
How to Use WPI409 dubbele H-brug driver L298N voor DC- of stappenmotor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
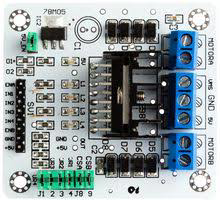
 Design with WPI409 dubbele H-brug driver L298N voor DC- of stappenmotor in Cirkit Designer
Design with WPI409 dubbele H-brug driver L298N voor DC- of stappenmotor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The WPI409 Dual H-Bridge Driver Module, manufactured by Whadda, is a versatile and robust motor driver based on the L298N chip. This module is designed to control DC motors or stepper motors, providing bidirectional control with a high current capacity. It is widely used in robotics, automation, and various DIY electronics projects.
Explore Projects Built with WPI409 dubbele H-brug driver L298N voor DC- of stappenmotor
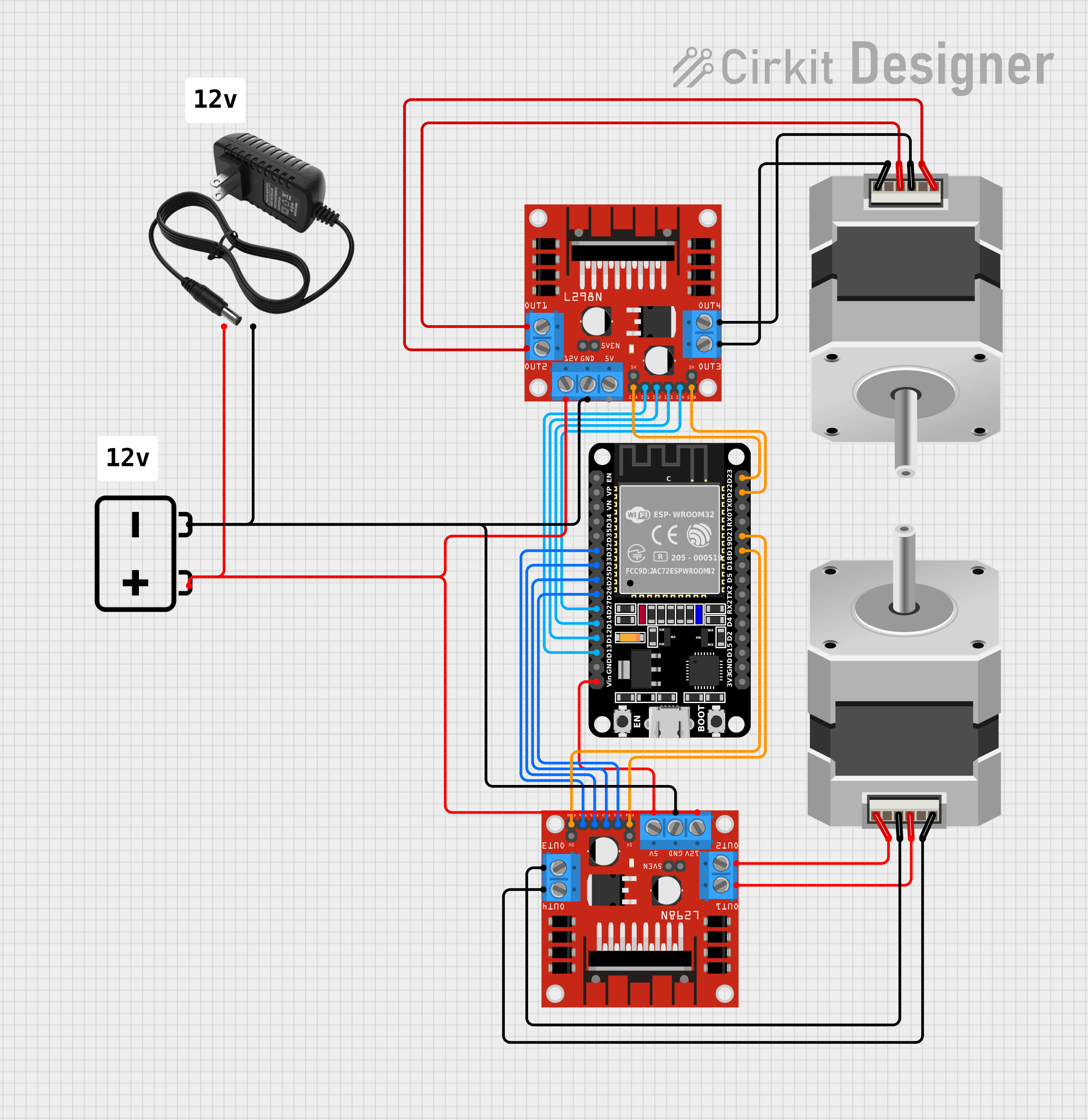
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer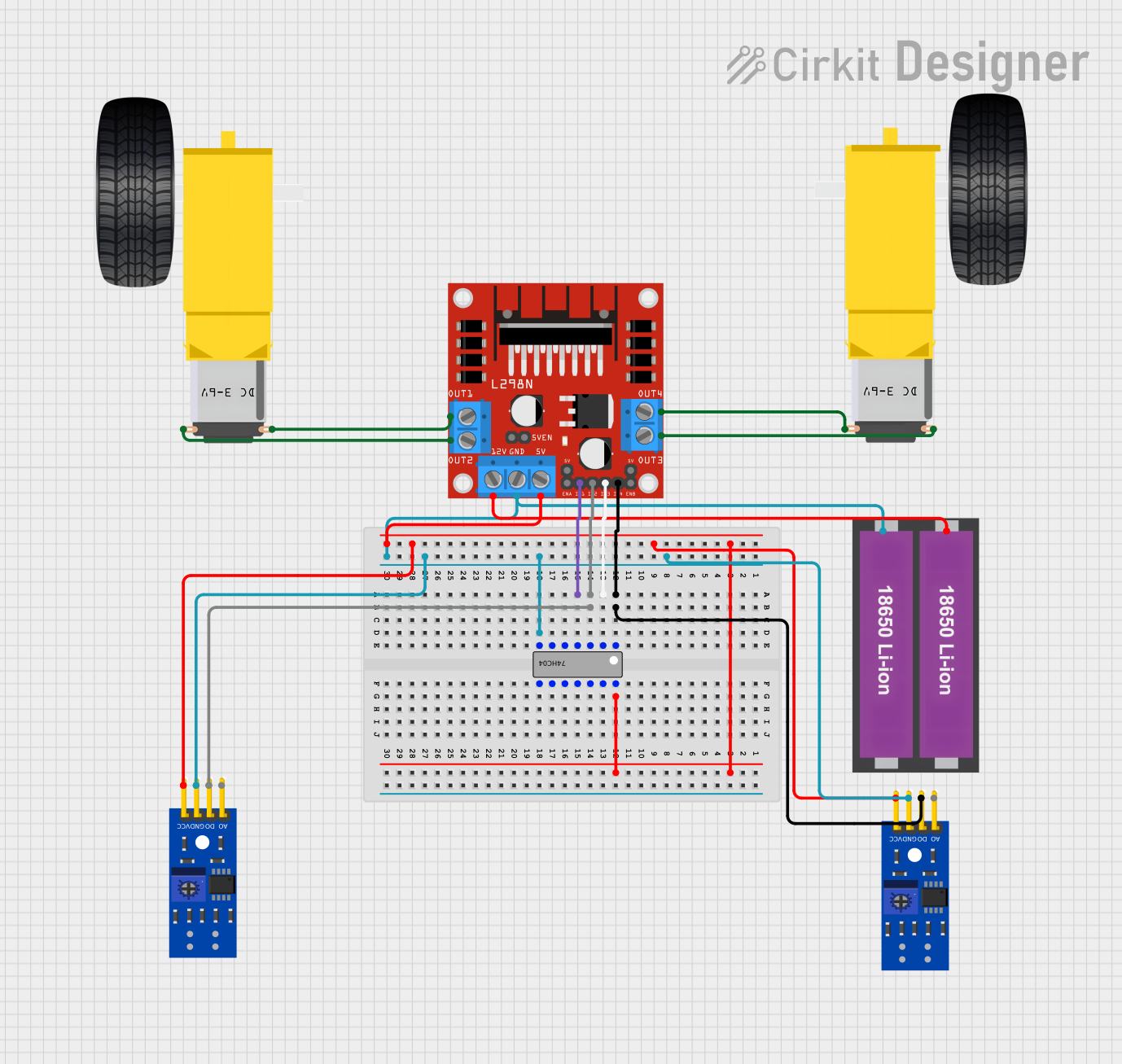
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer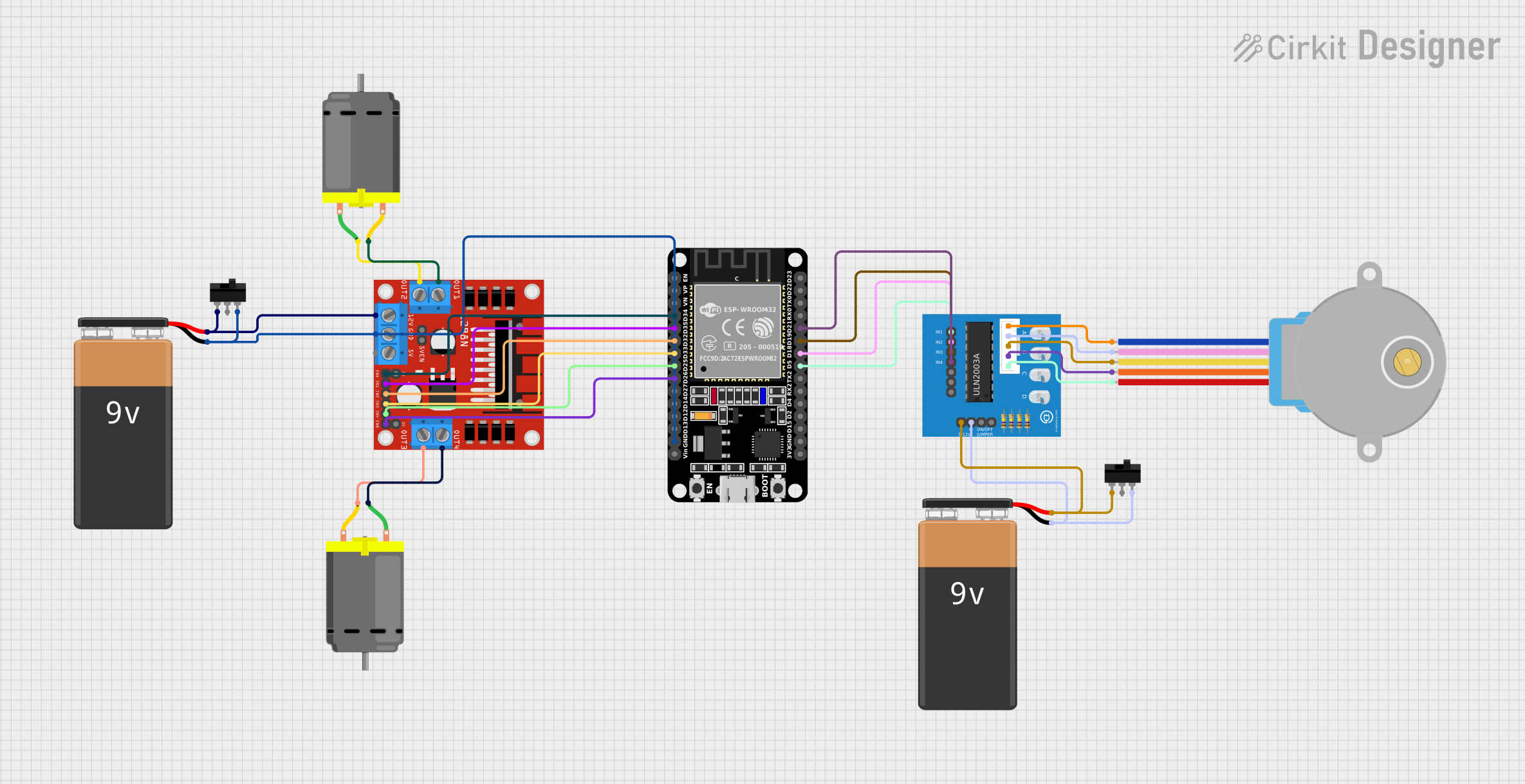
