
How to Use MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A in Cirkit Designer
Design with MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
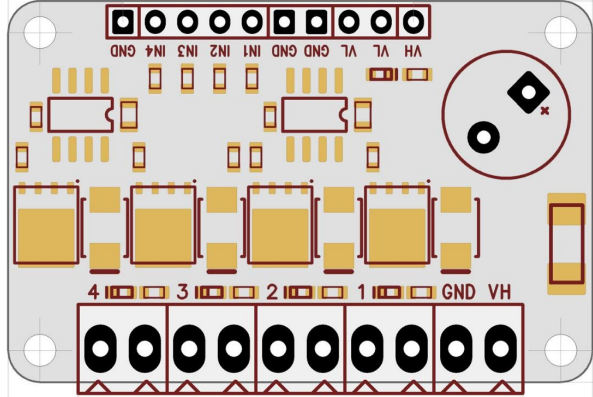
The MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A (Manufacturer Part ID: EKM014 - UCC27524) is a 4-channel MOSFET driver board designed by Electrokit. It is capable of handling up to 50V and 10A per channel, making it ideal for controlling high-power loads such as motors, LEDs, and heating elements. This driver board allows low-power control signals, such as those from microcontrollers, to efficiently drive high-power devices.
Explore Projects Built with MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer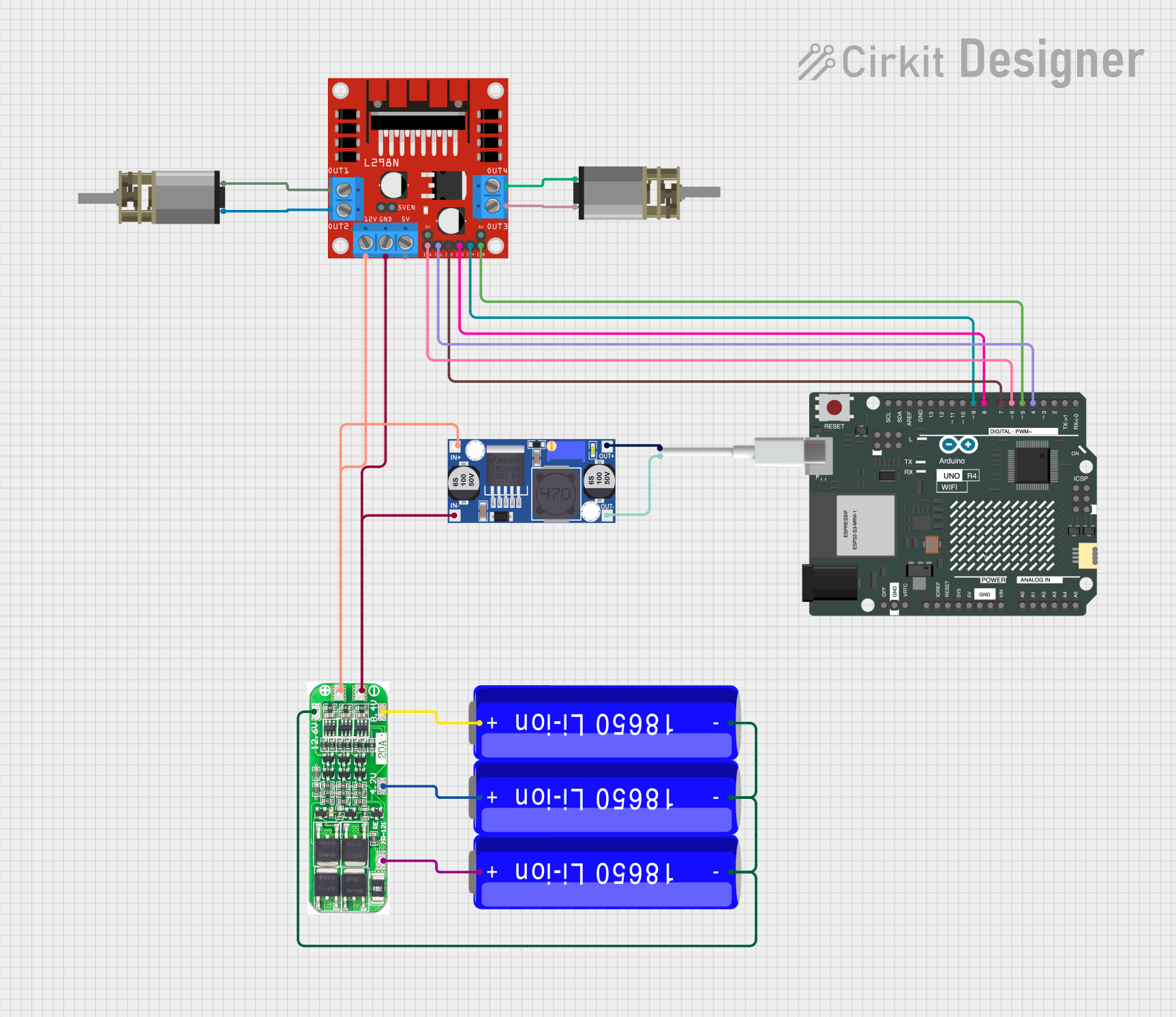
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer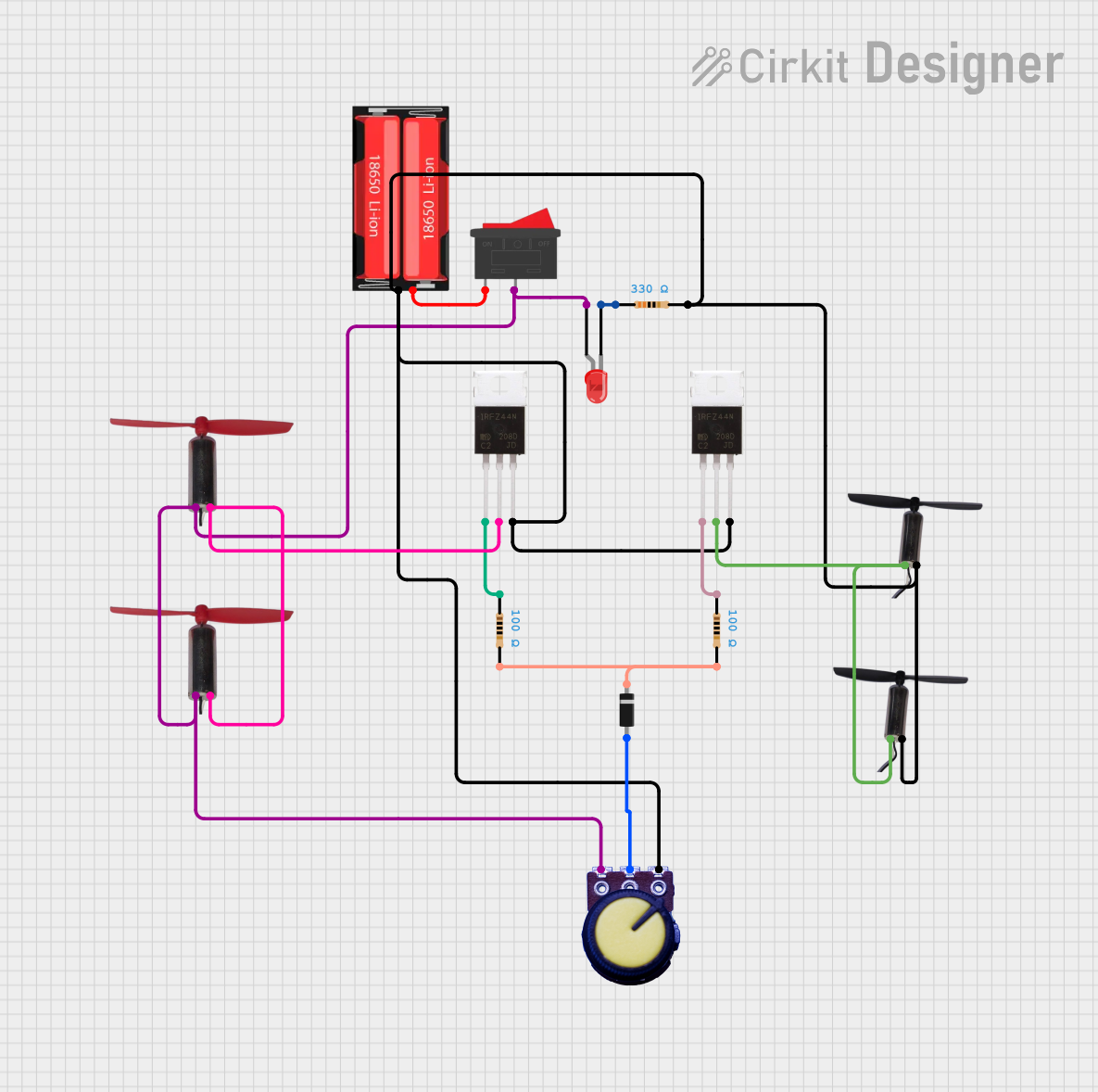
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer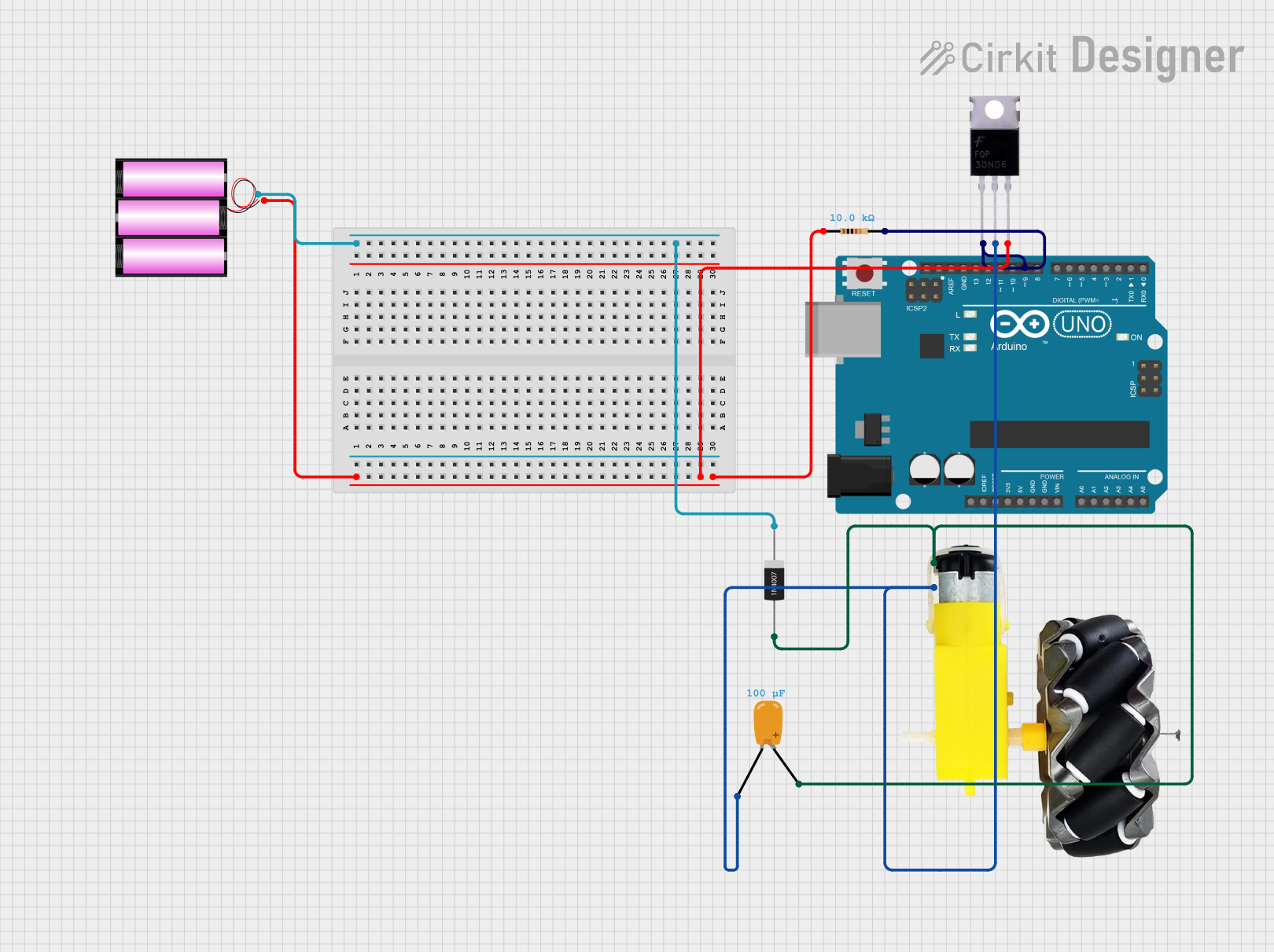
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MOSFET Drivkort 4-kan 50V 10A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
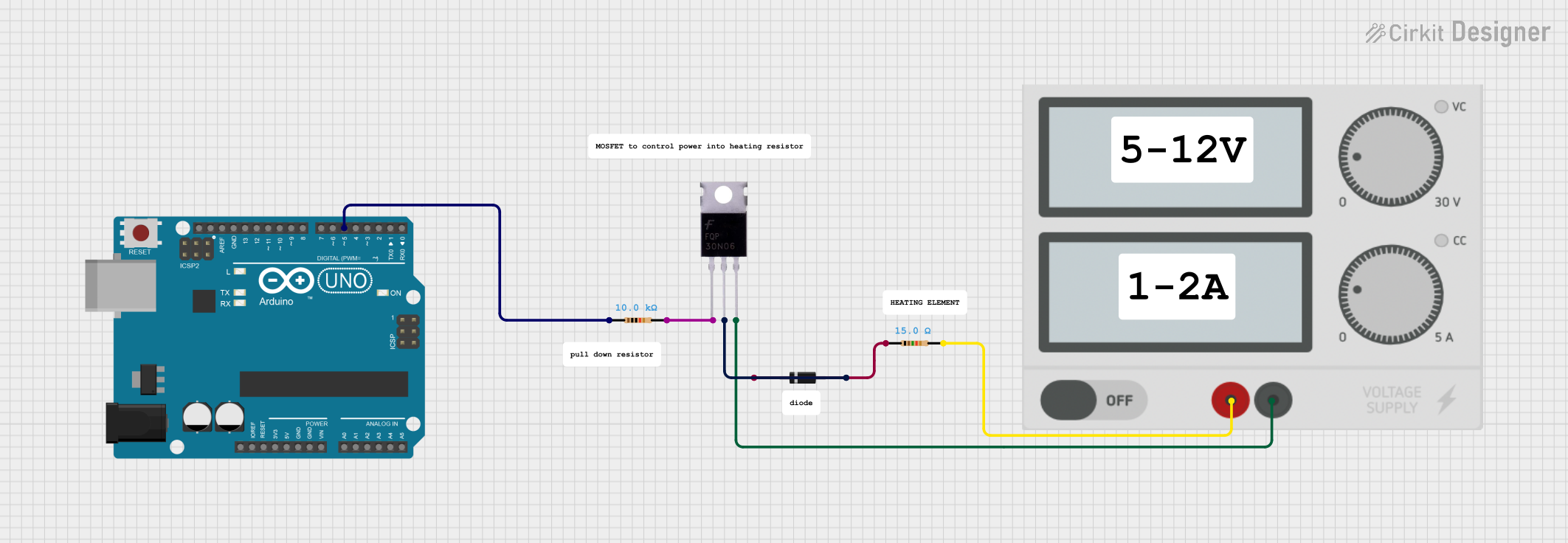
- Driving high-power DC motors
- Controlling high-current LED arrays
