AC. Using it with a 110V supply will result in insufficient performance or failure to operate.
Q: How do I determine the airflow direction of the fan?
A: Most fans have an arrow on the housing indicating the airflow direction. If not, the airflow typically moves from the open side of the fan towards the side with the motor.
Q: Can I control the fan speed?
A: Some 220V fans support speed control using a triac-based dimmer or a variable frequency drive (VFD). Check the fan's datasheet for compatibility.
Q: Is it safe to use a 220V fan outdoors?
A: Only if the fan is rated for outdoor use and has an appropriate IP (Ingress Protection) rating to withstand moisture and dust.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use a 220V fan in your projects and applications.