
How to Use ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
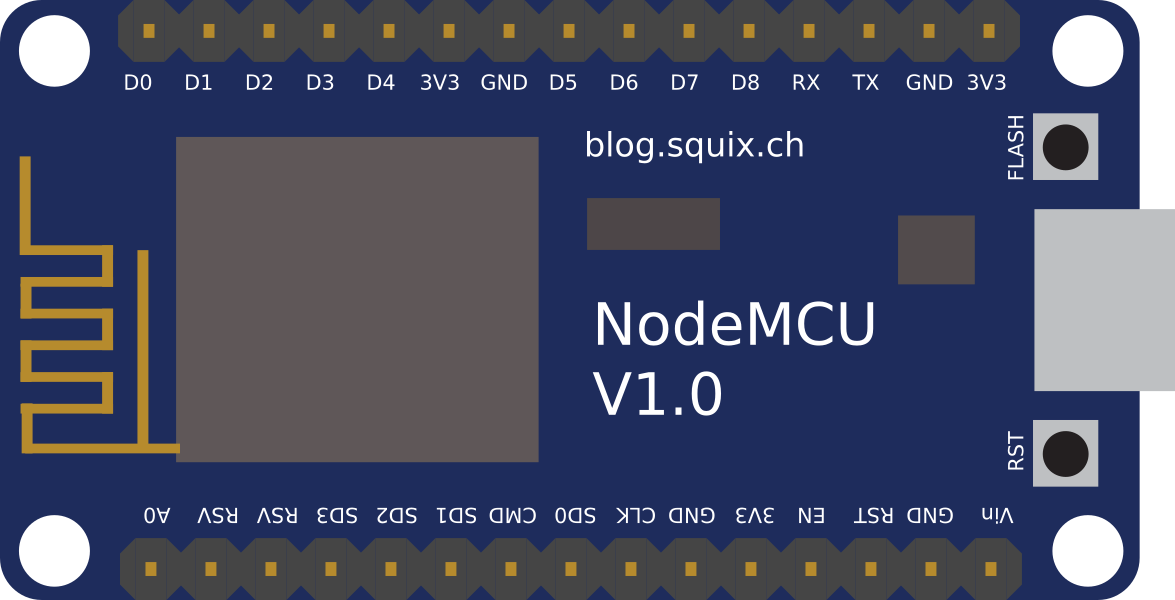
 Design with ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP8266 NodeMCU is a versatile Wi-Fi microcontroller board based on the ESP8266 chip, designed specifically for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It combines a powerful microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi capabilities, making it ideal for projects requiring wireless connectivity. The custom size variant allows for tailored dimensions to fit specific project requirements, offering flexibility for compact or space-constrained designs.
Explore Projects Built with ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size
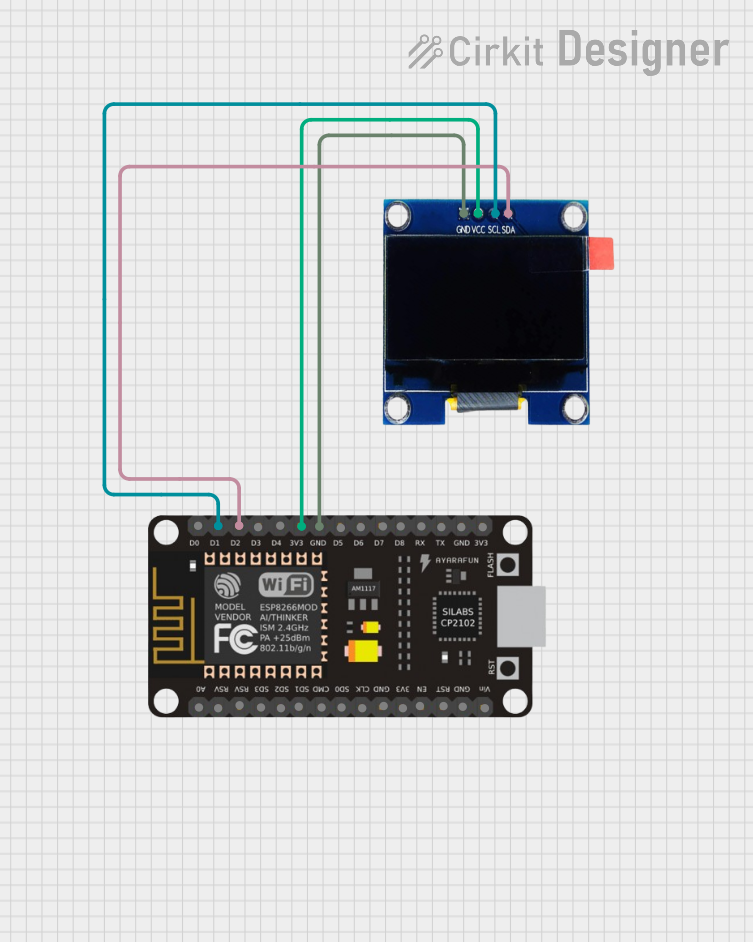
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer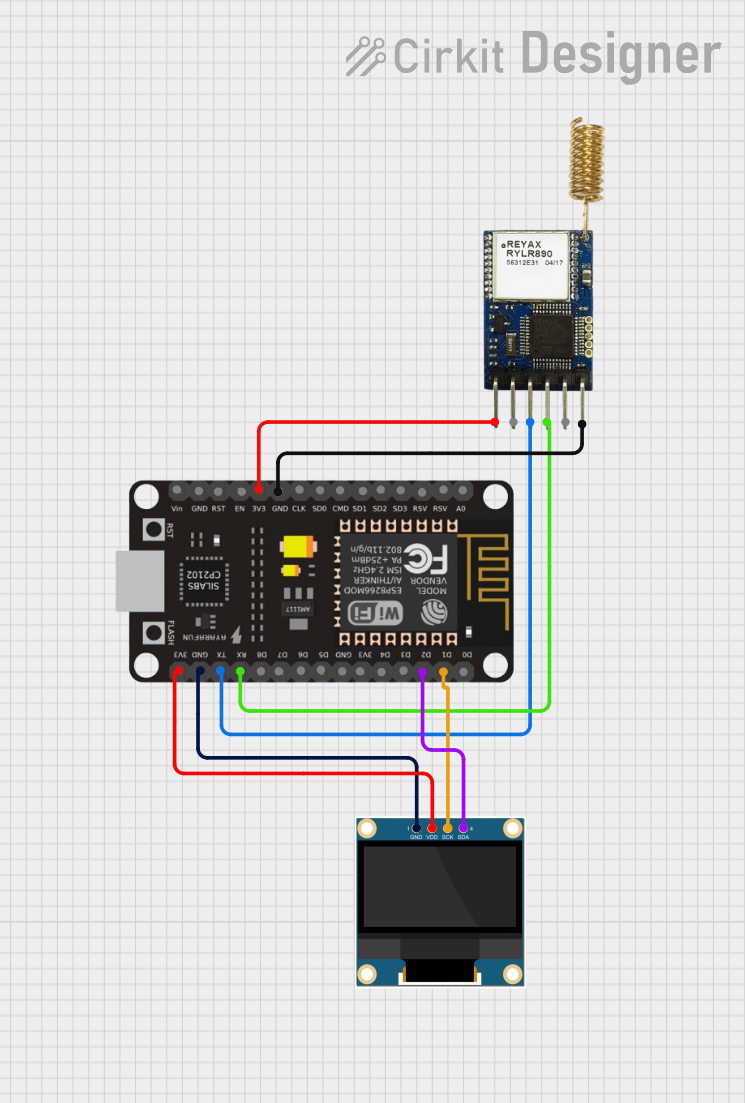
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer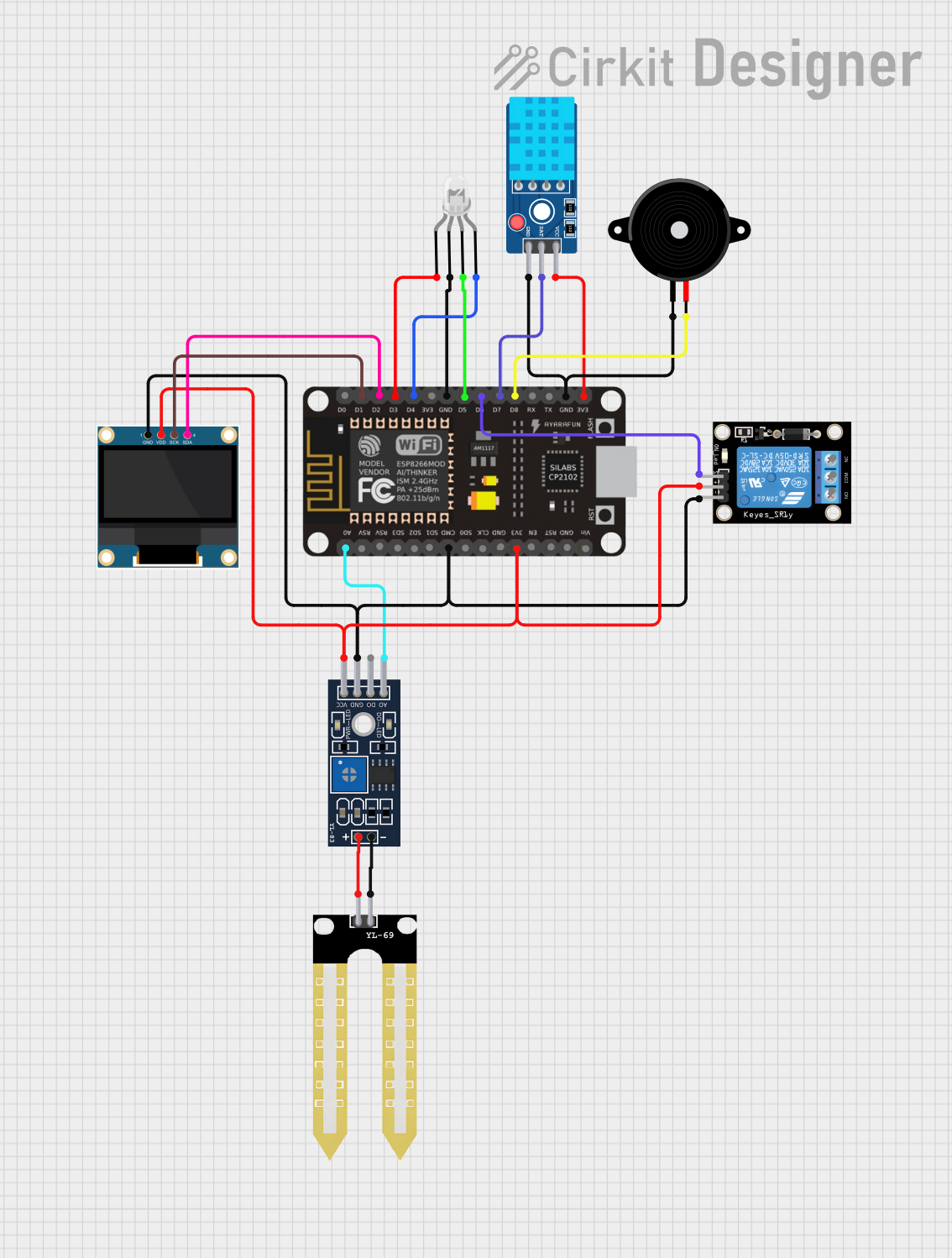
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems (e.g., smart lights, thermostats)
- IoT sensor networks
- Wireless data logging and monitoring
- Remote control of devices via mobile apps or web interfaces
- Prototyping and development of connected devices
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP8266 (Tensilica L106 32-bit processor)
- Clock Speed: 80 MHz (can be overclocked to 160 MHz)
- Flash Memory: 4 MB (customizable in some variants)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage: 4.5V–10V (via VIN pin) or 5V (via USB)
- Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11 b/g/n
- GPIO Pins: Up to 11 (configurable)
- Communication Protocols: UART, SPI, I2C, PWM
- USB Interface: Built-in CP2102 or CH340 USB-to-serial converter
- Power Consumption: ~70 mA (active), ~10 µA (deep sleep mode)
- Dimensions: Customizable to fit project needs
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP8266 NodeMCU custom size variant typically includes the following pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage (4.5V–10V). Powers the board when USB is not connected. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | 3V3 | 3.3V output. Can power external components (max 50 mA). |
| 4 | D0 (GPIO16) | General-purpose I/O pin. Can also be used for deep sleep wake-up. |
| 5 | D1 (GPIO5) | General-purpose I/O pin. Commonly used for I2C SCL. |
| 6 | D2 (GPIO4) | General-purpose I/O pin. Commonly used for I2C SDA. |
| 7 | D3 (GPIO0) | General-purpose I/O pin. Must be HIGH during boot to avoid boot mode issues. |
| 8 | D4 (GPIO2) | General-purpose I/O pin. Built-in LED is connected to this pin. |
| 9 | RX (GPIO3) | UART receive pin. Used for serial communication. |
| 10 | TX (GPIO1) | UART transmit pin. Used for serial communication. |
| 11 | A0 | Analog input pin. Reads voltages from 0–1V (use a voltage divider for higher). |
Note: The number of GPIO pins available may vary depending on the custom size configuration.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP8266 NodeMCU in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Use the USB port for development and programming.
