
How to Use 12V to 5V: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 12V to 5V in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12V to 5V in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 12V to 5V voltage regulator is an essential electronic component designed to step down a 12V input voltage to a stable 5V output. This regulator is widely used in applications where 5V devices, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and USB-powered peripherals, need to be powered from a higher voltage source like a car battery or a 12V power supply. Its compact design and reliable performance make it a popular choice for embedded systems, automotive electronics, and DIY projects.
Explore Projects Built with 12V to 5V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer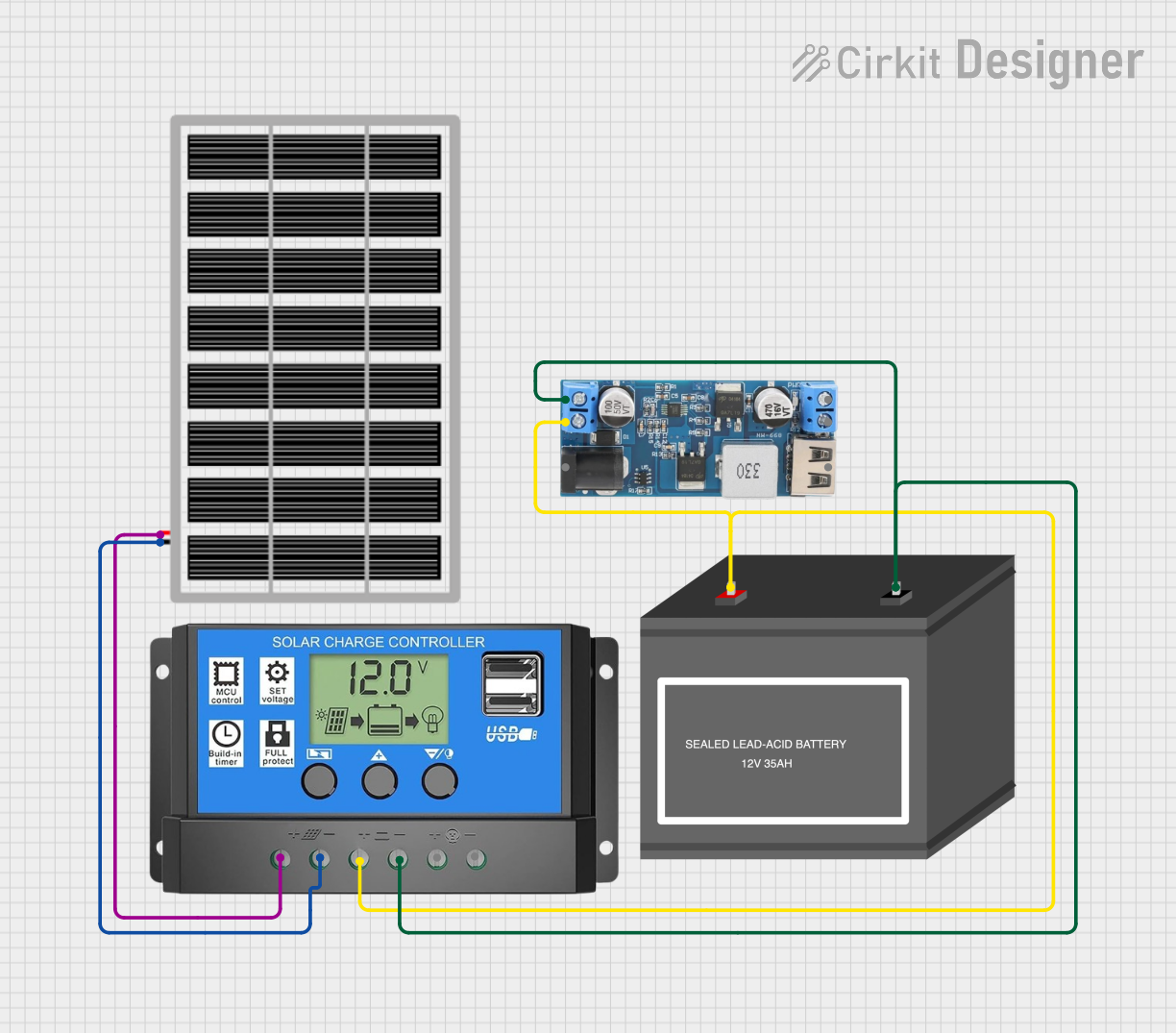
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12V to 5V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Powering 5V microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- USB device power supplies
- Automotive electronics (e.g., powering GPS modules, dash cams)
- Battery-powered systems requiring voltage regulation
- General-purpose voltage step-down circuits
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 12V to 5V voltage regulator:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 7V to 24V |
| Output Voltage | 5V ± 0.1V |
| Maximum Output Current | 2A (varies by model) |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% (depending on load) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Protection Features | Overcurrent, Overtemperature, |
| and Short-Circuit Protection |
Pin Configuration
The pinout of the 12V to 5V voltage regulator module is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin (connect to 12V source) |
| GND | Ground pin (common ground for input/output) |
| VOUT | Regulated 5V output pin |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (VIN):
Attach the VIN pin to a 12V DC power source. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (7V to 24V) to avoid damaging the regulator.Connect the Ground (GND):
Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit. This serves as the common reference point for both input and output.Connect the Output Voltage (VOUT):
Attach the VOUT pin to the 5V device or circuit you wish to power. Ensure the connected load does not exceed the maximum output current rating (2A).Optional Capacitors:
For improved stability, you can add a 10µF capacitor across the input (VIN and GND) and a 22µF capacitor across the output (VOUT and GND). These capacitors help reduce voltage ripple and noise.
Important Considerations
Heat Dissipation:
If the regulator is operating near its maximum current rating, it may generate heat. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.Input Voltage Range:
Always ensure the input voltage is within the specified range. Exceeding the maximum input voltage can permanently damage the regulator.Load Current:
Do not exceed the maximum output current rating. Overloading the regulator may trigger protection features or cause it to fail.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
The 12V to 5V regulator can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a 12V source. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the VIN pin of the regulator to a 12V DC power source.
- Connect the GND pin of the regulator to the ground of the power source and the Arduino.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the regulator to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code to blink an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO
// Ensure the Arduino is powered via the 12V to 5V regulator
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is too low or not connected properly.
- Solution: Verify that the input voltage is within the specified range (7V to 24V) and that all connections are secure.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive load current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or add a heatsink to the regulator.
Voltage Drop Under Load:
- Cause: Insufficient input voltage or inadequate wiring.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is stable and use thicker wires to reduce resistance.
Regulator Shuts Down:
- Cause: Overcurrent or short-circuit protection triggered.
- Solution: Check for short circuits in the output and ensure the load does not exceed the maximum current rating.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this regulator to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, but ensure the regulator can supply sufficient current (at least 2A) for the Raspberry Pi model you are using.
Q: Can I use this regulator with a 24V input?
A: Yes, as long as the input voltage does not exceed the maximum rating (24V) and the regulator's efficiency is sufficient for your application.
Q: Do I need external capacitors?
A: While not mandatory, adding capacitors (10µF on the input and 22µF on the output) can improve stability and reduce noise.
Q: Is this regulator suitable for automotive use?
A: Yes, it is commonly used in automotive applications to power 5V devices from a 12V car battery. However, ensure the regulator has adequate protection against voltage spikes.