
How to Use Fuel Pressure Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
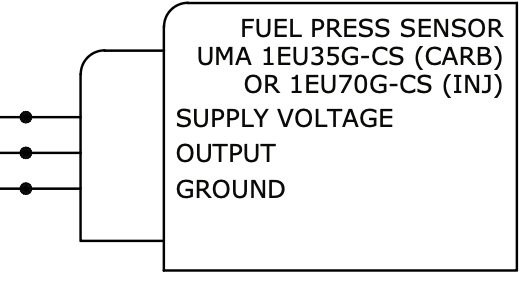
 Design with Fuel Pressure Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Fuel Pressure Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Fuel Pressure Sensor is a critical electronic component designed to measure the pressure of fuel within a fuel system. It provides real-time data to the engine control unit (ECU), enabling precise fuel delivery and optimizing engine performance. This sensor is essential for maintaining fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and ensuring the overall health of the engine.
Explore Projects Built with Fuel Pressure Sensor
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer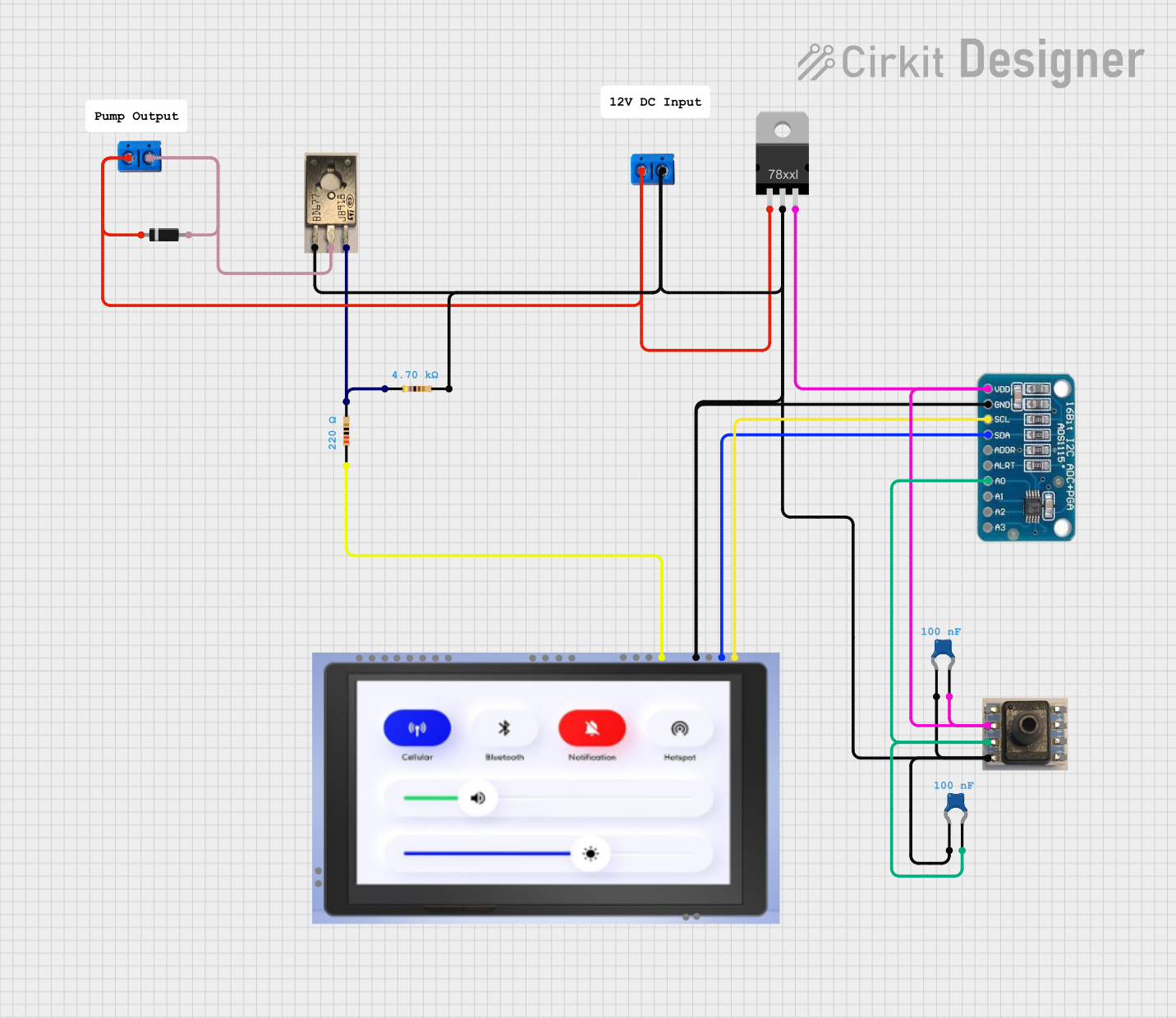
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Fuel Pressure Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive fuel injection systems
- Engine performance monitoring
- Fuel system diagnostics
- Industrial machinery with fuel-powered engines
- Marine and aviation fuel systems
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Fuel Pressure Sensor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Fuel Pressure |
| Part ID | Fuel Pressure Sensor |
| Operating Voltage | 5V DC |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0.5V to 4.5V) |
| Pressure Range | 0 to 150 PSI |
| Accuracy | ±1% of full scale |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Connector Type | 3-pin (Power, Ground, Signal) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Fuel Pressure Sensor typically has a 3-pin configuration. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (5V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | Signal | Analog output signal (proportional to fuel pressure) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Fuel Pressure Sensor in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a stable 5V DC power source. Ensure the power supply is regulated to avoid damaging the sensor.
- Ground Connection: Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Signal Output: Connect the Signal pin to an analog input pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for processing.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: Ensure the sensor is calibrated to match the fuel system's specifications for accurate readings.
- Wiring: Use shielded cables to minimize electrical noise, especially in automotive environments.
- Mounting: Install the sensor securely in the fuel system to prevent vibrations or leaks.
- Temperature: Operate the sensor within its specified temperature range to avoid damage or inaccurate readings.
- Safety: Always depressurize the fuel system before installing or removing the sensor to prevent fuel leaks or accidents.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the Fuel Pressure Sensor to an Arduino UNO and read its output:
