
How to Use magnetic contactor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
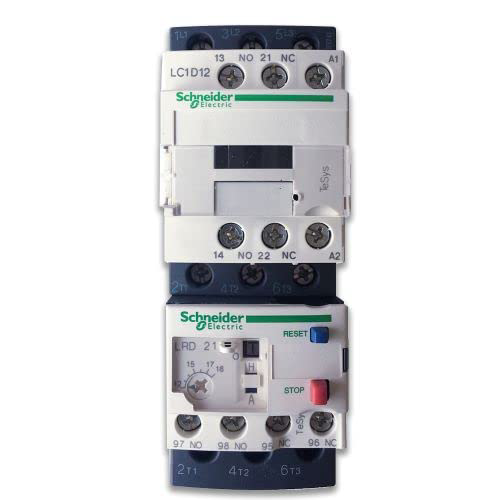

 Design with magnetic contactor in Cirkit Designer
Design with magnetic contactor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A magnetic contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching power circuits. It operates similarly to a relay but is specifically designed to handle higher current applications. The core of the magnetic contactor is an electromagnet that, when energized, closes the contacts to allow current to flow through the circuit. Magnetic contactors are widely used in industrial and commercial applications for controlling electric motors, lighting systems, heating equipment, and other high-power devices.
Explore Projects Built with magnetic contactor
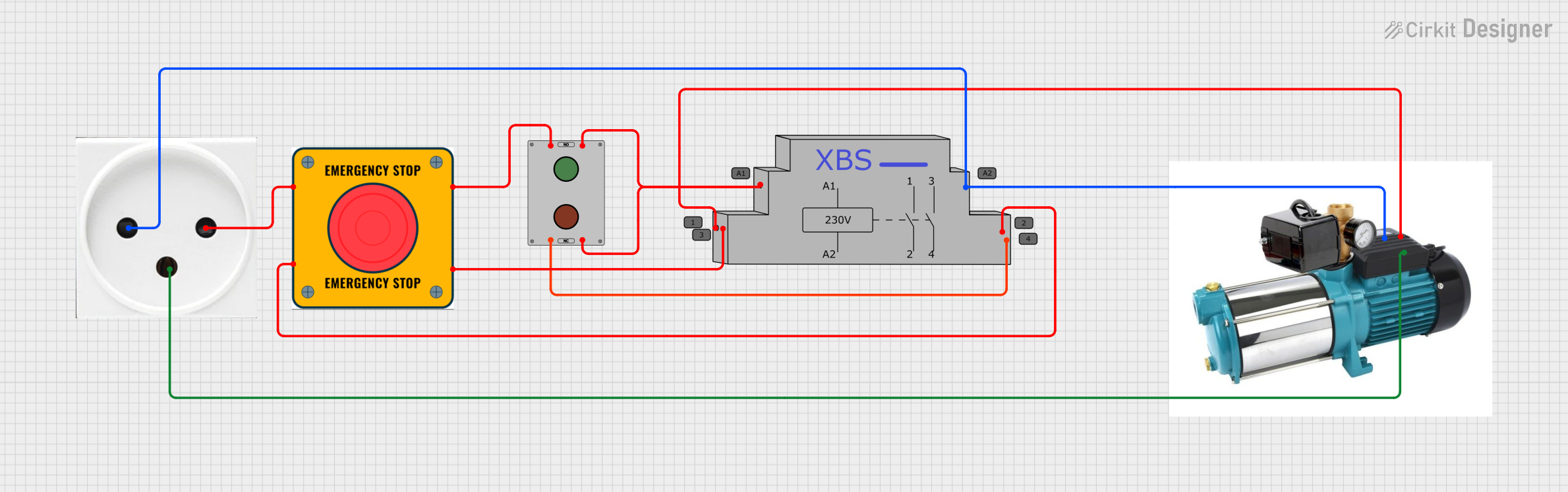
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer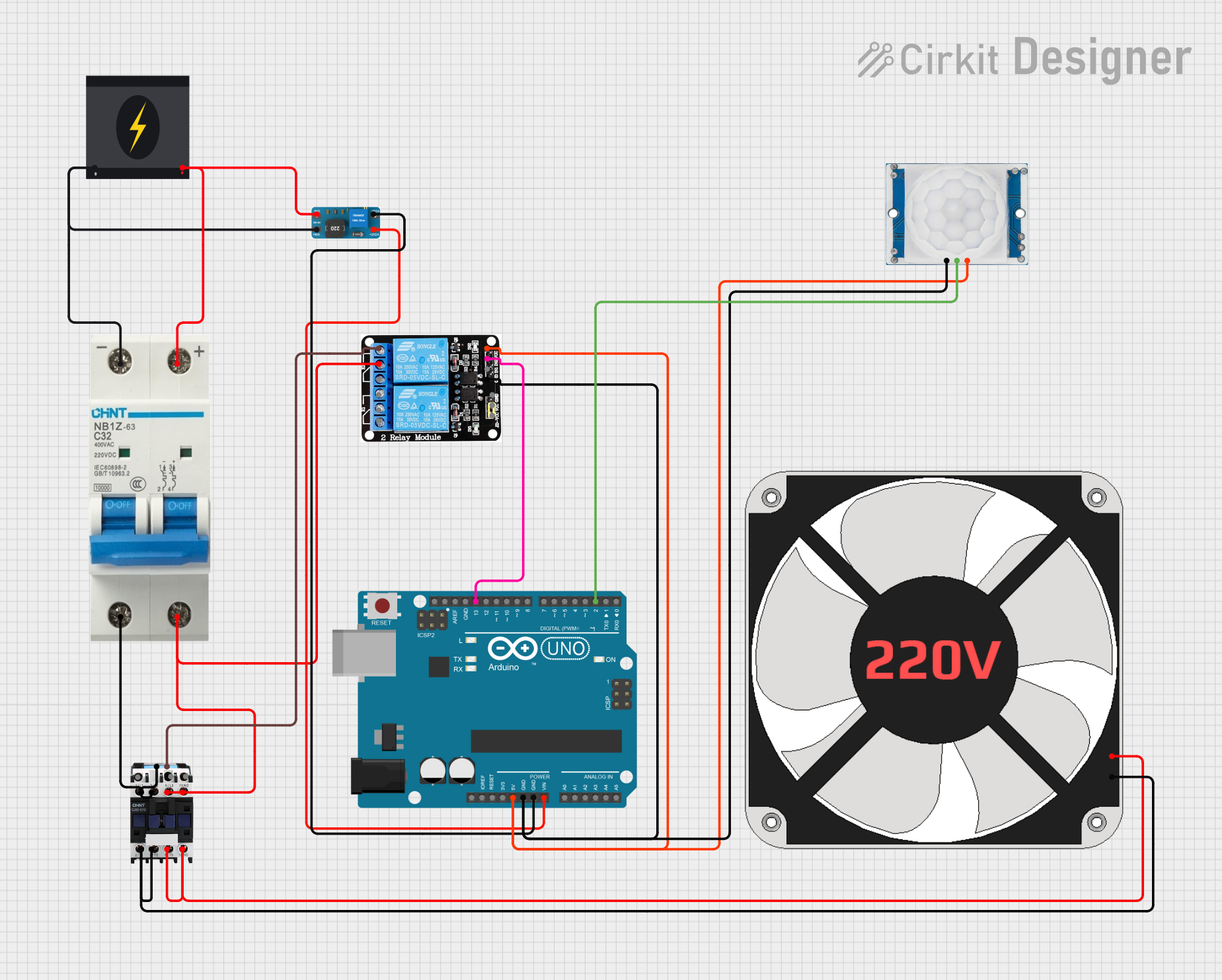
