
How to Use YDLIDAR GS5 : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with YDLIDAR GS5 in Cirkit Designer
Design with YDLIDAR GS5 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The YDLIDAR GS5 is a 360-degree laser scanner designed for high-precision distance measurement and mapping. Manufactured by YDLIDAR, this compact and lightweight LiDAR sensor is ideal for robotic applications, including autonomous navigation, obstacle detection, and environmental mapping. Its ability to operate effectively in diverse environments makes it a versatile choice for developers and engineers working on robotics, drones, and other automation projects.
Explore Projects Built with YDLIDAR GS5
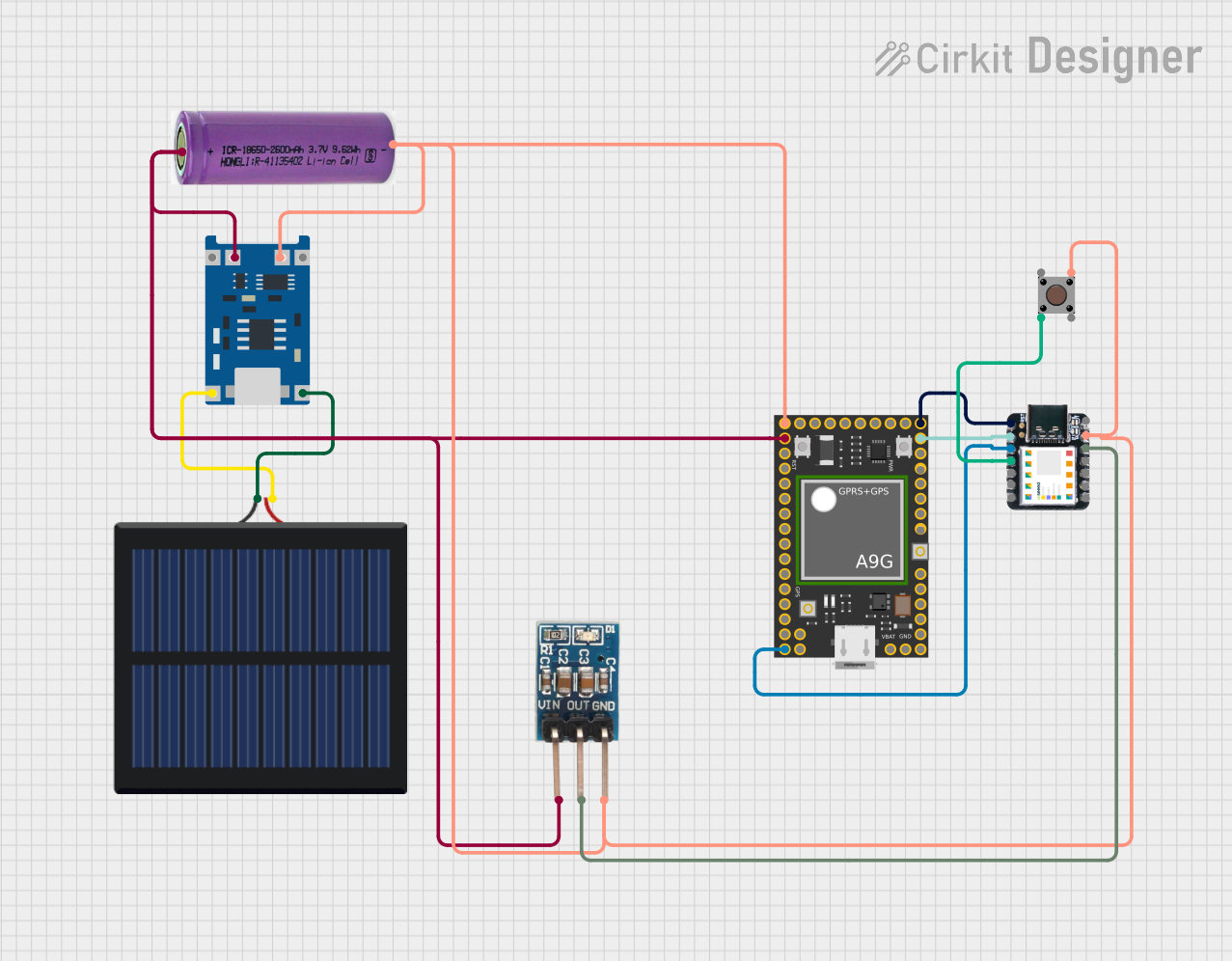
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer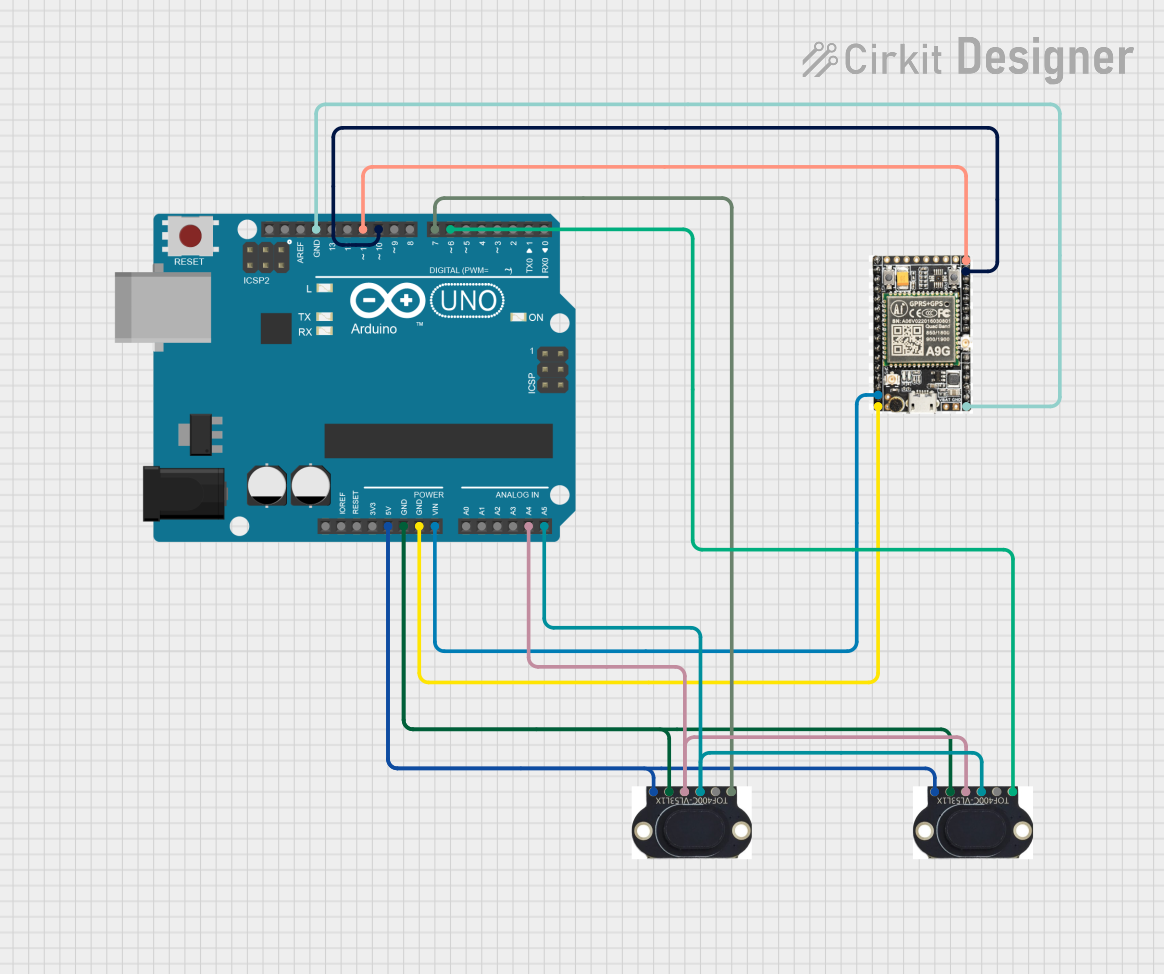
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer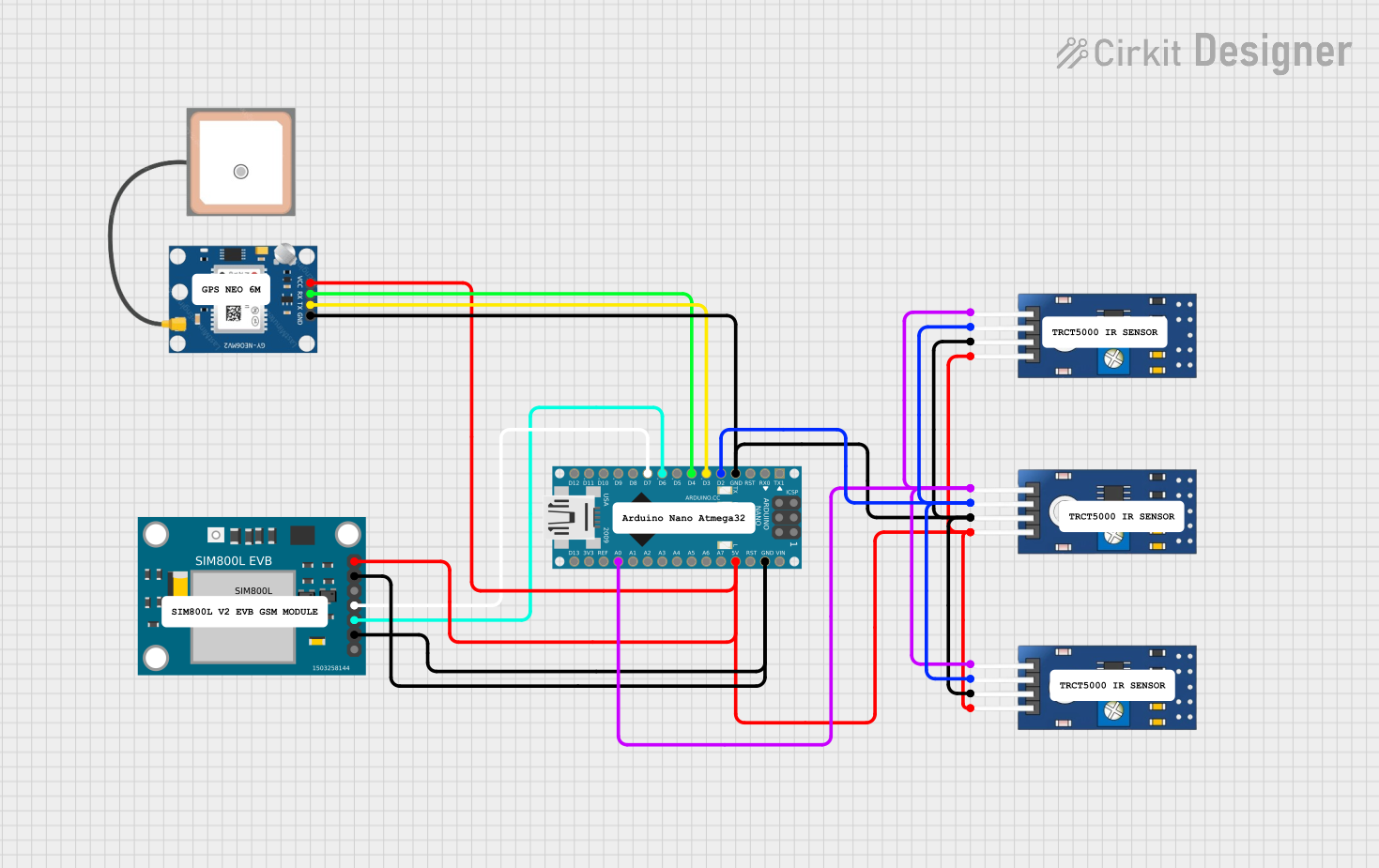
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer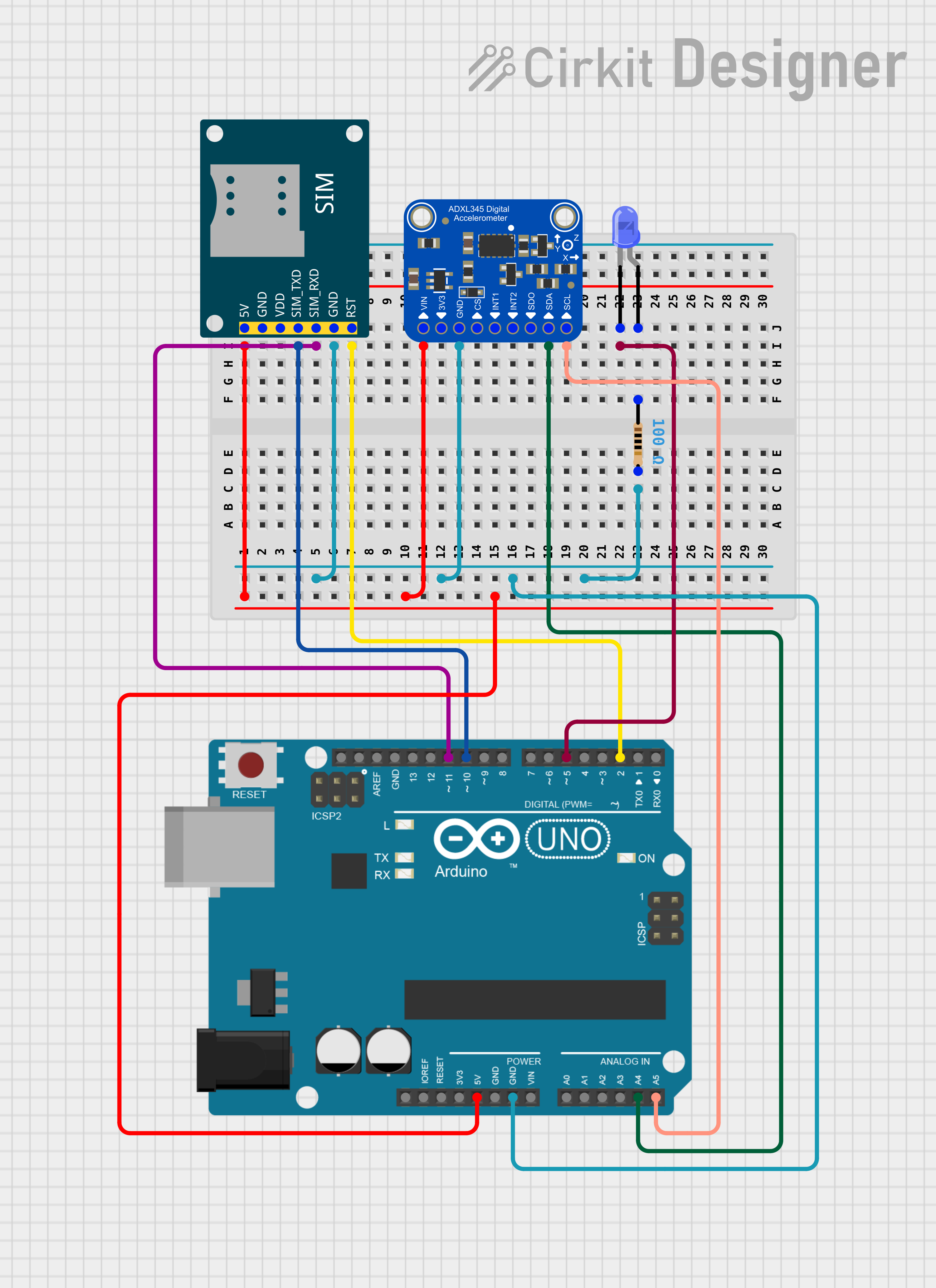
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with YDLIDAR GS5

