
How to Use ESP32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
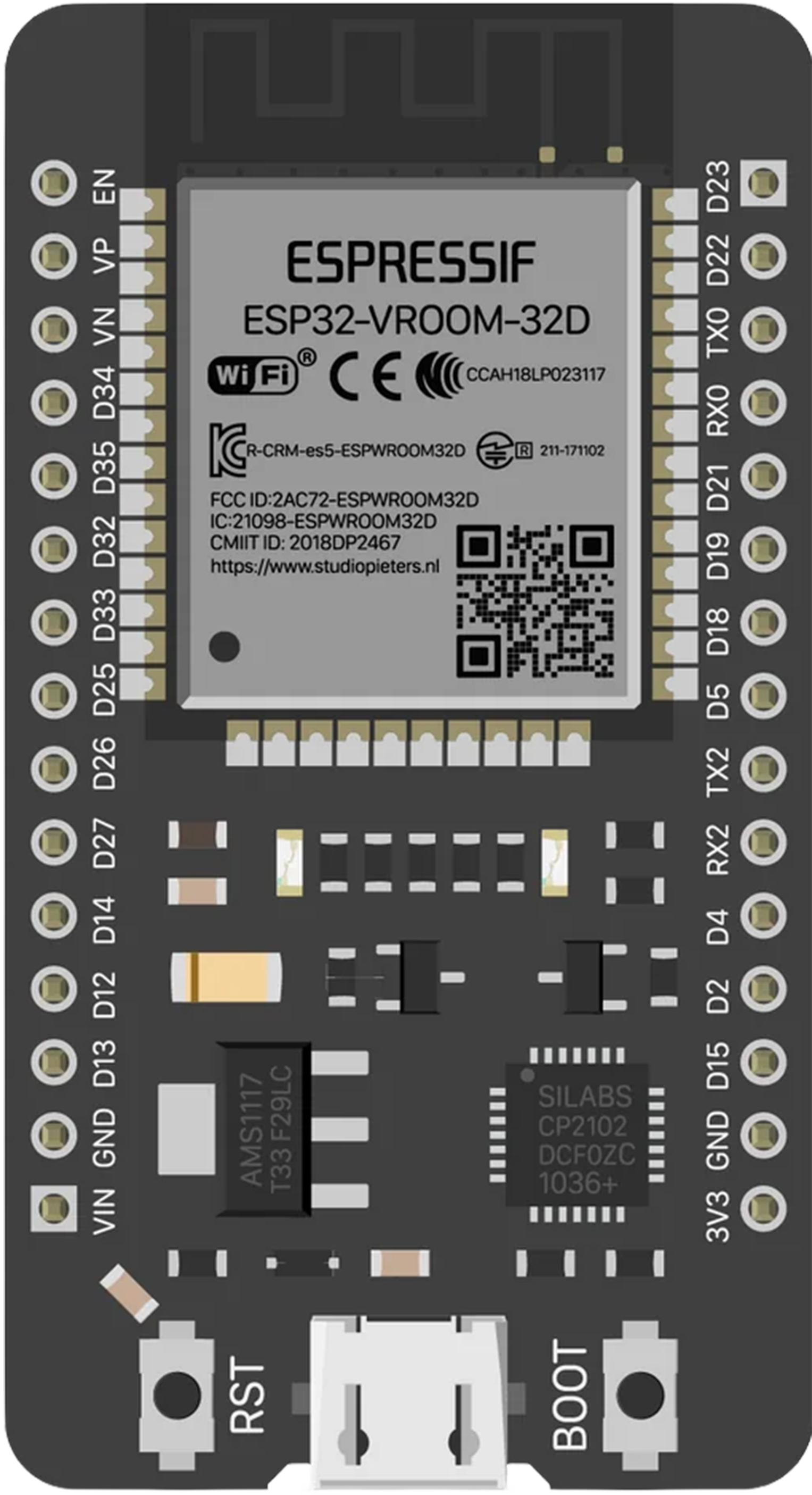
 Design with ESP32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32, manufactured by Espressif Systems, is a low-cost, low-power system on a chip (SoC) with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. The specific model, DOIT ESP32 Devkit V1, is a development board designed to simplify prototyping and development for IoT (Internet of Things) applications. It features a dual-core processor, multiple GPIO pins, and a wide range of peripherals, making it a versatile choice for embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32
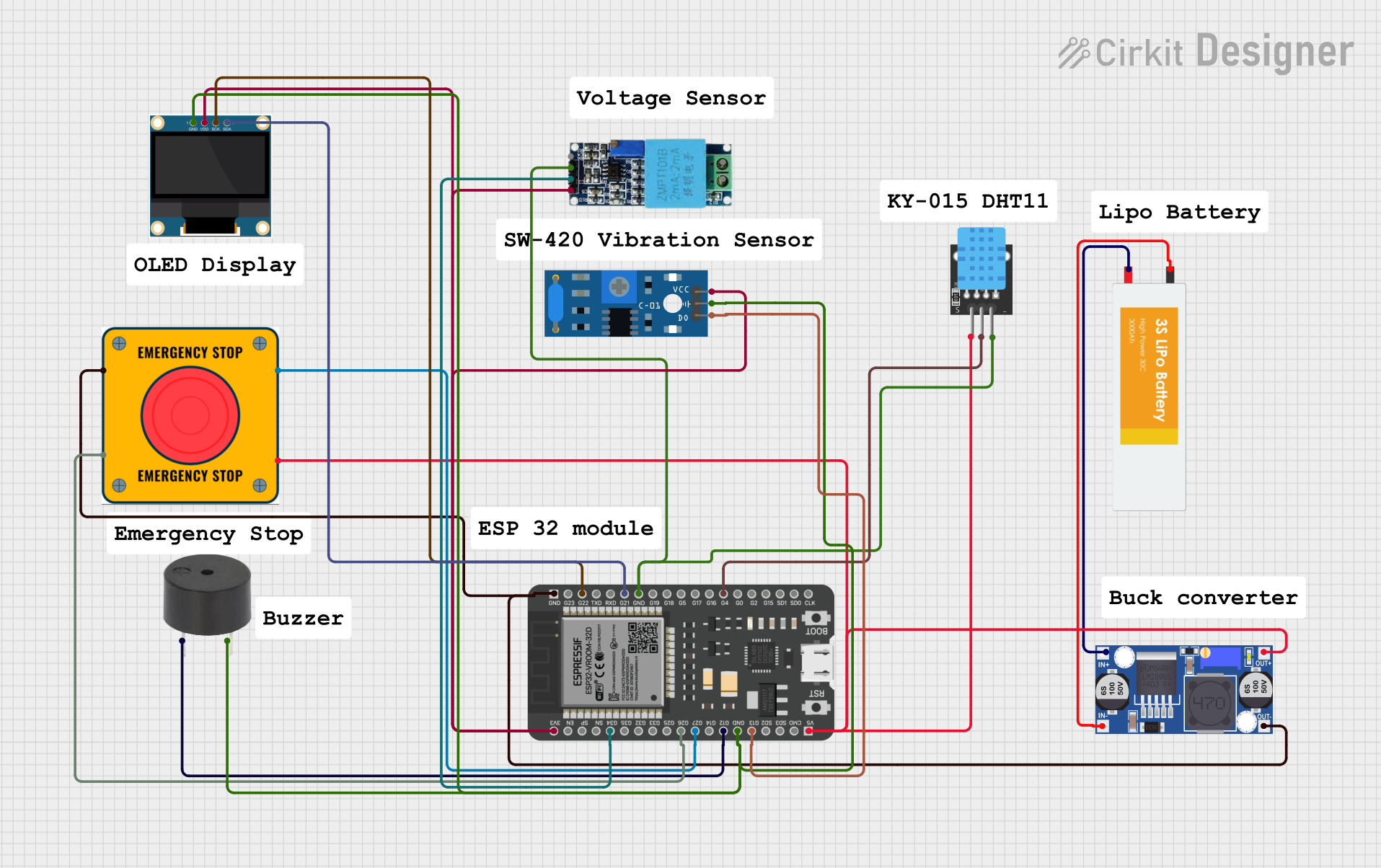
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer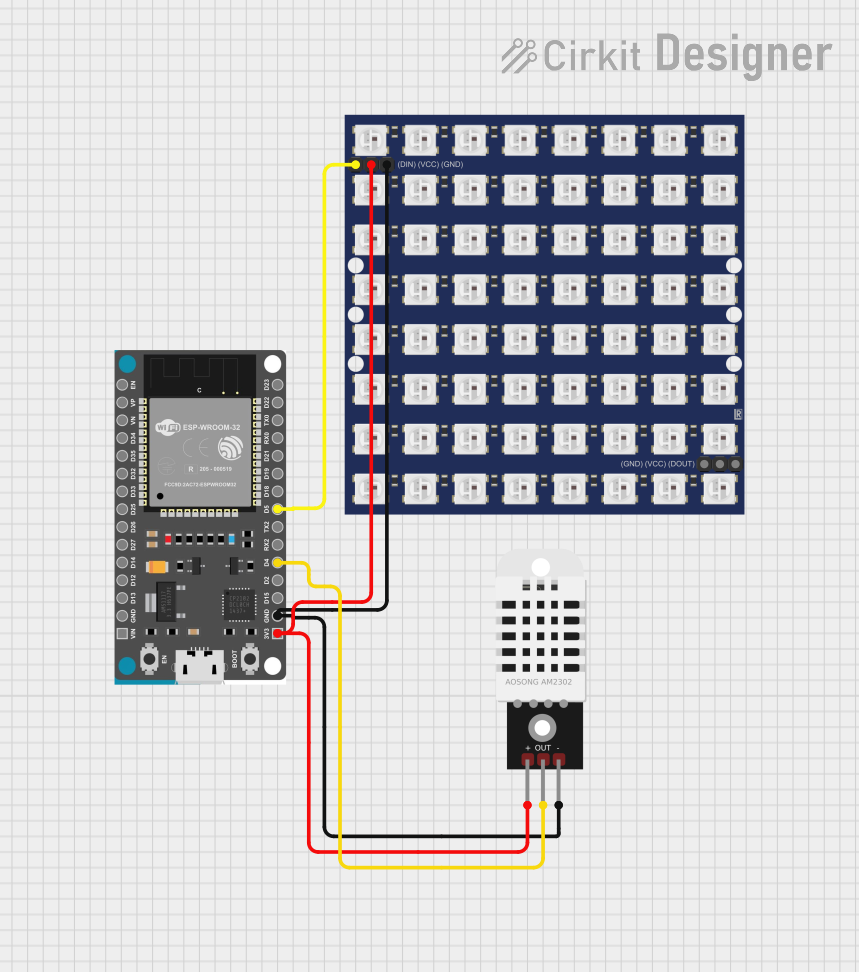
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer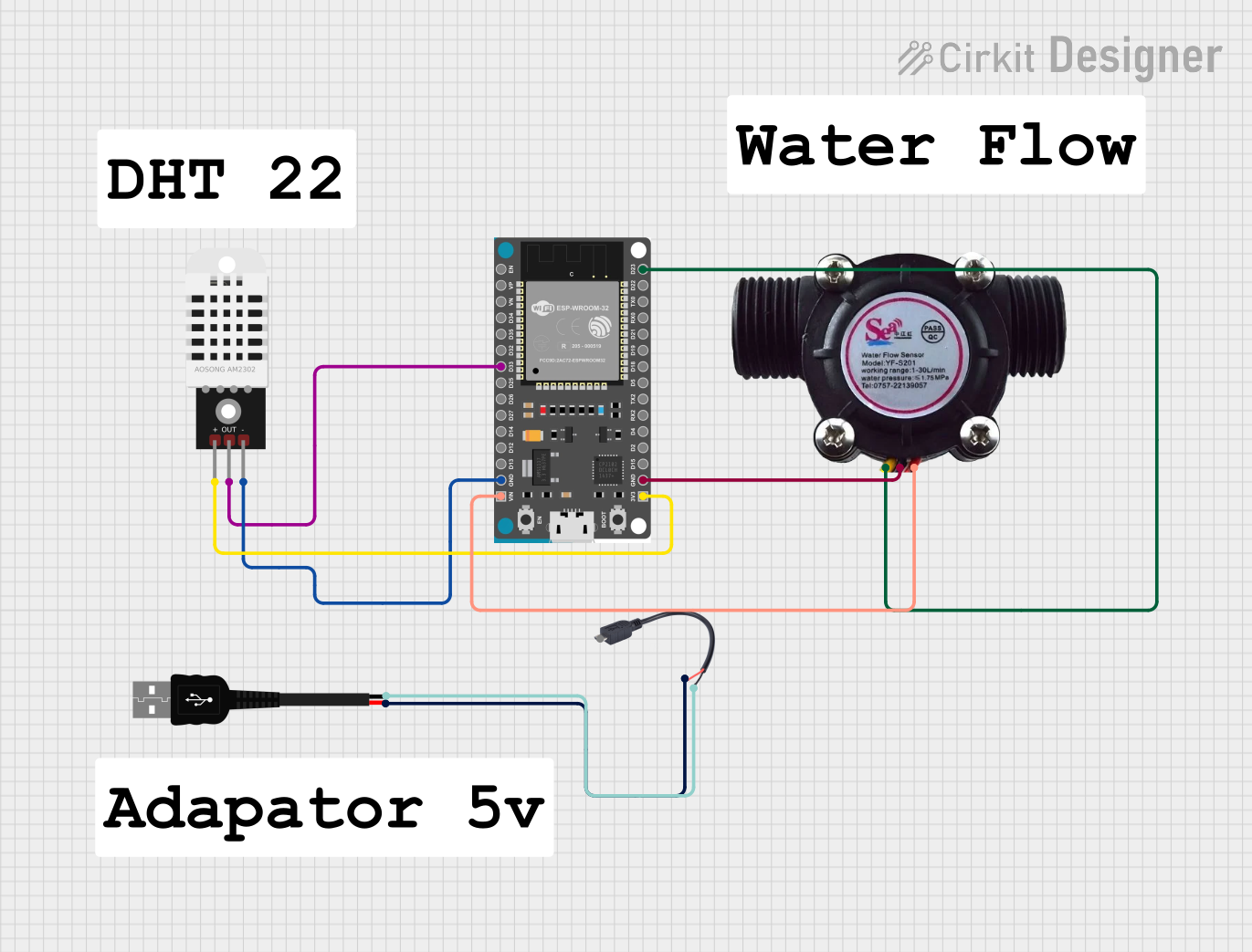
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer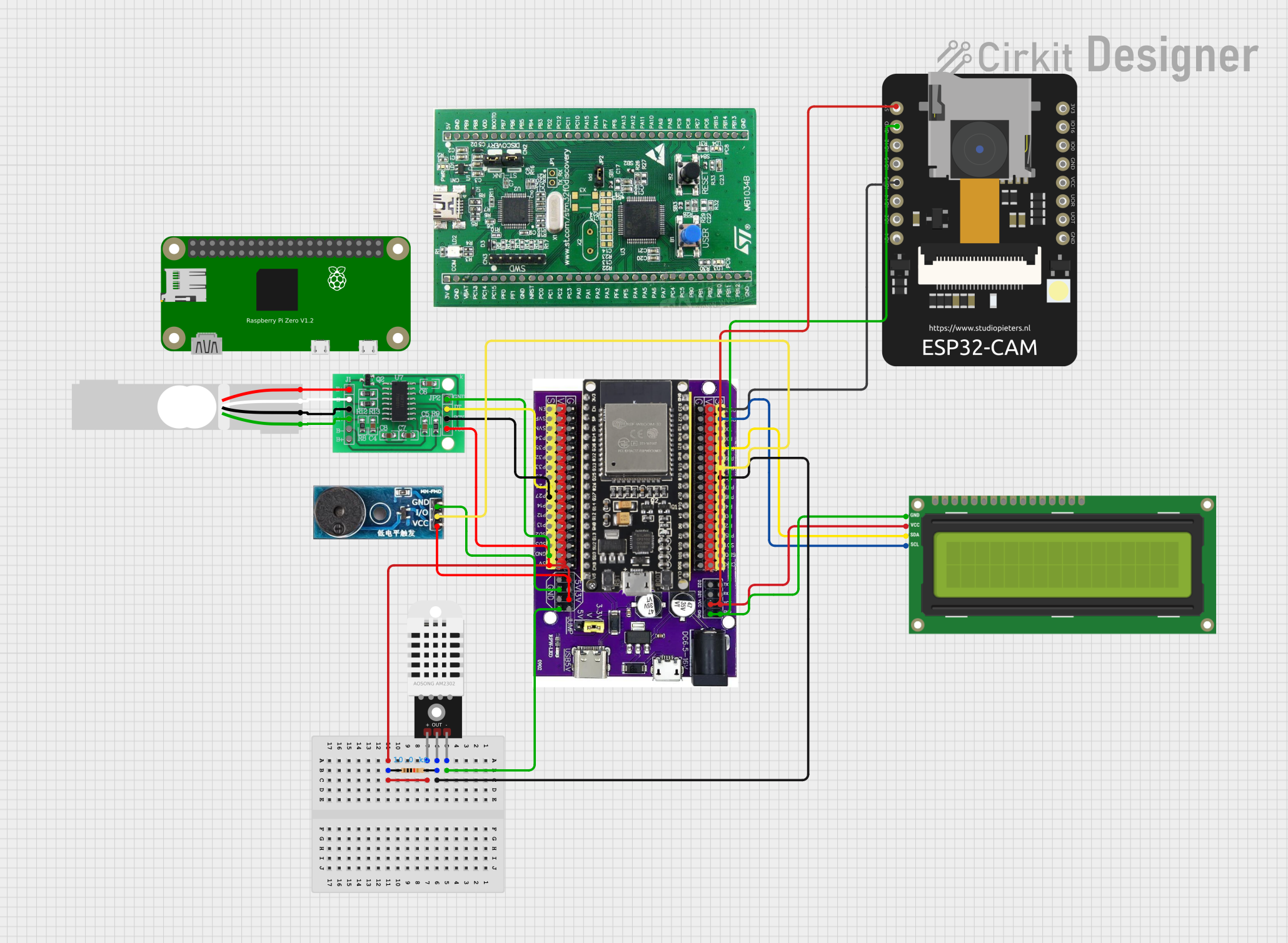
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wireless sensor networks
- Wearable devices
- Industrial automation
