
How to Use N20 Motor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with N20 Motor in Cirkit Designer
Design with N20 Motor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The N20 motor is a small, compact DC motor widely used in robotics and automation projects. Known for its high torque and efficiency, this motor is designed to deliver reliable performance in a lightweight and space-saving form factor. Its versatility makes it ideal for applications such as small robots, motorized toys, precision mechanisms, and other projects requiring controlled motion.
Explore Projects Built with N20 Motor
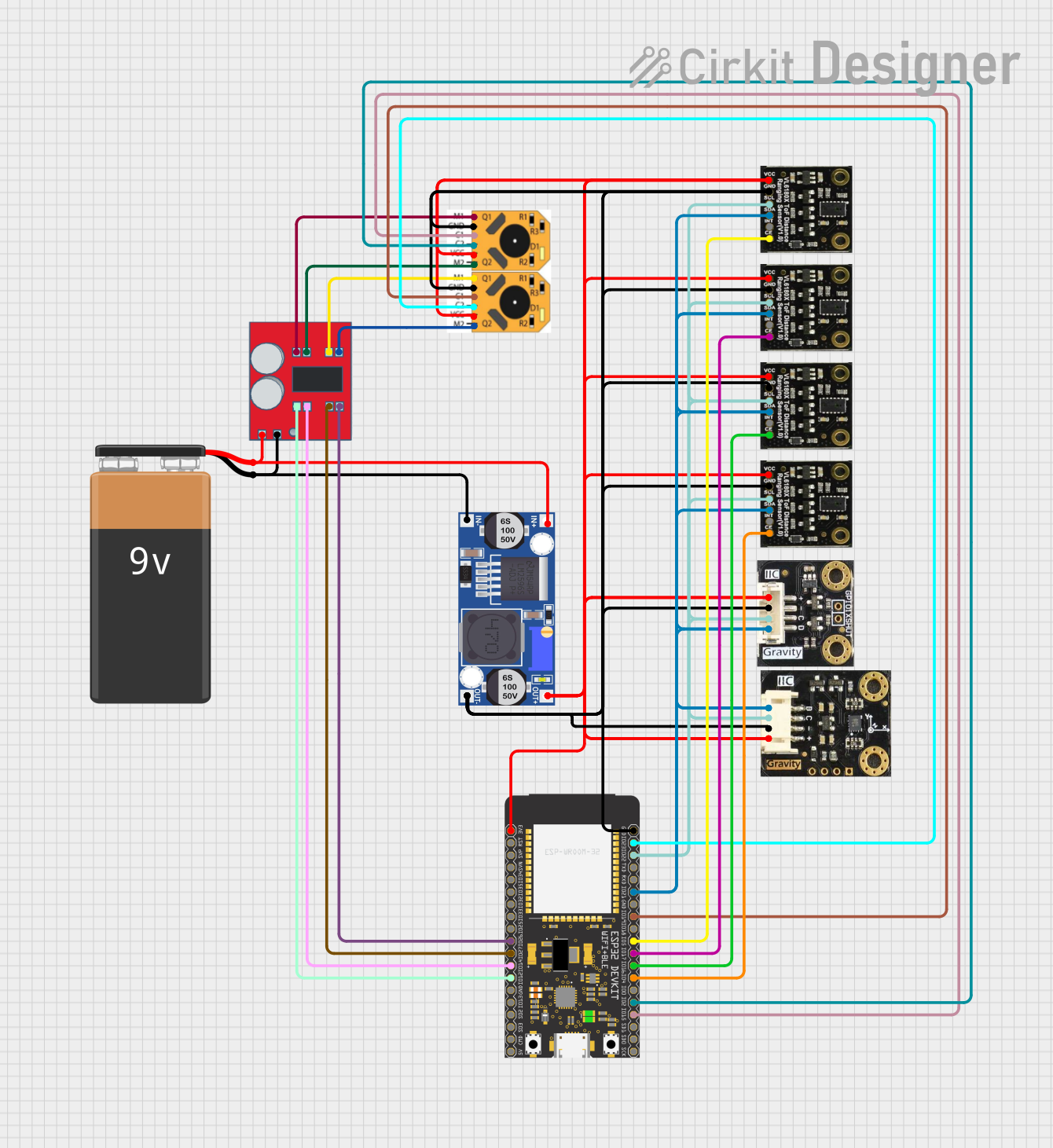
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer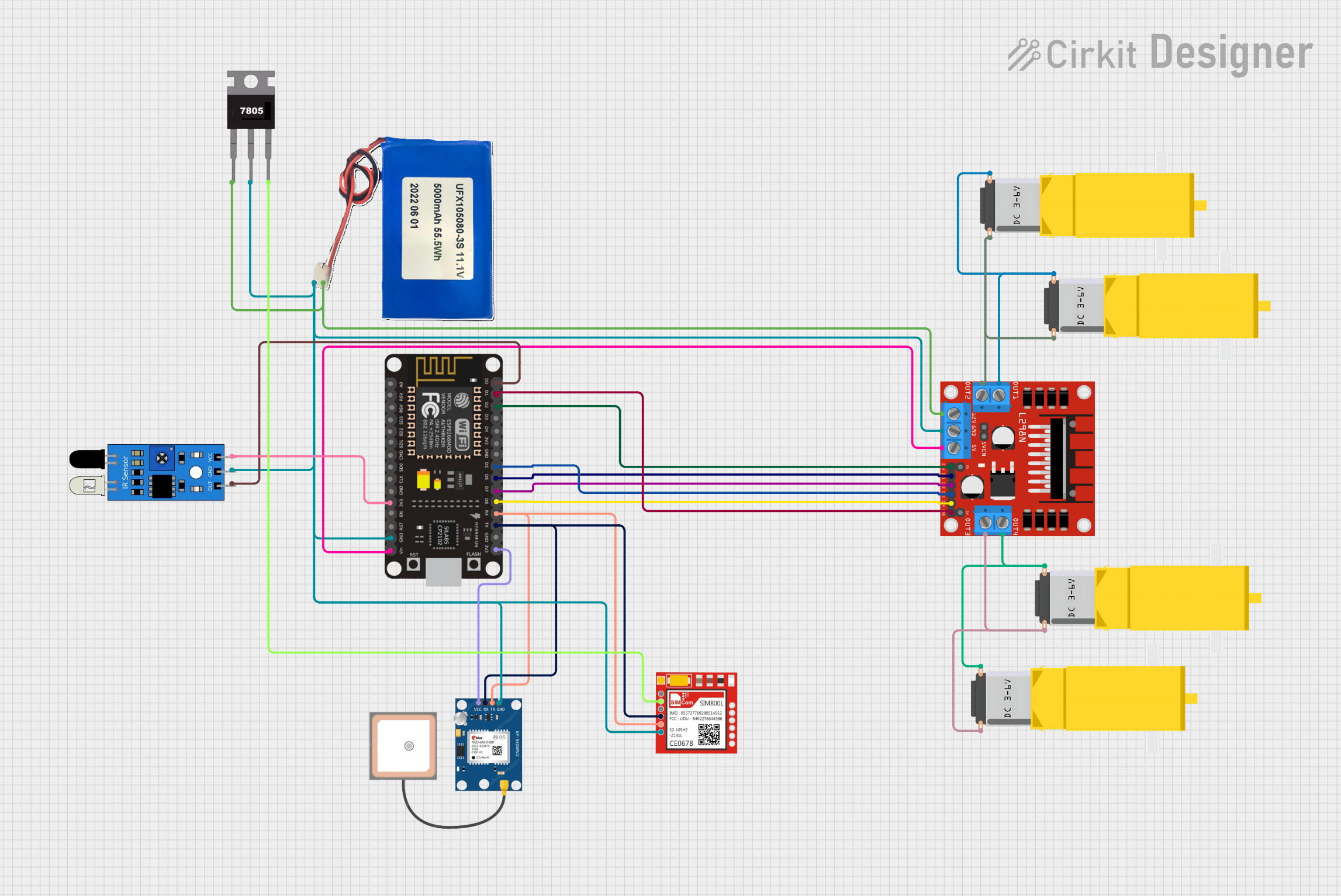
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer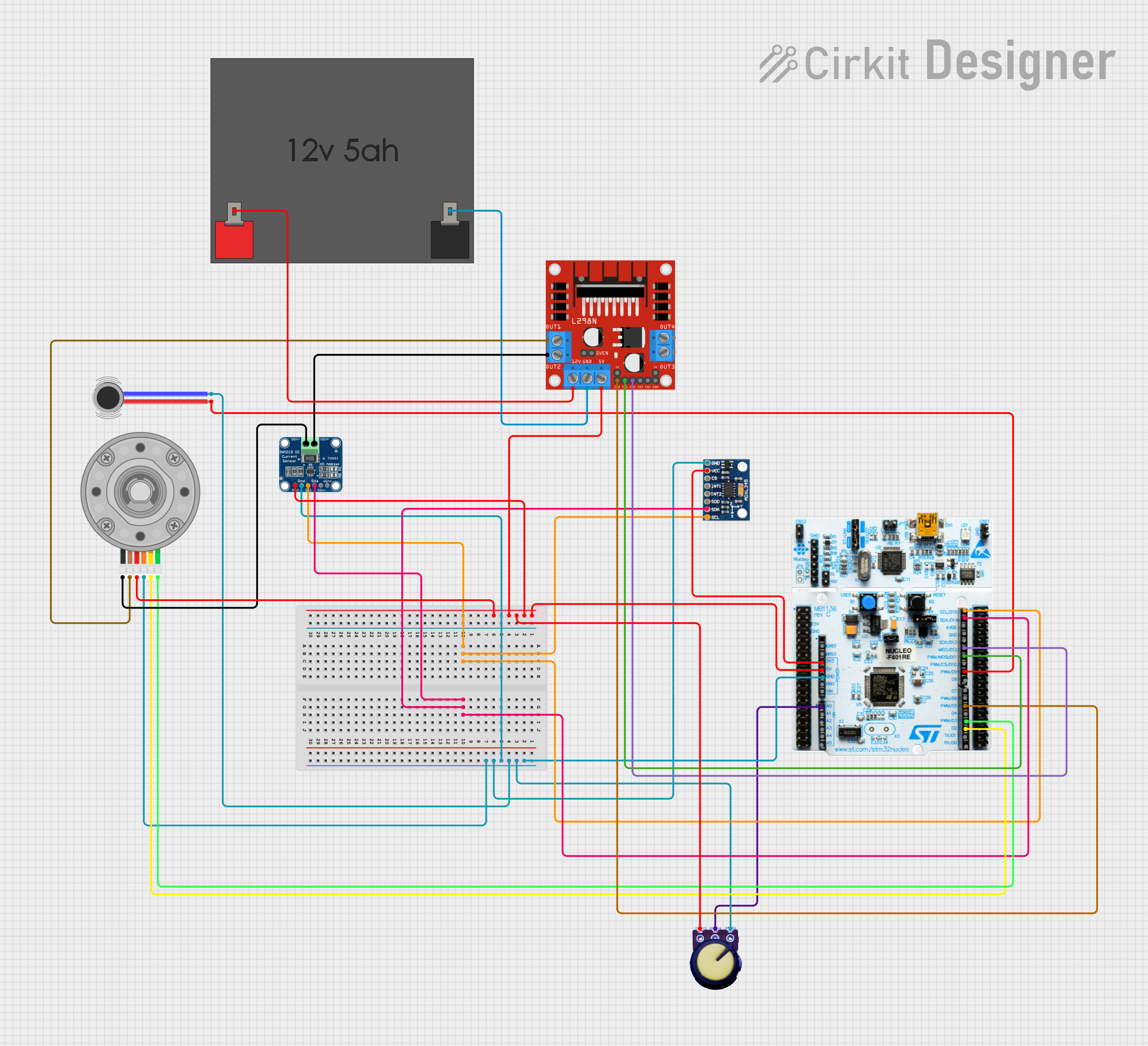
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer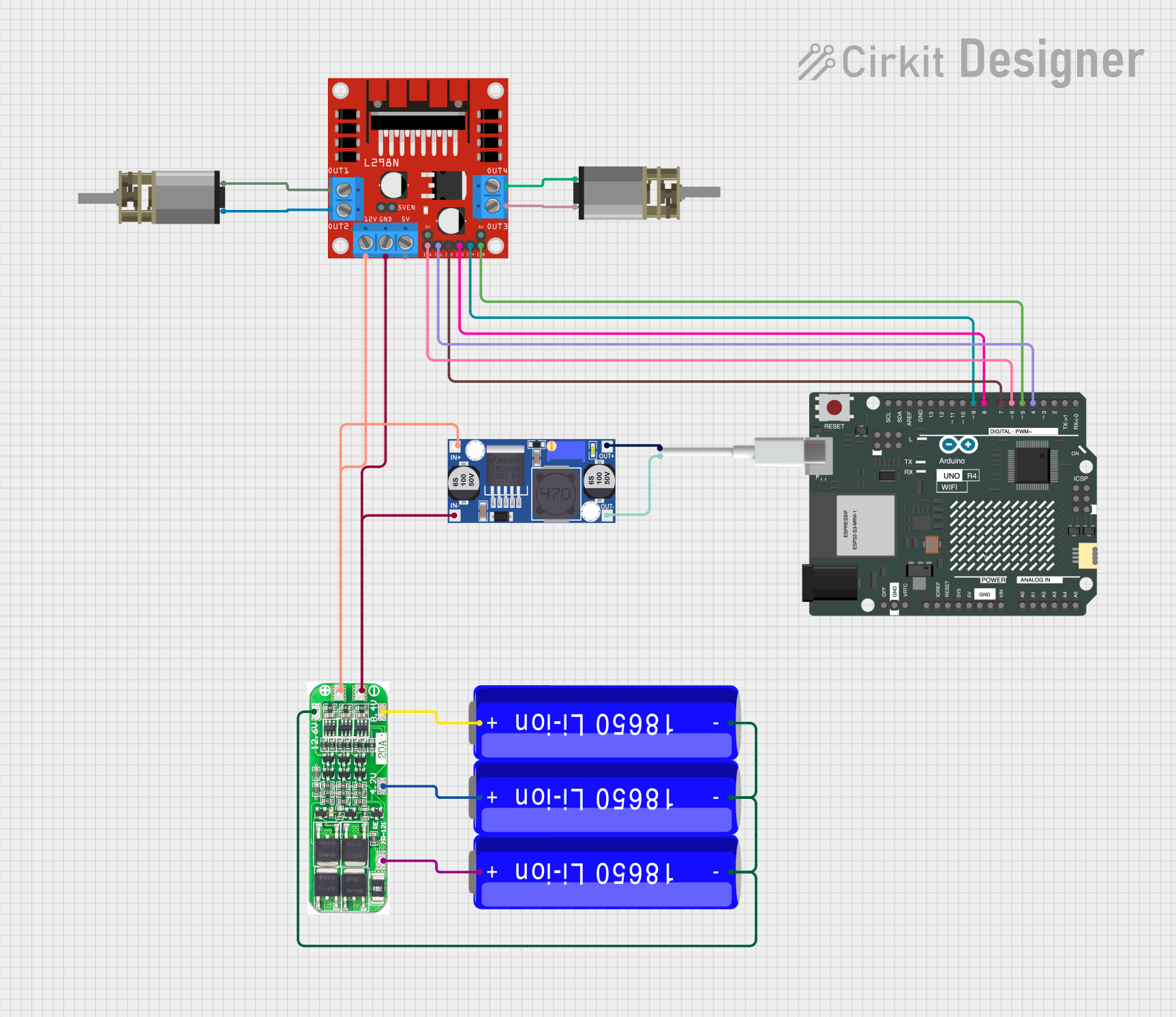
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with N20 Motor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The N20 motor is available in various configurations, including different gear ratios and voltage ratings. Below are the general specifications for a standard N20 motor:
