
How to Use Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17) is a type of stepper motor that uses two coils to generate magnetic fields, enabling precise control of rotational movement. The "NEMA 17" designation refers to the motor's faceplate dimensions, which measure 1.7 inches (43.2 mm) on each side. This motor is widely used in applications requiring accurate positioning and repeatable motion, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics, and automated systems. Its compact size, reliability, and high torque make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17)
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer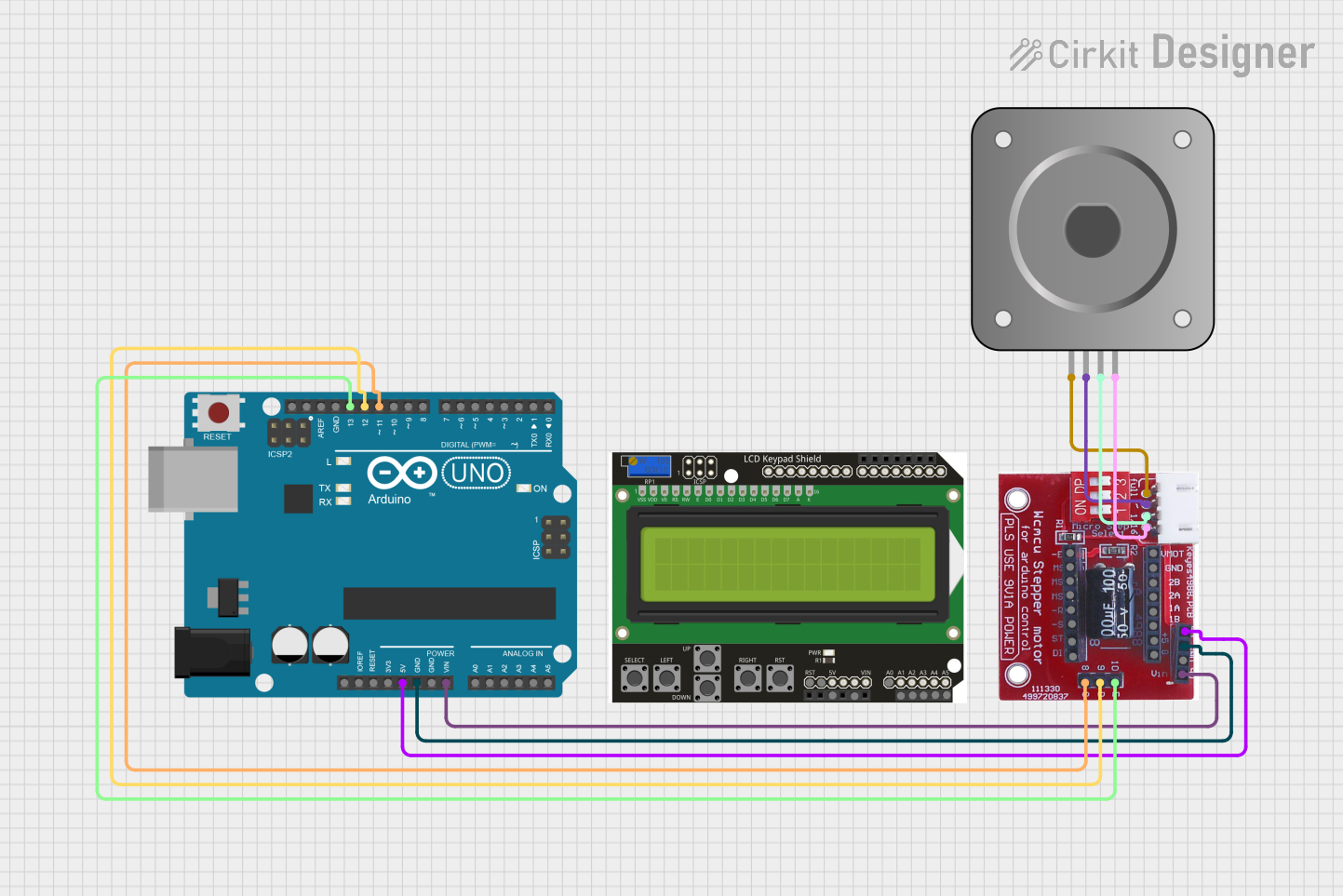
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17):
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Step Angle | 1.8° per step |
| Number of Steps per Revolution | 200 steps |
| Rated Voltage | 2.8 V (varies by model) |
| Rated Current | 1.2 A per phase (varies by model) |
| Holding Torque | 40 N·cm (varies by model) |
| Shaft Diameter | 5 mm |
| Body Dimensions | 42 x 42 x 48 mm |
| Weight | ~280 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17) has four wires, corresponding to two coils. The wire colors and their respective coil connections may vary depending on the manufacturer, but the general configuration is as follows:
| Wire Color | Connection | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Coil A+ | Positive terminal of Coil A |
| Blue | Coil A- | Negative terminal of Coil A |
| Green | Coil B+ | Positive terminal of Coil B |
| Black | Coil B- | Negative terminal of Coil B |
Note: Always refer to the datasheet or use a multimeter to confirm the wiring configuration for your specific motor.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Motor to a Driver:
- A stepper motor driver (e.g., A4988 or DRV8825) is required to control the NEMA 17 motor. The driver provides the necessary current and voltage to the motor while allowing precise control of steps.
- Connect the motor's wires to the driver's output terminals (e.g., Coil A+ and A-, Coil B+ and B-).
Power the Driver:
- Provide the driver with an appropriate power supply. Ensure the voltage and current ratings match the motor's requirements.
Control the Motor:
- Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to send step and direction signals to the driver. These signals determine the motor's rotation direction and step size.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Adjust the current limit on the driver to match the motor's rated current. This prevents overheating and ensures optimal performance.
- Cooling: If the motor or driver becomes excessively hot, consider adding a heatsink or fan for cooling.