- Robotics and drones
- Real-time data monitoring and logging
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the DOIT ESP32 Devkit V1:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | Tensilica Xtensa LX6 dual-core processor |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (varies by model) |
| SRAM | 520 KB |
| Wi-Fi | 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz) |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 4.2 and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Input Voltage | 5V (via USB) or 7-12V (via VIN pin) |
| GPIO Pins | 30 (varies by board version) |
| ADC Channels | 18 (12-bit resolution) |
| DAC Channels | 2 (8-bit resolution) |
| Communication Protocols | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, CAN, PWM |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power consumption in deep sleep mode (~10 µA) |
| Dimensions | 25.4 mm x 50.8 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DOIT ESP32 Devkit V1 has a total of 30 GPIO pins, with multiple functions. Below is a table summarizing the key pins and their descriptions:
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Power Input | Accepts 7-12V input for powering the board. |
| 3V3 | Power Output | Provides 3.3V output for external components. |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for the circuit. |
| EN | Enable | Enables or disables the chip. |
| GPIO0 | Boot Mode Selection | Used to enter bootloader mode (connect to GND during boot). |
| GPIO2 | General Purpose I/O | Can be used as a standard GPIO pin. |
| GPIO12 | ADC2 Channel 5 | Analog input or digital I/O. |
| GPIO13 | ADC2 Channel 4, Touch Sensor 4 | Analog input, digital I/O, or touch input. |
| GPIO14 | ADC2 Channel 6, Touch Sensor 6 | Analog input, digital I/O, or touch input. |
| GPIO15 | ADC2 Channel 3, Touch Sensor 3 | Analog input, digital I/O, or touch input. |
| GPIO16 | General Purpose I/O | Can be used as a standard GPIO pin. |
| GPIO17 | General Purpose I/O | Can be used as a standard GPIO pin. |
| TXD0 | UART0 Transmit | UART0 TX pin for serial communication. |
| RXD0 | UART0 Receive | UART0 RX pin for serial communication. |
| SDA | I2C Data | Data line for I2C communication. |