- Operating Voltage: 3V to 12V (typical: 6V)
- No-Load Speed: 30 RPM to 1000 RPM (depending on gear ratio)
- Stall Torque: Up to 1.5 kg·cm (varies with gear ratio)
- Stall Current: ~0.3A to 1.2A
- No-Load Current: ~40mA to 200mA
- Motor Dimensions: 12mm x 10mm x 15mm (excluding shaft)
- Shaft Diameter: 3mm
- Weight: ~10g
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The N20 motor typically has two terminals for electrical connections. These terminals are not polarized, meaning the motor's direction of rotation depends on the polarity of the applied voltage.
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Connect to the positive or negative terminal of the power supply. |
| Terminal 2 | Connect to the opposite terminal of the power supply to complete the circuit. |
Note: Reversing the polarity of the connections will reverse the motor's rotation direction.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the N20 Motor in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the motor to a DC power supply within its operating voltage range (3V to 12V). Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for the motor's operation.
- Direction Control: To control the direction of rotation, reverse the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor terminals.
- Speed Control: Use a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal to control the motor's speed. This can be achieved using a motor driver or a microcontroller like an Arduino.
- Motor Driver: For precise control, use an H-bridge motor driver (e.g., L298N or L293D) to manage speed and direction.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the motor's stall torque or current rating, as this can damage the motor.
- Heat Management: Prolonged operation at high loads may cause the motor to overheat. Allow for adequate cooling.
- Gear Ratio Selection: Choose a gear ratio that suits your application's speed and torque requirements.
- Decoupling Capacitor: Add a small capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) across the motor terminals to reduce electrical noise.
Example: Controlling the N20 Motor with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the N20 motor using an Arduino UNO and an L298N motor driver.
