
How to Use Male plug: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Male plug in Cirkit Designer
Design with Male plug in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The male plug is a type of electrical connector characterized by protruding pins designed to fit into a corresponding female socket. It facilitates the transmission of electrical power or signals between devices or components. Male plugs are widely used in various applications, including power supplies, audio/video connections, and data transmission.
Explore Projects Built with Male plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer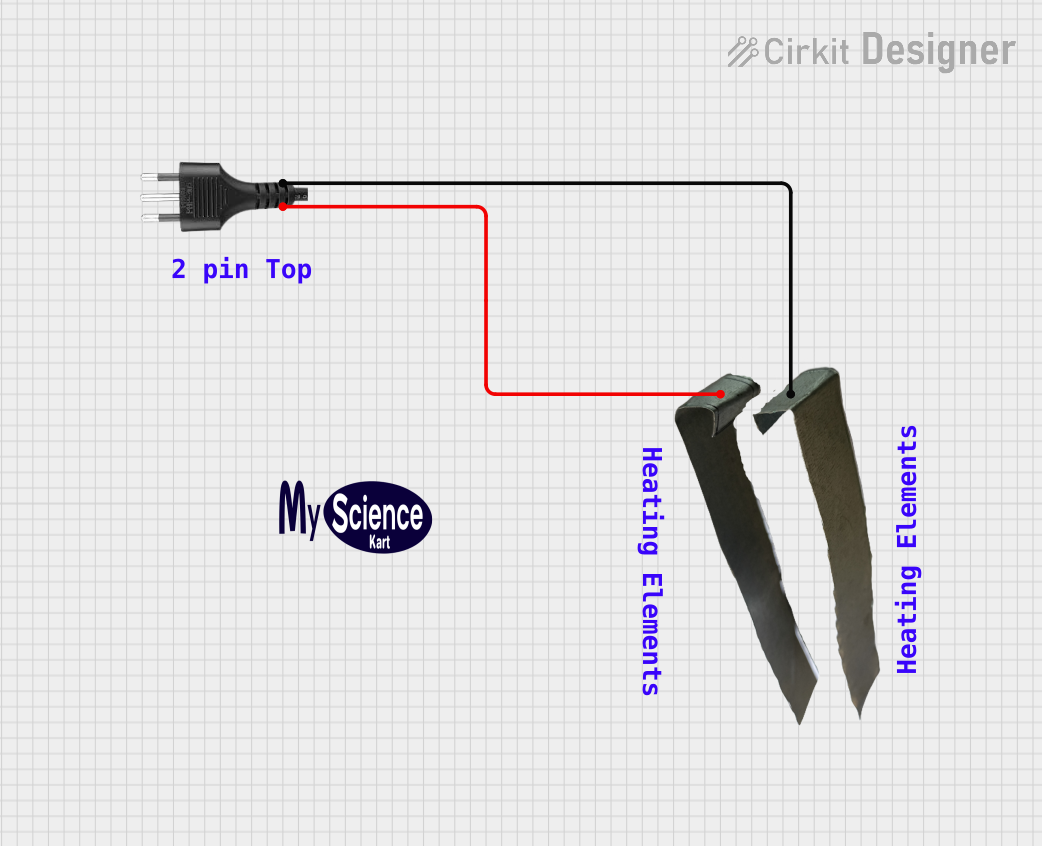
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer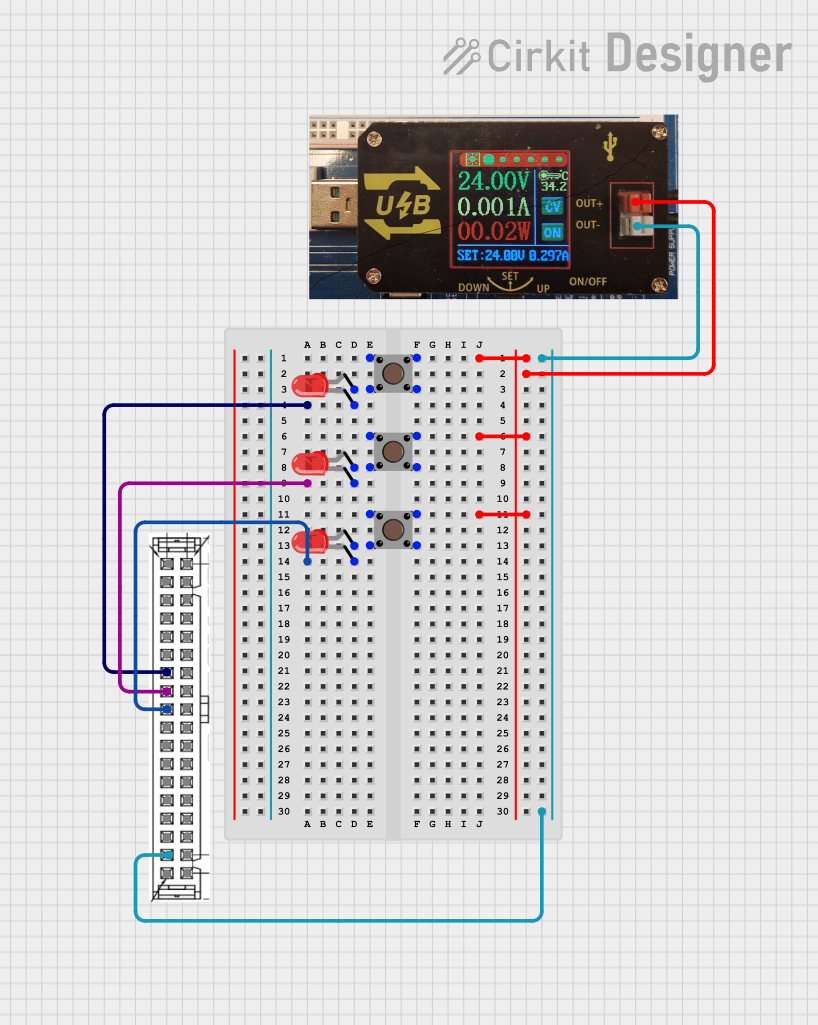
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Male plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power connections for household appliances and electronic devices
- Audio and video equipment, such as headphones and AV cables
- Data communication in computer peripherals and networking
- Prototyping and breadboard connections in electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of a male plug can vary depending on its type and intended application. Below are general specifications for a standard male plug:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 5V to 250V (depending on type) |
| Current Rating | 0.5A to 15A (depending on type) |
| Pin Material | Brass, copper, or gold-plated metal |
| Insulation Material | Plastic, rubber, or thermoplastic |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a male plug depends on its type. Below is an example for a 3-pin male plug commonly used in AC power connections:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Live (L) | Carries the live current from the power source. |
| 2 | Neutral (N) | Completes the circuit by returning current. |
| 3 | Ground (G) | Provides a safety path for fault currents. |
For other types of male plugs, such as audio jacks or data connectors, the pin configuration will differ.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Male Plug in a Circuit
- Identify the Pinout: Refer to the pin configuration table to understand the function of each pin.
- Connect to the Female Socket: Align the male plug with the corresponding female socket and insert it securely.