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer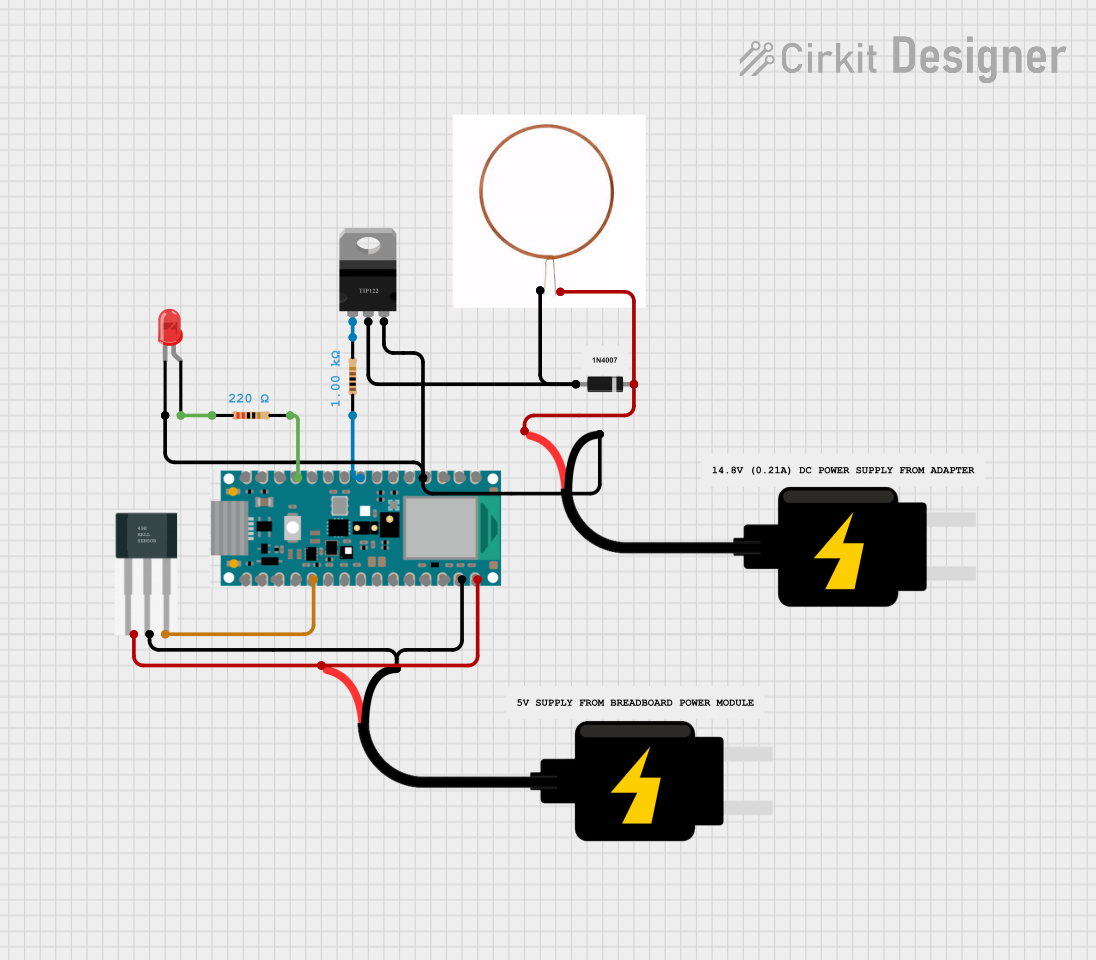
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer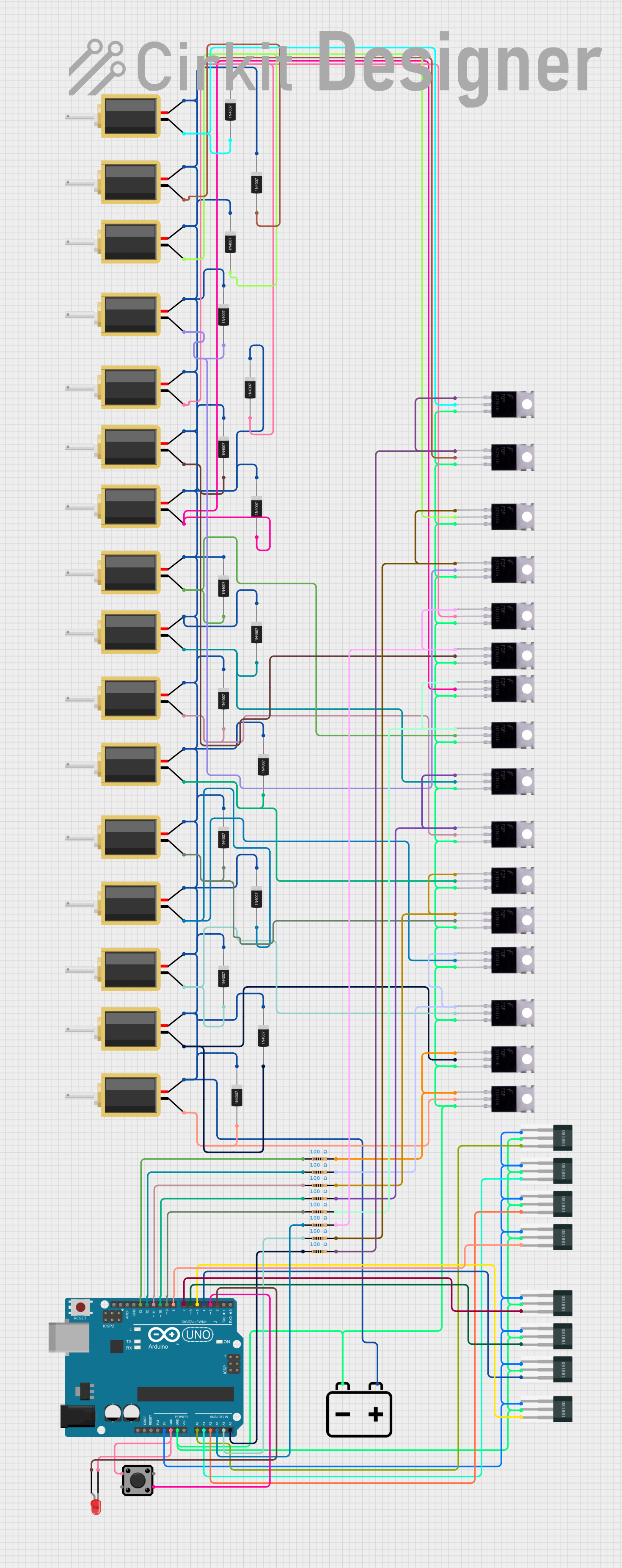
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with magnetic contactor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Electric Motor Control: Starting, stopping, and reversing motors in industrial machinery.