// Example: Controlling an N20 Motor with Arduino and L298N Motor Driver
// Define motor control pins
const int motorPin1 = 9; // IN1 on L298N
const int motorPin2 = 10; // IN2 on L298N
const int enablePin = 11; // ENA on L298N (PWM pin)
void setup() {
// Set motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(motorPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorPin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, HIGH); // Set IN1 high
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW); // Set IN2 low
analogWrite(enablePin, 128); // Set speed (0-255, 128 = ~50% speed)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(enablePin, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW); // Set IN1 low
digitalWrite(motorPin2, HIGH); // Set IN2 high
analogWrite(enablePin, 128); // Set speed (~50%)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(enablePin, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Does Not Spin:
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify that the power supply voltage and current meet the motor's requirements. Check all connections.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction:
- Cause: Polarity of the connections is reversed.
- Solution: Swap the connections at the motor terminals or adjust the control signals.
Motor Overheats:
- Cause: Prolonged operation at high loads or stall conditions.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the motor or allow it to cool periodically.
Excessive Noise or Vibration:
- Cause: Electrical noise or mechanical imbalance.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor across the motor terminals and ensure the motor is securely mounted.
FAQs
Can the N20 motor be powered directly from an Arduino?
- No, the Arduino cannot supply sufficient current to drive the motor. Use a motor driver or external power supply.
What is the lifespan of an N20 motor?
- The lifespan depends on operating conditions, but with proper use, it can last for thousands of hours.
Can I use the N20 motor for precise positioning?
- The N20 motor is not inherently designed for precise positioning. However, you can pair it with an encoder for feedback control.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the N20 motor into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.