
How to Use 2.42 Inch Small OLED Display I2C Interface 128*64 Resolution With 4pin: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 2.42 Inch Small OLED Display I2C Interface 128*64 Resolution With 4pin in Cirkit Designer
Design with 2.42 Inch Small OLED Display I2C Interface 128*64 Resolution With 4pin in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The CH240L004A-PW by Shenzhen ChengHao Optoelectronic Co., Ltd. is a compact OLED display module with a resolution of 128x64 pixels. It utilizes an I2C interface, making it easy to integrate with microcontrollers and development boards like the Arduino UNO. The display is energy-efficient, offers high contrast, and provides excellent readability, even in low-light conditions. Its 4-pin connection simplifies wiring and reduces the risk of errors during setup.
Explore Projects Built with 2.42 Inch Small OLED Display I2C Interface 128*64 Resolution With 4pin

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer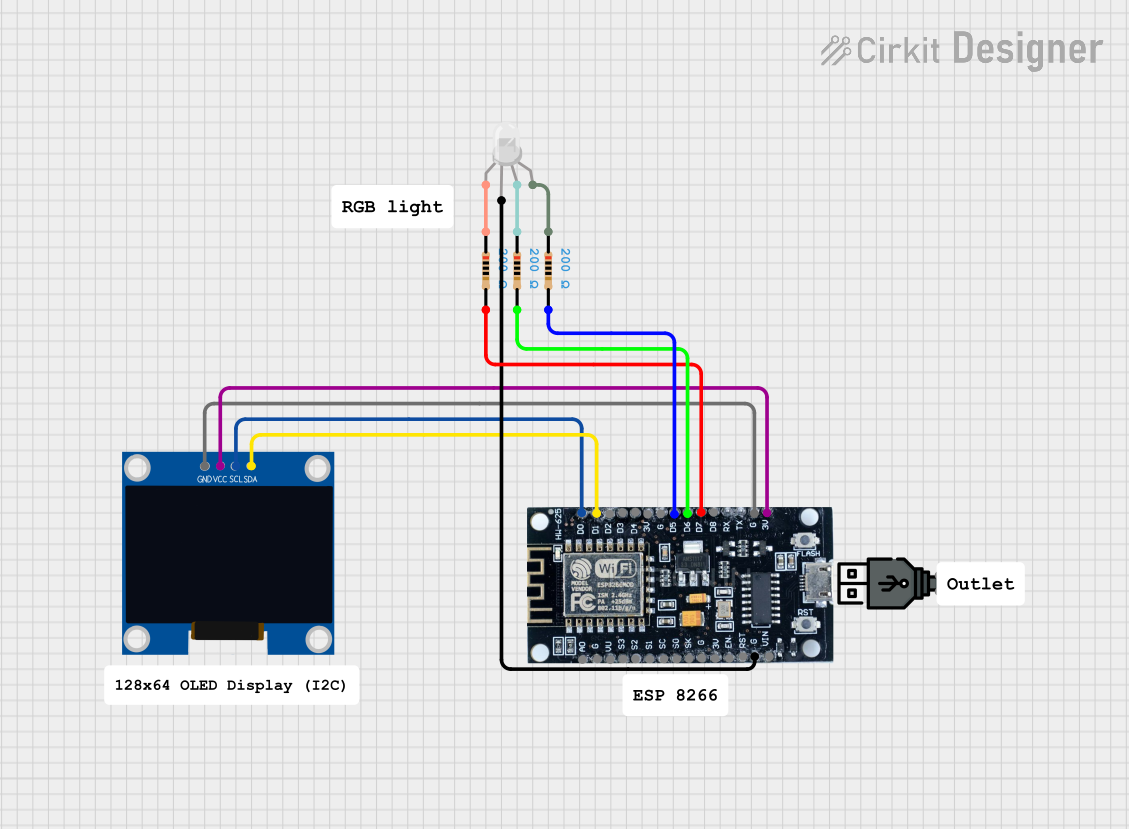
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer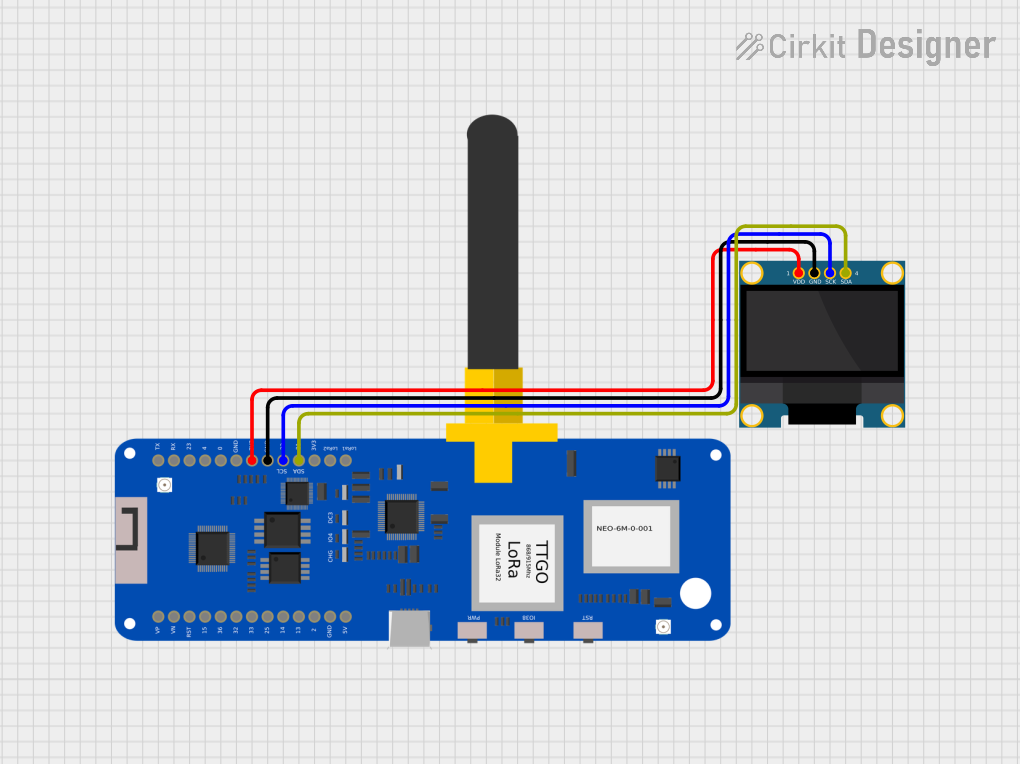
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer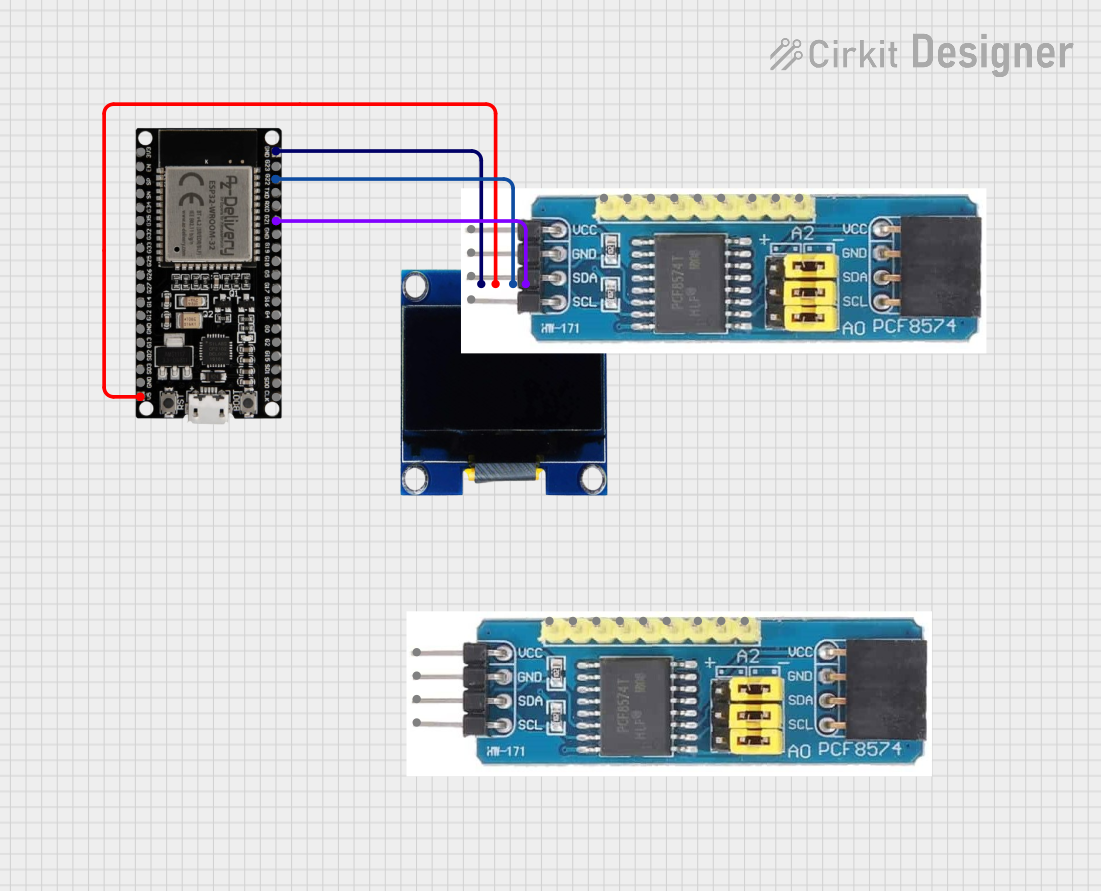
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 2.42 Inch Small OLED Display I2C Interface 128*64 Resolution With 4pin

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wearable devices
- IoT projects and smart home systems
- Portable electronics
- Industrial control panels
- Educational and prototyping projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Shenzhen ChengHao Optoelectronic Co., Ltd. |
| Part ID | CH240L004A-PW |
| Display Type | OLED |
| Resolution | 128x64 pixels |
| Interface | I2C |
| Number of Pins | 4 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C |