Circuit Diagram
- VCC: Connect to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- GND: Connect to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Signal: Connect to the Arduino's analog input pin (e.g., A0).
Arduino Code
// Fuel Pressure Sensor Example Code
// Reads the analog signal from the sensor and converts it to pressure in PSI.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's Signal pin
const float sensorMinVoltage = 0.5; // Minimum output voltage of the sensor (in volts)
const float sensorMaxVoltage = 4.5; // Maximum output voltage of the sensor (in volts)
const int sensorMaxPressure = 150; // Maximum pressure the sensor can measure (in PSI)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the analog value (0-1023)
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to voltage (0-5V)
// Map the voltage to pressure in PSI
float pressure = (voltage - sensorMinVoltage) *
(sensorMaxPressure / (sensorMaxVoltage - sensorMinVoltage));
// Ensure pressure is within valid range
if (pressure < 0) pressure = 0;
if (pressure > sensorMaxPressure) pressure = sensorMaxPressure;
// Print the pressure to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(pressure);
Serial.println(" PSI");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no power supply.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the sensor is receiving 5V DC.
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: Sensor not calibrated or operating outside its temperature range.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor and ensure it is within the specified temperature range.
Fluctuating Signal:
- Cause: Electrical noise or loose connections.
- Solution: Use shielded cables and check all connections for stability.
Sensor Damage:
- Cause: Exposure to fuel system pressures beyond the sensor's range.
- Solution: Replace the sensor and ensure the fuel system pressure is within the sensor's limits.
FAQs
Q1: Can this sensor be used with diesel fuel systems?
A1: Yes, the Fuel Pressure Sensor is compatible with both gasoline and diesel fuel systems.
Q2: What happens if the sensor is exposed to pressures above 150 PSI?
A2: Exceeding the pressure range may damage the sensor or result in inaccurate readings. Always ensure the fuel system pressure is within the sensor's specified range.
Q3: How do I clean the sensor?
A3: Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe the sensor. Avoid using solvents or exposing the sensor to water.
Q4: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A4: The sensor requires a 5V power supply. If your microcontroller operates at 3.3V, use a level shifter or voltage divider for the Signal pin.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Fuel Pressure Sensor into your projects and ensure reliable performance.