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer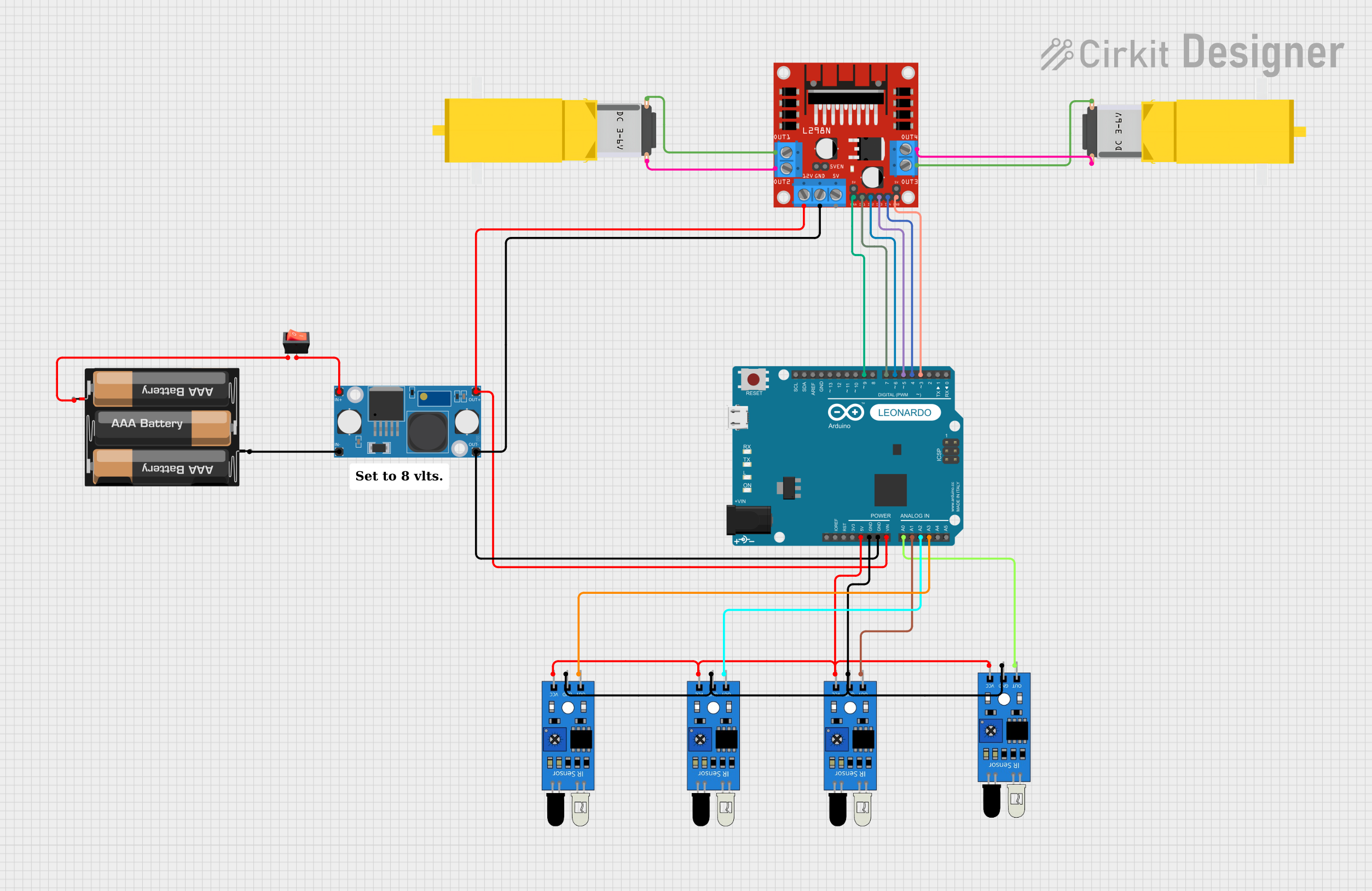
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with WPI409 dubbele H-brug driver L298N voor DC- of stappenmotor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Controlling the movement of robot wheels or arms.