- Switching heating elements in industrial applications
- General-purpose high-power switching in automation systems
- Interfacing with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or other logic-level devices
Technical Specifications
The following are the key technical details of the MOSFET driver board:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage (Logic) | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Voltage (Load) | Up to 50V |
| Maximum Output Current | 10A per channel |
| Number of Channels | 4 |
| MOSFET Driver IC | UCC27524 |
| Switching Frequency | Up to 1 MHz |
| Board Dimensions | 50mm x 50mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MOSFET driver board has the following pinout:
Input Side (Logic Control)
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IN1 | Control signal for Channel 1 (3.3V or 5V logic) |
| 2 | IN2 | Control signal for Channel 2 (3.3V or 5V logic) |
| 3 | IN3 | Control signal for Channel 3 (3.3V or 5V logic) |
| 4 | IN4 | Control signal for Channel 4 (3.3V or 5V logic) |
| 5 | GND | Ground connection for logic signals |
| 6 | VCC | Power supply for logic signals (3.3V to 5V) |
Output Side (Load Control)
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | OUT1 | Output for Channel 1 (connect to load) |
| 2 | OUT2 | Output for Channel 2 (connect to load) |
| 3 | OUT3 | Output for Channel 3 (connect to load) |
| 4 | OUT4 | Output for Channel 4 (connect to load) |
| 5 | GND | Ground connection for load |
| 6 | VIN | Power supply for the load (up to 50V) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the VIN pin to the positive terminal of your load power supply (up to 50V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your load power supply.
- Connect the VCC pin to the power supply for the logic signals (3.3V or 5V).
- Ensure that the ground of the logic power supply is connected to the ground of the load power supply.
Control Signals:
- Connect the control signals (e.g., from a microcontroller) to the IN1, IN2, IN3, and IN4 pins.
- Use 3.3V or 5V logic levels to control the MOSFETs.
Load Connections:
- Connect your load (e.g., motor, LED array) to the OUT1, OUT2, OUT3, and OUT4 pins as needed.
Testing:
- Apply the appropriate control signals to the input pins and verify that the load is switching on and off as expected.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the load does not exceed the maximum current rating of 10A per channel.