- Ensure Proper Insulation: Verify that the insulation material is intact to prevent short circuits or electric shocks.
- Test the Connection: Use a multimeter to check for continuity and ensure proper electrical contact.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Always ensure the male plug is rated for the voltage and current of your application to avoid overheating or damage.
- Secure Connections: Ensure the male plug is firmly inserted into the female socket to prevent loose connections.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the maximum current rating of the male plug.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly check the pins and insulation for wear or damage.
Example: Using a Male Plug with an Arduino UNO
If you are using a male plug to connect a power supply to an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
- Identify the positive (VCC) and negative (GND) terminals of the male plug.
- Connect the positive terminal to the Arduino's VIN pin and the negative terminal to the GND pin.
- Ensure the power supply voltage matches the Arduino's input voltage range (7-12V).
// Example code to blink an LED on Arduino UNO
// Ensure the male plug is properly connected to the Arduino's power input
int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Loose Connection: The male plug does not fit securely into the female socket.
- Solution: Check for debris or damage in the socket and ensure the plug is properly aligned.
- Overheating: The male plug becomes hot during use.
- Solution: Verify that the plug is not exceeding its current rating and inspect for short circuits.
- No Signal or Power: The connected device does not receive power or signals.
- Solution: Use a multimeter to check for continuity and ensure proper pin connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a male plug with a higher voltage rating than required?
A: Yes, a higher voltage rating is acceptable as long as the current rating is not exceeded.
Q: How do I clean the pins of a male plug?
A: Use a soft cloth or a small brush with isopropyl alcohol to clean the pins. Avoid abrasive materials that may damage the surface.
Q: Can I repair a damaged male plug?
A: Minor repairs, such as replacing a broken pin, may be possible. However, for safety-critical applications, it is recommended to replace the plug entirely.