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Autonomous robot navigation and SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)
- Obstacle detection and avoidance in robotics
- Environmental mapping and 3D modeling
- Indoor and outdoor distance measurement
- Drones and UAVs for terrain mapping
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the YDLIDAR GS5:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | 0.05 m to 25 m |
| Scanning Frequency | 5 Hz to 12 Hz (adjustable) |
| Angular Resolution | 0.18° to 0.36° |
| Field of View (FOV) | 360° |
| Distance Accuracy | ±2 mm (at 1 m) |
| Laser Wavelength | 905 nm (Infrared) |
| Laser Safety Class | Class 1 (Eye-safe) |
| Communication Interface | USB 2.0 / UART |
| Input Voltage | 5 V DC |
| Power Consumption | ≤3 W |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C |
| Dimensions | 70 mm × 70 mm × 41 mm |
| Weight | 190 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The YDLIDAR GS5 uses a standard 4-pin interface for communication and power. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power input (5 V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TXD | UART Transmit Data (to host device) |
| 4 | RXD | UART Receive Data (from host device) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the YDLIDAR GS5 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a stable 5 V DC power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Communication: Use the TXD and RXD pins to establish a UART connection with a microcontroller, such as an Arduino UNO, or a computer via a USB-to-UART adapter.
- Mounting: Secure the GS5 on a stable platform to ensure accurate scanning. Avoid vibrations or unstable surfaces.
- Software Setup: Install the YDLIDAR SDK or use compatible libraries to interface with the sensor. The SDK provides tools for data acquisition, visualization, and processing.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Laser Safety: The GS5 uses a Class 1 laser, which is eye-safe under normal operating conditions. However, avoid direct exposure to the laser beam.
- Environmental Factors: Ensure the sensor is not exposed to excessive dust, moisture, or direct sunlight, as these can affect performance.
- Power Stability: Use a regulated power supply to prevent voltage fluctuations that could damage the sensor.