- Automation Systems: Driving conveyor belts or automated gates.
- DIY Projects: Building remote-controlled cars, drones, or other motorized devices.
- Educational Purposes: Teaching motor control and electronics concepts.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V to 35V |
| Output Current | 2A per channel (continuous), 3A peak |
| Logic Voltage | 5V |
| Control Logic | TTL compatible |
| Power Dissipation | 25W (at 75°C) |
| Dimensions | 43mm x 43mm x 27mm |
| Weight | 26g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Power and Motor Connections
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Motor power supply (5V to 35V) |
| GND | Ground |
| 5V | Logic power supply (5V) |
| OUT1 | Motor A output 1 |
| OUT2 | Motor A output 2 |
| OUT3 | Motor B output 1 |
| OUT4 | Motor B output 2 |
Control Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ENA | Enable pin for Motor A (High to enable) |
| IN1 | Control input 1 for Motor A |
| IN2 | Control input 2 for Motor A |
| ENB | Enable pin for Motor B (High to enable) |
| IN3 | Control input 1 for Motor B |
| IN4 | Control input 2 for Motor B |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the VCC pin to the motor power supply (5V to 35V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power supply.
- Connect the 5V pin to the 5V logic power supply.
Motor Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to OUT1 and OUT2 for Motor A.
- Connect the motor terminals to OUT3 and OUT4 for Motor B.
Control Connections:
- Connect the ENA pin to a digital output pin on your microcontroller to enable Motor A.
- Connect the IN1 and IN2 pins to digital output pins on your microcontroller to control the direction of Motor A.
- Connect the ENB pin to a digital output pin on your microcontroller to enable Motor B.
- Connect the IN3 and IN4 pins to digital output pins on your microcontroller to control the direction of Motor B.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: The L298N chip can get hot during operation. Ensure proper heat dissipation by using a heat sink or cooling fan if necessary.
- Power Supply: Use a power supply that can provide sufficient current for your motors. Overloading the module can cause damage.
- Logic Levels: Ensure that the control logic voltage is compatible with your microcontroller (typically 5V).
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define motor control pins
const int ENA = 9;
const int IN1 = 8;
const int IN2 = 7;
const int ENB = 3;
const int IN3 = 5;
const int IN4 = 4;
void setup() {
// Set all the motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4, OUTPUT);
// Initialize motors to off
digitalWrite(ENA, LOW);
digitalWrite(ENB, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Move Motor A forward
digitalWrite(ENA, HIGH); // Enable Motor A
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 high
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 low
// Example: Move Motor B backward
digitalWrite(ENB, HIGH); // Enable Motor B
digitalWrite(IN3, LOW); // Set IN3 low
digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH); // Set IN4 high
delay(2000); // Run motors for 2 seconds
// Stop motors
digitalWrite(ENA, LOW);
digitalWrite(ENB, LOW);
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Motor Not Running:
- Solution: Check power connections and ensure the power supply is adequate. Verify that the enable pins (ENA and ENB) are set high.
Motor Running in Wrong Direction:
- Solution: Check the control pin connections (IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4) and ensure they are set correctly for the desired direction.
Overheating:
- Solution: Ensure proper heat dissipation with a heat sink or cooling fan. Reduce the load on the motors if necessary.
No Response from Module:
- Solution: Verify that the logic voltage (5V) is correctly supplied. Check all connections and ensure there are no loose wires.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correctly placed according to the pin configuration.
- Use a Multimeter: Measure voltages at various points in the circuit to ensure proper power supply and signal levels.
- Consult Datasheets: Refer to the L298N datasheet for detailed information on the chip's operation and characteristics.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the WPI409 Dual H-Bridge Driver Module for controlling DC or stepper motors in various applications. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide provides the necessary information to get started and troubleshoot common issues.