- Lighting Systems: Switching large lighting loads in commercial buildings.
- HVAC Systems: Controlling compressors, fans, and pumps in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Power Distribution: Managing high-current circuits in industrial power systems.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical magnetic contactor. Specifications may vary depending on the model and manufacturer.
General Specifications
- Rated Voltage: 24V, 110V, 220V, 380V AC or DC (depending on the coil type)
- Rated Current: 9A to 800A (varies by model)
- Contact Configuration: 3-pole (3-phase) or 4-pole
- Coil Power Consumption: Typically 3-10W
- Mechanical Life: Up to 10 million operations
- Electrical Life: Up to 1 million operations
- Operating Temperature: -25°C to +55°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Magnetic contactors typically have terminals for the main power circuit and the control circuit. Below is a table describing the common terminal designations:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| L1, L2, L3 | Input terminals for the three-phase power supply (main circuit). |
| T1, T2, T3 | Output terminals connected to the load (e.g., motor, lighting system). |
| A1, A2 | Coil terminals for the control circuit. A1 is typically the positive terminal. |
| NO (Normally Open) | Auxiliary contact used for control or signaling purposes. |
| NC (Normally Closed) | Auxiliary contact used for control or signaling purposes. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Magnetic Contactor in a Circuit
- Determine the Specifications: Select a magnetic contactor that matches the voltage and current requirements of your application.
- Connect the Main Circuit:
- Connect the three-phase power supply to the input terminals (L1, L2, L3).
- Connect the load (e.g., motor) to the output terminals (T1, T2, T3).
- Connect the Control Circuit:
- Connect the control voltage source to the coil terminals (A1 and A2).
- Use a push-button switch or relay to control the coil voltage.
- Use Auxiliary Contacts (if needed):
- Connect auxiliary contacts (NO or NC) to control or monitor the operation of the contactor.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Overload Protection: Always use an overload relay in conjunction with the magnetic contactor to protect the load from overcurrent conditions.
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the coil voltage matches the control circuit voltage.
- Proper Wiring: Use appropriately rated wires and ensure all connections are secure.
- Avoid Frequent Switching: Excessive switching can reduce the lifespan of the contactor.
- Mounting: Install the contactor in a well-ventilated enclosure to prevent overheating.
Example: Controlling a Magnetic Contactor with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a magnetic contactor using an Arduino UNO and a relay module.
// Magnetic Contactor Control with Arduino UNO
// This code demonstrates how to use a relay module to control a magnetic contactor.
// The relay module is connected to pin 7 of the Arduino.
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off at startup
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the magnetic contactor
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Activate the relay
delay(5000); // Keep the contactor on for 5 seconds
// Turn off the magnetic contactor
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Deactivate the relay
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before repeating
}
Notes:
- The relay module acts as an intermediary between the Arduino and the magnetic contactor.
- Ensure the relay module is rated to handle the coil voltage and current of the contactor.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Contactor Does Not Energize:
- Cause: No voltage at the coil terminals (A1, A2).
- Solution: Check the control circuit wiring and ensure the correct voltage is applied.
Excessive Noise or Chattering:
- Cause: Insufficient or unstable control voltage.
- Solution: Verify the control voltage and ensure it meets the contactor's specifications.
Overheating:
- Cause: Overcurrent or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Check the load current and ensure the contactor is properly rated. Improve ventilation.
Contacts Sticking:
- Cause: Worn or damaged contacts due to excessive switching.
- Solution: Replace the contactor and avoid frequent switching.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a magnetic contactor for single-phase loads?
A: Yes, you can use a magnetic contactor for single-phase loads by connecting only one pair of input and output terminals.Q: What is the difference between a relay and a magnetic contactor?
A: A relay is designed for low-current applications, while a magnetic contactor is built to handle high-current loads.Q: How do I know if my contactor is faulty?
A: Signs of a faulty contactor include failure to energize, excessive noise, or visible damage to the contacts.Q: Can I manually operate a magnetic contactor?
A: Some contactors have a manual override feature, but this is typically for testing purposes only.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and troubleshoot a magnetic contactor in your applications.