
How to Use Esp32C3 0.42 Oled: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Esp32C3 0.42 Oled in Cirkit Designer
Design with Esp32C3 0.42 Oled in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32-C3 0.42 OLED by ABRobot is a compact and versatile microcontroller module that integrates the ESP32-C3 chip with a 0.42-inch OLED display. This module combines the power of the ESP32-C3's Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) capabilities with a built-in OLED screen, making it ideal for IoT applications, wearable devices, and compact display-based projects.
Explore Projects Built with Esp32C3 0.42 Oled

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer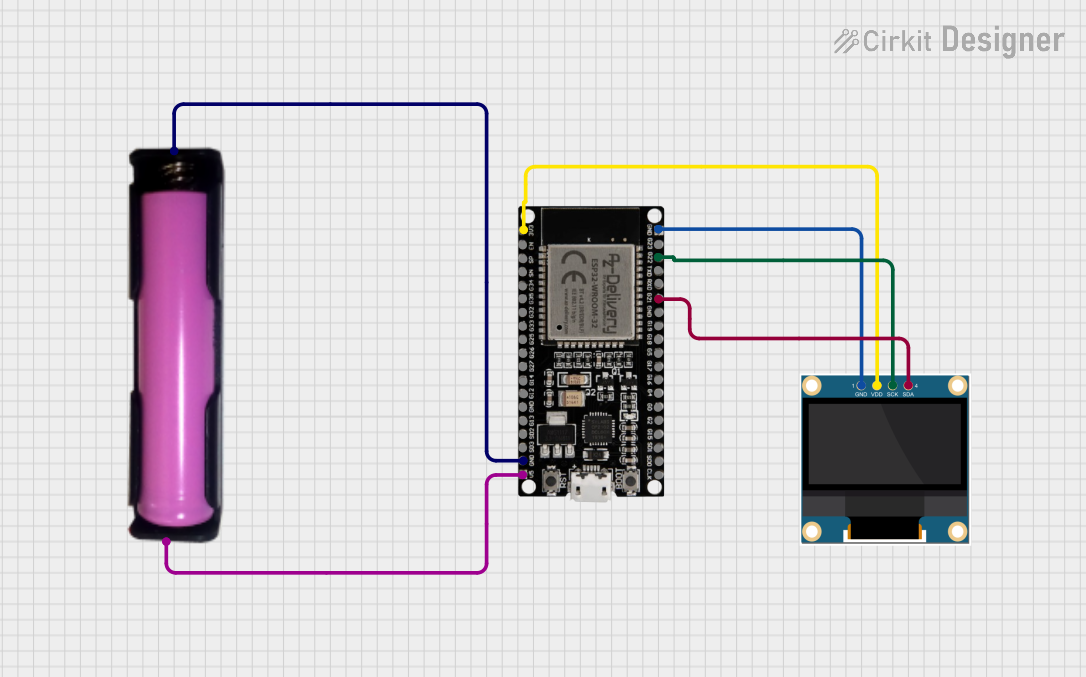
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer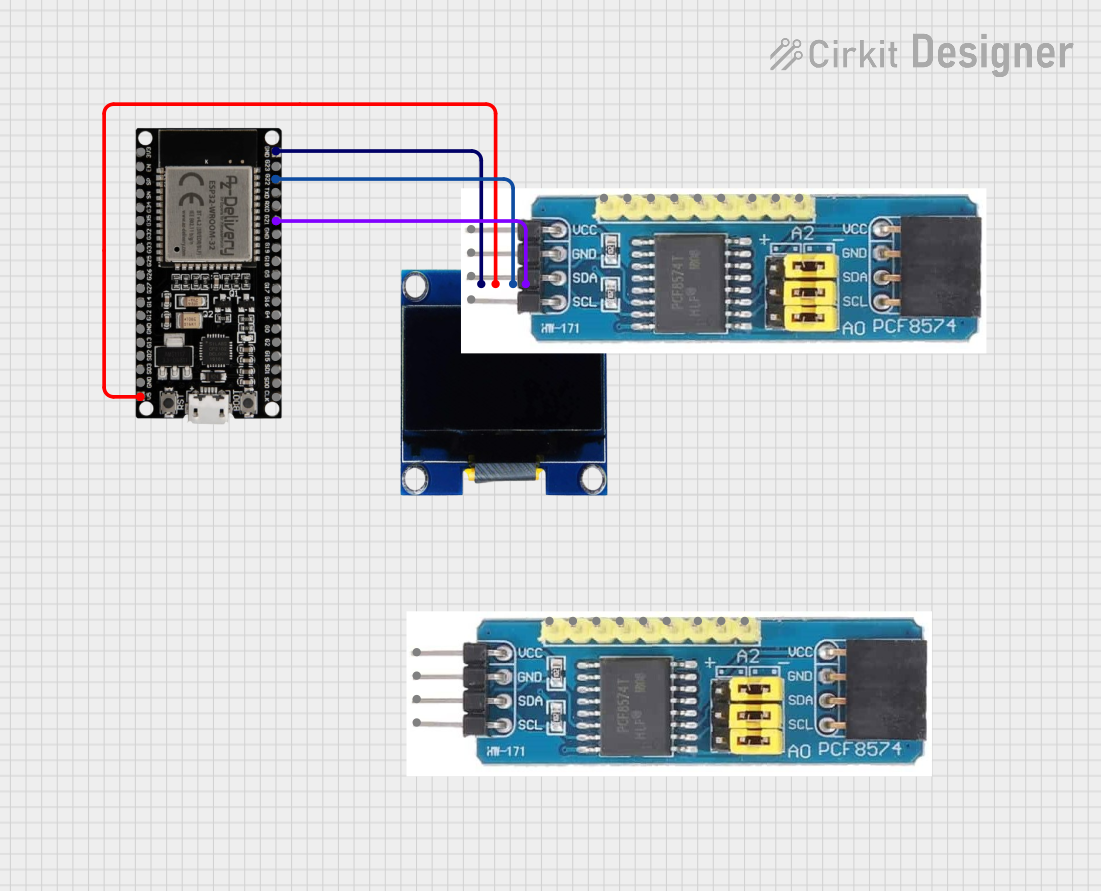
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer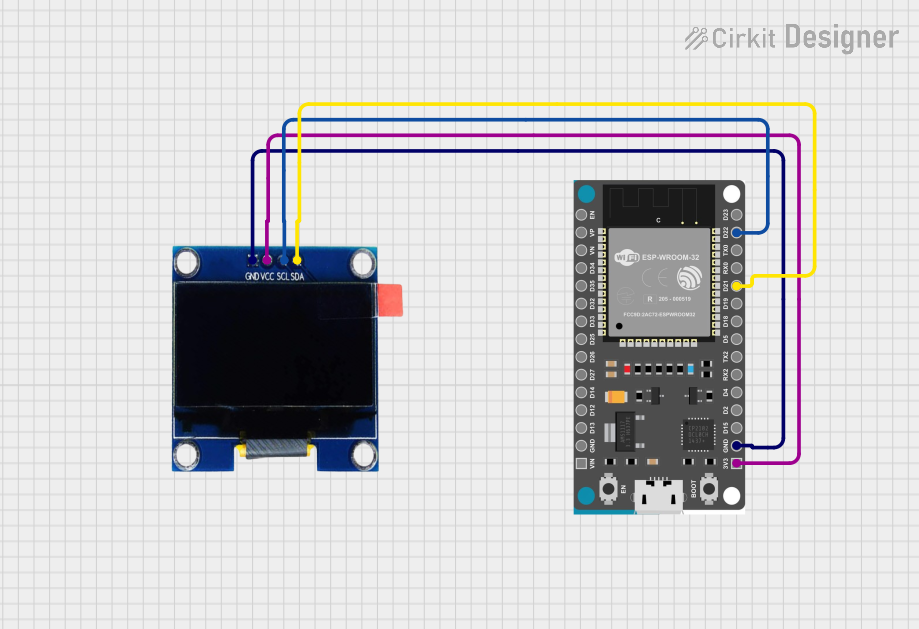
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Esp32C3 0.42 Oled

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices with real-time data display
- Wearable electronics
- Smart home automation systems
- Portable monitoring devices
- Educational and prototyping projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-C3 (RISC-V architecture) |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 5 (LE) |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| OLED Display | 0.42-inch, 72x40 resolution, monochrome |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power in deep sleep mode |
| Interface | I2C for OLED communication |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 15mm x 5mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power input (3.3V) |
| GND | 2 | Ground |
| SDA | 3 | I2C data line for OLED communication |
| SCL | 4 | I2C clock line for OLED communication |
| GPIO0 | 5 | General-purpose I/O pin |
| GPIO1 | 6 | General-purpose I/O pin |
| RST | 7 | Reset pin for the ESP32-C3 |
| EN | 8 | Enable pin to power up the module |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Powering the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- I2C Communication: Use the SDA and SCL pins to interface with the OLED display. Ensure the I2C address of the OLED is correctly configured in your code (default:
0x3C). - Programming the ESP32-C3: Use a USB-to-serial adapter to upload code to the ESP32-C3. Ensure the correct board and port are selected in your IDE (e.g., Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable 3.3V power source to avoid damaging the module.
- Pull-up Resistors: Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines if not already integrated.