- For standalone operation, supply 4.5V–10V to the VIN pin or 3.3V to the 3V3 pin.
Connecting to Wi-Fi:
- Use the built-in Wi-Fi module to connect to a network. Ensure the SSID and password are correctly configured in your code.
Programming:
- Install the Arduino IDE and add the ESP8266 board package.
- Select "NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E Module)" as the board type.
- Connect the board to your computer via USB and upload your code.
GPIO Usage:
- Configure GPIO pins as input or output in your code.
- Avoid using GPIO0, GPIO2, and GPIO15 for critical functions, as they affect the boot process.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected components operate at 3.3V logic levels. Use level shifters if interfacing with 5V devices.
- Deep Sleep Mode: Use deep sleep mode to conserve power in battery-operated projects.
- Custom Size: Verify the pinout and dimensions of your custom-sized board before designing your PCB or enclosure.
- Boot Mode: Ensure GPIO0 is HIGH during boot to avoid entering flash mode unintentionally.
Example Code for Arduino IDE
The following example demonstrates how to connect the ESP8266 NodeMCU to a Wi-Fi network and control the built-in LED:
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); // Set built-in LED pin as output
// Connect to Wi-Fi
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
}
void loop() {
// Blink the built-in LED
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // Turn LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // Turn LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Board Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the correct USB driver (CP2102 or CH340) is installed.
- Try a different USB cable or port.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Double-check the SSID and password in your code.
- Ensure the router is within range and supports 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi (ESP8266 does not support 5 GHz).
Code Upload Fails:
- Verify the correct board and port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Press and hold the FLASH button on the board while uploading.
GPIO Pin Issues:
- Avoid using GPIO0, GPIO2, and GPIO15 for critical functions, as they affect the boot process.
- Check for conflicting pin assignments in your code.
FAQs
Can I use the ESP8266 NodeMCU with 5V sensors?
- No, the ESP8266 operates at 3.3V logic levels. Use a level shifter for 5V sensors.
What is the maximum range of the Wi-Fi module?
- The range is approximately 30 meters indoors and 100 meters outdoors, depending on obstacles and interference.
How do I enable deep sleep mode?
- Connect GPIO16 to the RESET pin and use the
ESP.deepSleep()function in your code.
- Connect GPIO16 to the RESET pin and use the
Can I customize the board size and pinout?
- Yes, custom-sized variants are available. Contact your supplier for details.