
How to Use LiFePo4 12V 50AH: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with LiFePo4 12V 50AH in Cirkit Designer
Design with LiFePo4 12V 50AH in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The LiFePo4 12V 50AH is a lithium iron phosphate battery with a nominal voltage of 12 volts and a capacity of 50 amp-hours. This battery is renowned for its safety, long cycle life, and stable performance, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries, LiFePo4 batteries offer higher energy density, faster charging, and a significantly longer lifespan.
Explore Projects Built with LiFePo4 12V 50AH
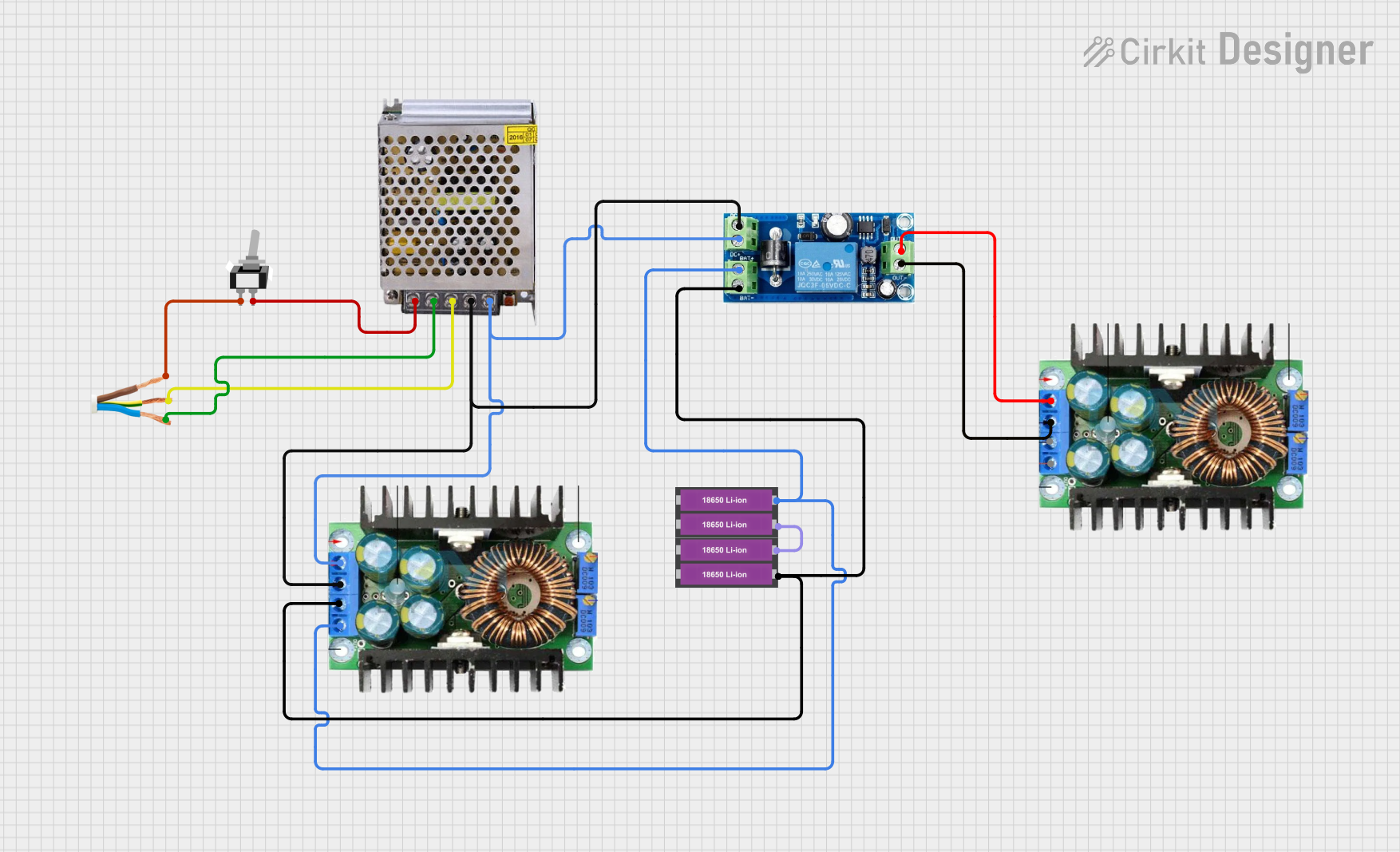
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer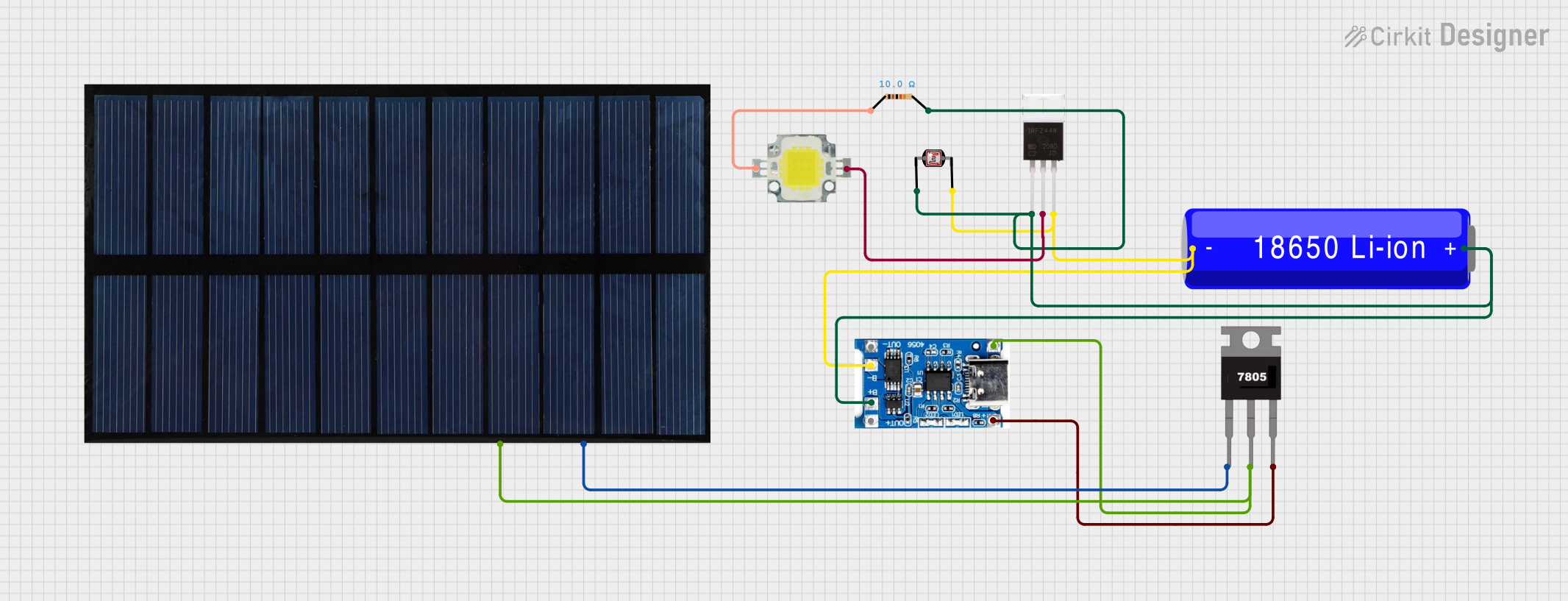