| Dimensions | 2.42 inches (diagonal) |
| Power Consumption | Low (varies with usage) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V - 5V) |
| 3 | SCL | I2C clock line |
| 4 | SDA | I2C data line |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Wiring the Display:
- Connect the GND pin of the display to the ground (GND) of your microcontroller.
- Connect the VCC pin to the 3.3V or 5V power supply of your microcontroller.
- Connect the SCL pin to the I2C clock line (e.g., A5 on Arduino UNO).
- Connect the SDA pin to the I2C data line (e.g., A4 on Arduino UNO).
Install Required Libraries:
- For Arduino, install the
Adafruit_GFXandAdafruit_SSD1306libraries via the Arduino Library Manager.
- For Arduino, install the
Upload Example Code: Use the following example code to display text on the OLED:
// Include necessary libraries #include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_GFX.h> #include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h> // Define OLED display width and height #define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 #define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // Create an SSD1306 display object with I2C address 0x3C #define OLED_RESET -1 Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET); void setup() { // Initialize the display if (!display.begin(SSD1306_I2C_ADDRESS, 0x3C)) { Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed")); for (;;); // Halt execution if initialization fails } // Clear the display buffer display.clearDisplay(); // Set text size and color display.setTextSize(1); // Small text size display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE); // Display a message display.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to top-left corner display.println(F("Hello, OLED!")); display.display(); // Render the text on the screen } void loop() { // Nothing to do here }