- OLED Brightness: Prolong the OLED's lifespan by reducing brightness or using sleep modes when not in use.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the ESP32-C3 firmware updated for optimal performance and security.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-C3 0.42 OLED with the Arduino IDE to display text on the OLED screen.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
// Define OLED display dimensions
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 72
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 40
// I2C address for the OLED display
#define OLED_ADDRESS 0x3C
// Create an instance of the SSD1306 display
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, -1);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the OLED display
if (!display.begin(SSD1306_I2C_ADDRESS, OLED_ADDRESS)) {
Serial.println(F("OLED initialization failed!"));
while (true); // Halt execution if OLED fails to initialize
}
// Clear the display buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Set text size and color
display.setTextSize(1); // Small text size
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
// Display a message
display.setCursor(0, 0); // Start at top-left corner
display.println(F("Hello, ESP32-C3!"));
display.display(); // Render the text on the OLED
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
OLED Display Not Turning On:
- Ensure the VCC and GND connections are secure.
- Verify the I2C address (
0x3C) in your code matches the OLED's address. - Check for proper pull-up resistors on the SDA and SCL lines.
ESP32-C3 Not Detected by IDE:
- Confirm the correct board and port are selected in the Arduino IDE.
- Ensure the USB-to-serial adapter drivers are installed on your computer.
Flickering or Dim OLED Display:
- Check the power supply voltage and current capacity.
- Reduce the brightness in your code to prevent overloading the OLED.
I2C Communication Errors:
- Verify the SDA and SCL connections.
- Use a logic analyzer to debug I2C signals if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the ESP32-C3 0.42 OLED with 5V?
A: No, the module operates at 3.3V. Using 5V may damage the module.
Q: What is the default I2C address of the OLED?
A: The default I2C address is 0x3C.
Q: Can I use the ESP32-C3 0.42 OLED with MicroPython?
A: Yes, the ESP32-C3 is compatible with MicroPython. You can use libraries like ssd1306.py to control the OLED.
Q: How do I reset the module?
A: Use the RST pin to reset the module by momentarily pulling it low.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the ESP32-C3 0.42 OLED module effectively. For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or support resources.