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer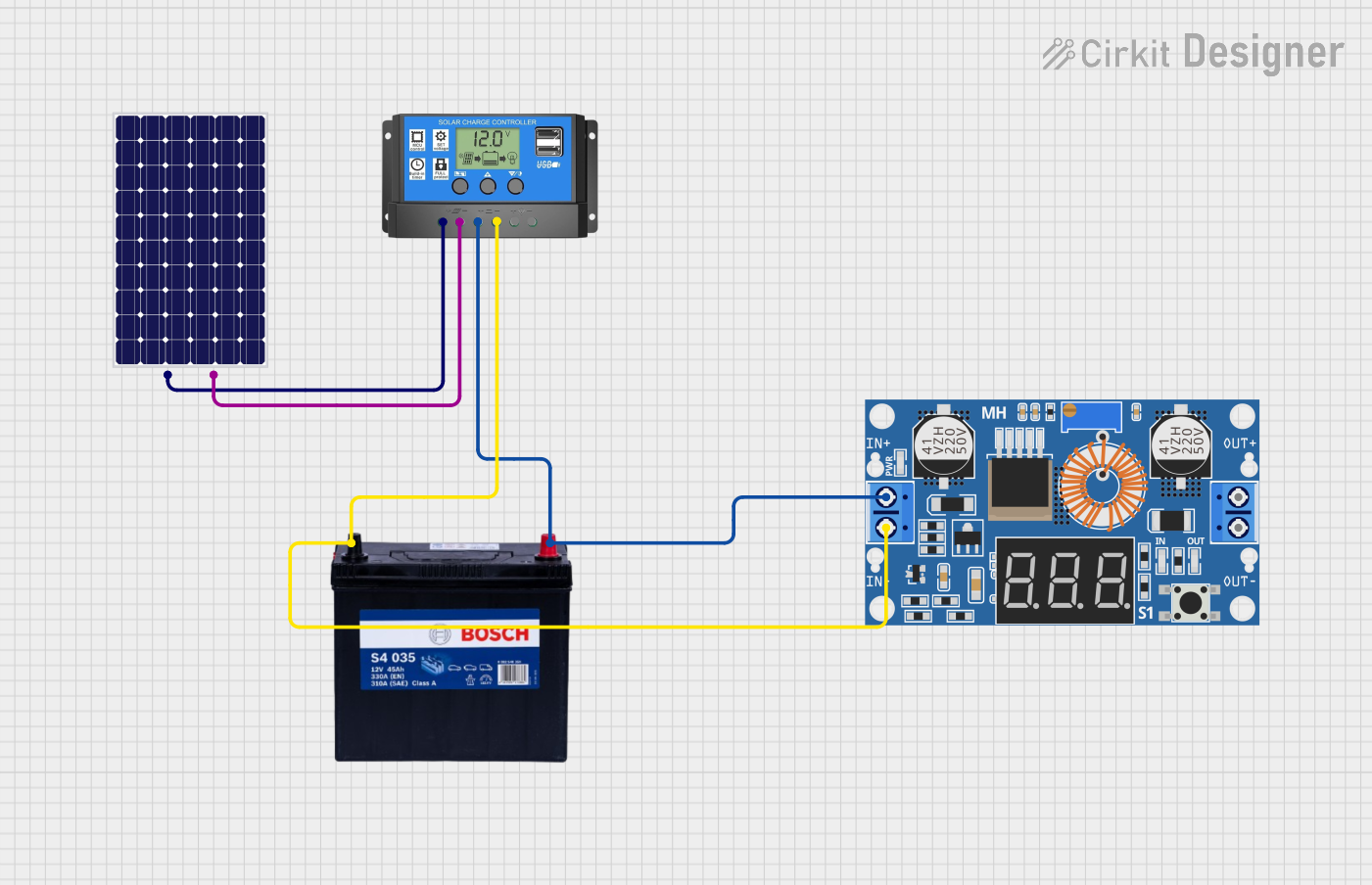
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LiFePo4 12V 50AH

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Solar energy storage systems
- Backup power supplies (UPS systems)
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and e-bikes
- Marine and RV power systems
- Portable power stations
- Robotics and industrial equipment
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the LiFePo4 12V 50AH battery:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 12.8V |
| Capacity | 50Ah |
| Energy | 640Wh |
| Charge Voltage Range | 14.2V - 14.6V |
| Discharge Voltage Range | 10.0V - 12.8V |
| Maximum Continuous Current | 50A |
| Peak Discharge Current | 100A (for 10 seconds) |
| Cycle Life | >2000 cycles (at 80% depth of discharge) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C (discharge) |
| Charging Temperature | 0°C to 45°C |
| Weight | ~6.5 kg |
| Dimensions (LxWxH) | ~195mm x 165mm x 170mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The LiFePo4 12V 50AH battery typically has two terminals for electrical connections:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Connects to the positive side of the circuit |
| Negative (-) | Connects to the negative side of the circuit |
Some models may include additional features such as a Battery Management System (BMS) with communication ports (e.g., RS485 or CAN bus) for monitoring and control.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Use appropriately rated wires and connectors to ensure safe and efficient power transfer.