- Use proper heat dissipation methods (e.g., heatsinks) if operating at high currents for extended periods.
- Avoid short circuits between the output pins and ground or power supply.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
Example: Using with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a motor connected to Channel 1 using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the control pin for Channel 1
const int controlPin1 = 9;
void setup() {
// Set the control pin as an output
pinMode(controlPin1, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the motor ON
digitalWrite(controlPin1, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the motor ON for 1 second
// Turn the motor OFF
digitalWrite(controlPin1, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the motor OFF for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The load is not turning on:
- Verify that the control signal voltage matches the logic level (3.3V or 5V).
- Check the power supply connections for both the logic and load sides.
- Ensure that the load is properly connected to the output pins.
The MOSFET driver board overheats:
- Ensure that the load current does not exceed 10A per channel.
- Use a heatsink or active cooling if operating at high currents.
The load behaves erratically:
- Check for noise or instability in the power supply.
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
The board does not respond to control signals:
- Verify that the ground of the logic power supply is connected to the ground of the load power supply.
- Ensure that the control signals are properly connected to the input pins.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this board to control an AC load?
A: No, this board is designed for DC loads only. For AC loads, consider using a relay or a solid-state relay.
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum current rating?
A: Exceeding the 10A per channel limit can damage the MOSFETs and the driver IC. Always ensure that your load stays within the specified limits.
Q: Can I use this board with a 12V logic signal?
A: No, the logic input voltage must be between 3.3V and 5V. Using higher voltages can damage the driver IC.
Q: Is it possible to control all four channels independently?
A: Yes, each channel has its own control input, allowing independent operation of all four channels.