| SCL | I2C Clock | Clock line for I2C communication. |
Note: Some GPIO pins have specific restrictions or dual functions. Refer to the official datasheet for detailed pin multiplexing information.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32 in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the ESP32 to your computer via a micro-USB cable for power and programming.
- Alternatively, supply 7-12V to the VIN pin or 3.3V to the 3V3 pin.
Programming the ESP32:
- Install the Arduino IDE and add the ESP32 board support package.
- Select "DOIT ESP32 Devkit V1" from the Tools > Board menu.
- Connect the board to your computer and select the appropriate COM port.
- Write your code and upload it to the ESP32.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- Ensure that the voltage levels of connected devices are compatible with the ESP32 (3.3V logic).
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Setup:
- Use the built-in libraries (
WiFi.handBluetoothSerial.h) to configure wireless communication.
- Use the built-in libraries (
Example Code: Blinking an LED
The following example demonstrates how to blink an LED connected to GPIO2:
// Define the GPIO pin for the LED
#define LED_PIN 2
void setup() {
// Set the LED pin as an output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED on
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Turn the LED off
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The ESP32 operates at 3.3V logic. Avoid connecting 5V devices directly to its GPIO pins without level shifters.
- Boot Mode: Ensure GPIO0 is not pulled low during normal operation, as this will put the ESP32 into bootloader mode.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid unexpected resets or instability.
- Deep Sleep Mode: Utilize the deep sleep mode for battery-powered applications to minimize power consumption.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
ESP32 Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is functional and supports data transfer.
- Install the correct USB-to-serial driver for your operating system.
Upload Fails with Timeout Error:
- Press and hold the "BOOT" button on the ESP32 while uploading the code.
- Check the selected COM port and board type in the Arduino IDE.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Verify the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is operating on the 2.4 GHz band (ESP32 does not support 5 GHz).
Random Resets or Instability:
- Check the power supply for sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Avoid using GPIO pins that are reserved for specific functions (e.g., GPIO0, GPIO2).
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP32 be powered directly from a 5V source?
A: Yes, you can power the ESP32 via the VIN pin with a 5V source, as it has an onboard voltage regulator.Q: How do I reset the ESP32?
A: Press the "EN" button on the board to reset the ESP32.Q: Can I use the ESP32 with a 5V sensor?
A: Use a level shifter to safely interface 5V sensors with the 3.3V GPIO pins of the ESP32.Q: How do I enable Bluetooth on the ESP32?
A: Use theBluetoothSeriallibrary to initialize and manage Bluetooth communication.
By following this documentation, you can effectively utilize the DOIT ESP32 Devkit V1 for a wide range of applications.