- Connect the positive terminal to the positive side of your load or circuit and the negative terminal to the negative side.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a LiFePo4-compatible charger with a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile.
- Set the charger to a maximum voltage of 14.6V and a current limit of 10A (or as specified by the manufacturer).
- Avoid overcharging or undercharging the battery to maintain its lifespan.
Discharging the Battery:
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum continuous current rating (50A).
- Monitor the battery voltage to avoid deep discharge below 10.0V, which can damage the battery.
Safety Precautions:
- Do not short-circuit the terminals.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures or physical damage.
- Use a Battery Management System (BMS) to protect against overcharge, over-discharge, and overcurrent conditions.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Balancing Cells: If using multiple batteries in series or parallel, ensure proper cell balancing to avoid uneven wear and capacity loss.
- Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place at a partial charge (around 50%) for long-term storage.
- Monitoring: Use a voltage monitor or BMS to track the battery's state of charge (SOC) and health.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The LiFePo4 12V 50AH battery can be used to power an Arduino UNO via its VIN pin. Below is an example circuit and code to monitor the battery voltage using an analog input pin.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the VIN pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Use a voltage divider circuit (e.g., 10kΩ and 10kΩ resistors) to step down the battery voltage for safe measurement by the Arduino's analog input.
Arduino Code
// LiFePo4 Battery Voltage Monitoring with Arduino UNO
// This code reads the battery voltage using an analog pin and displays it
// on the Serial Monitor. Ensure the voltage divider reduces the input
// voltage to below 5V for safe measurement.
const int voltagePin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float resistorRatio = 2.0; // Ratio of the voltage divider (e.g., 10kΩ:10kΩ)
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's analog reference voltage
const int adcResolution = 1023; // 10-bit ADC resolution
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial communication
}
void loop() {
int adcValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the analog input
float measuredVoltage = (adcValue * referenceVoltage) / adcResolution;
float batteryVoltage = measuredVoltage * resistorRatio; // Calculate battery voltage
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect charger or damaged charging circuit.
- Solution: Use a LiFePo4-compatible charger and check the connections.
Battery Drains Quickly:
- Cause: Excessive load or degraded battery capacity.
- Solution: Reduce the load or test the battery capacity using a battery analyzer.
Overheating During Use:
- Cause: Overcurrent or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum current rating and provide adequate cooling.
Voltage Drops Below 10V:
- Cause: Deep discharge or faulty BMS.
- Solution: Recharge the battery immediately and inspect the BMS for proper operation.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Always use a multimeter to verify the battery voltage and connections.
- If the battery is not performing as expected, check for physical damage or swelling.
- For advanced diagnostics, use a BMS with communication capabilities to monitor the battery's internal parameters.
By following this documentation, users can safely and effectively utilize the LiFePo4 12V 50AH battery in their projects and applications.