- Microstepping: Enable microstepping on the driver for smoother motion and reduced noise.
- Power Supply: Use a power supply with sufficient current capacity to handle the motor's load.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a NEMA 17 motor using an Arduino UNO and an A4988 driver:
Circuit Connections
- Motor Wires: Connect the motor's wires to the A4988 driver's output terminals (e.g., Coil A+ to OUT1, Coil A- to OUT2, etc.).
- Power Supply: Connect a 12V power supply to the driver's VMOT and GND pins.
- Arduino Pins:
- Connect the driver's STEP pin to Arduino pin 3.
- Connect the driver's DIR pin to Arduino pin 4.
- Connect the driver's GND to Arduino GND.
Arduino Code
// Define pins for step and direction
const int stepPin = 3; // Pin connected to STEP on the driver
const int dirPin = 4; // Pin connected to DIR on the driver
void setup() {
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT); // Set step pin as output
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT); // Set direction pin as output
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH); // Set initial direction (HIGH = clockwise)
}
void loop() {
// Rotate the motor one step at a time
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH); // Generate a step pulse
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait for 500 microseconds
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW); // End the step pulse
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait before the next step
}
Note: Adjust the
delayMicrosecondsvalue to control the motor's speed. A smaller delay results in faster rotation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate:
- Cause: Incorrect coil pairing.
- Solution: Use a multimeter to identify the correct coil pairs and rewire accordingly.
Overheating:
- Cause: Current limit set too high on the driver.
- Solution: Adjust the driver's current limit to match the motor's rated current.
Jerky or Inconsistent Motion:
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or incorrect microstepping settings.
- Solution: Use a power supply with adequate current capacity and enable microstepping.
FAQs
Q: Can I run the NEMA 17 motor without a driver?
A: No, a driver is required to control the motor's steps and provide the necessary current.Q: How do I identify the motor's coil pairs?
A: Use a multimeter to measure resistance between wires. Wires with measurable resistance belong to the same coil.Q: What is the maximum speed of the NEMA 17 motor?
A: The maximum speed depends on the driver, power supply, and load. Typically, it ranges from 200 to 1000 RPM.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the Bipolar Stepper Motor (NEMA 17) in your projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.