- Data Processing: The GS5 outputs raw distance and angle data. Use SLAM algorithms or mapping software to process the data for navigation or mapping applications.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use the YDLIDAR GS5 with an Arduino UNO:
Wiring Diagram
| YDLIDAR GS5 Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TXD | RX (Pin 0) |
| RXD | TX (Pin 1) |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial lidarSerial(10, 11); // RX = Pin 10, TX = Pin 11
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor
lidarSerial.begin(115200); // Initialize LIDAR communication
Serial.println("YDLIDAR GS5 Initialized");
}
void loop() {
if (lidarSerial.available()) {
// Read data from the LIDAR
String lidarData = lidarSerial.readStringUntil('\n');
Serial.println("LIDAR Data: " + lidarData); // Print data to Serial Monitor
}
}
Note: Replace
10and11with the appropriate pins if using different connections. Ensure the baud rate matches the GS5's default UART settings.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Output
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or baud rate mismatch.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the UART baud rate is set to 115200.
Inaccurate Measurements
- Cause: Environmental interference or unstable mounting.
- Solution: Ensure the sensor is mounted securely and avoid reflective or transparent surfaces in the scanning area.
Device Not Detected
- Cause: USB driver not installed or faulty cable.
- Solution: Install the correct USB driver for the YDLIDAR GS5 and check the cable connection.
Intermittent Power Issues
- Cause: Unstable power supply.
- Solution: Use a regulated 5 V DC power source with sufficient current capacity.
FAQs
Q: Can the GS5 be used outdoors?
- A: Yes, but avoid direct sunlight and excessive dust, as these can affect performance.
Q: What software is compatible with the GS5?
- A: The YDLIDAR SDK, ROS (Robot Operating System), and other SLAM libraries support the GS5.
Q: How do I clean the sensor?
- A: Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently clean the sensor's surface. Avoid using liquids or abrasive materials.
Q: Can I adjust the scanning frequency?
- A: Yes, the scanning frequency can be adjusted between 5 Hz and 12 Hz using the YDLIDAR SDK or configuration tools.