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the I2C address of the display (default:
0x3C) matches the address in your code. - Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SCL and SDA lines if your microcontroller does not have internal pull-ups.
- Avoid exceeding the operating voltage range (3.3V - 5V) to prevent damage to the display.
- Handle the display carefully to avoid scratching or damaging the OLED screen.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Display does not turn on | Incorrect wiring or loose connections | Double-check all connections and wiring. |
| No text or graphics on the screen | Incorrect I2C address in the code | Verify and update the I2C address in the code. |
| Flickering or unstable display | Insufficient power supply | Ensure a stable 3.3V or 5V power source. |
| Display is dim | Low contrast settings in the code | Adjust contrast settings in the library. |
FAQs
Can I use this display with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- Yes, the display supports both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
What is the default I2C address of the display?
- The default I2C address is
0x3C. Some variants may use0x3D.
- The default I2C address is
Do I need external pull-up resistors for I2C?
- Most microcontrollers have internal pull-ups, but if you experience communication issues, add external 4.7kΩ resistors.
Can I use this display with platforms other than Arduino?
- Yes, the display is compatible with platforms like Raspberry Pi, ESP32, and STM32, provided you configure the I2C interface correctly.
By following this documentation, you can easily integrate the CH240L004A-PW OLED display into your projects and enjoy its high-quality visuals and ease of use.