
How to Use IR Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with IR Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with IR Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An IR (Infrared) sensor is an electronic device that detects infrared radiation emitted by objects. It is widely used in applications such as proximity sensing, motion detection, and remote control systems. IR sensors are versatile and can be found in devices like automatic doors, obstacle-avoiding robots, and TV remote controls. They are valued for their ability to detect objects without physical contact.
Explore Projects Built with IR Sensor
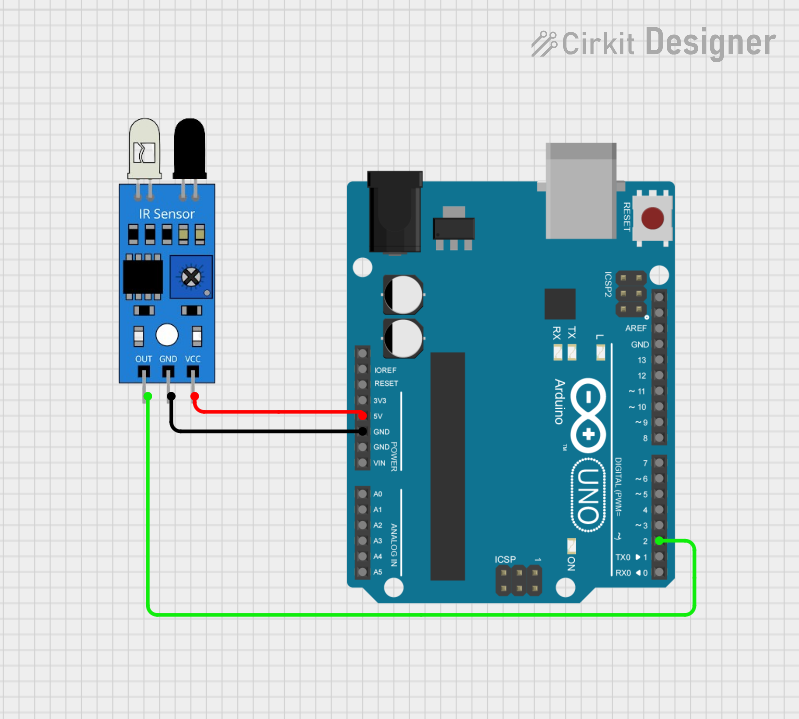
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer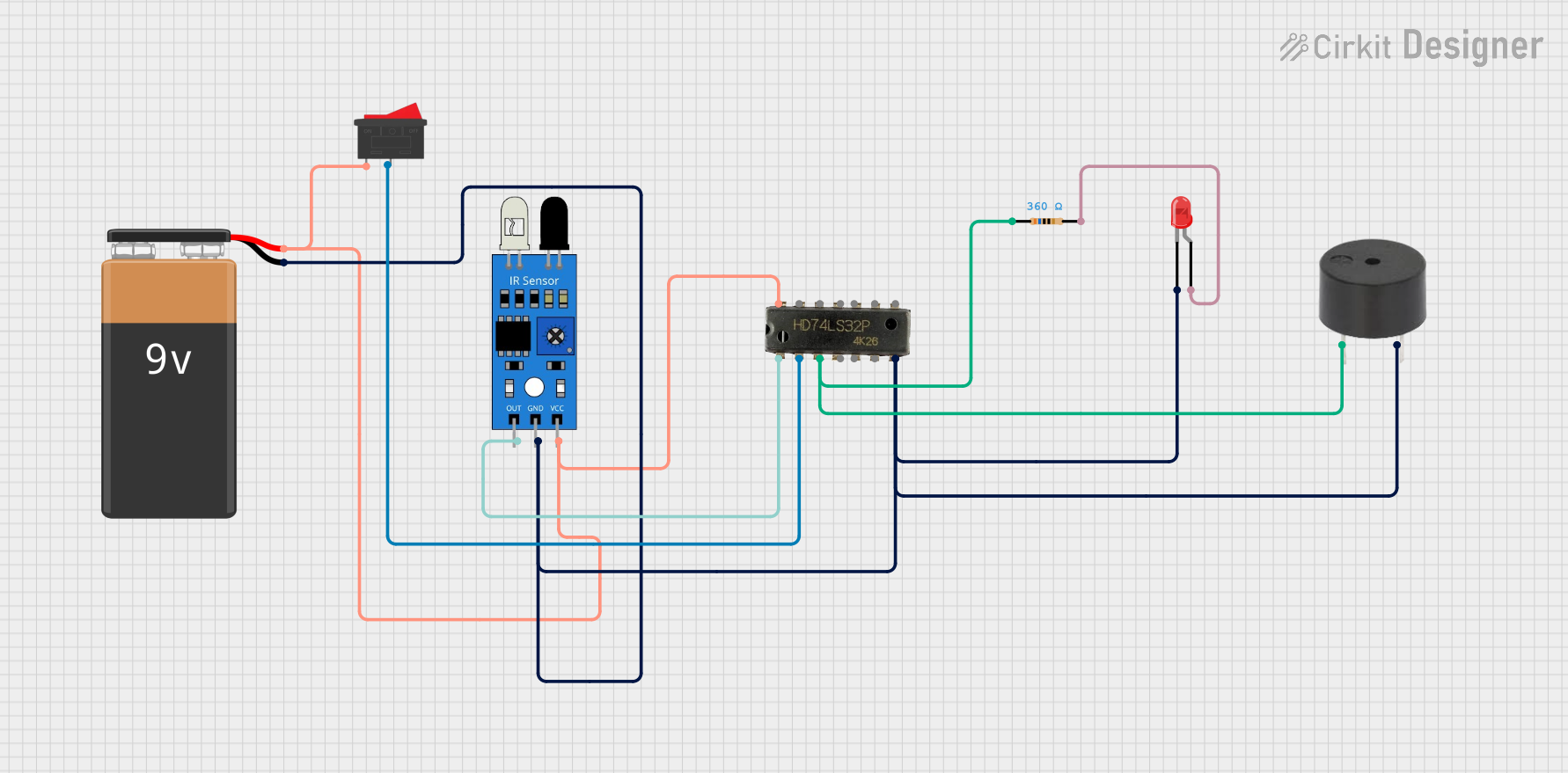
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer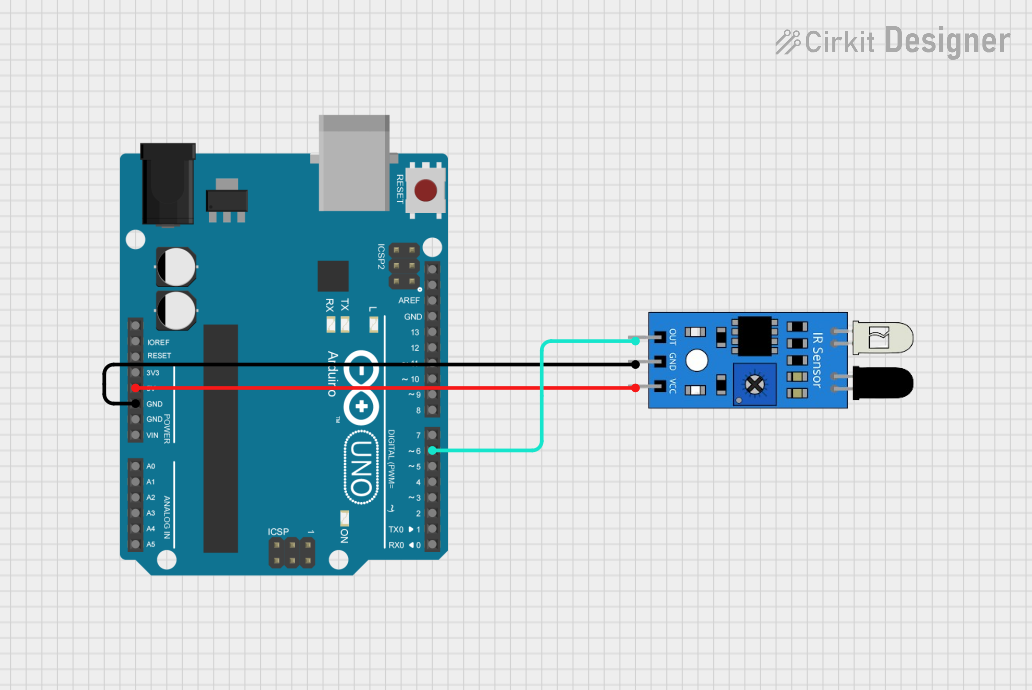
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer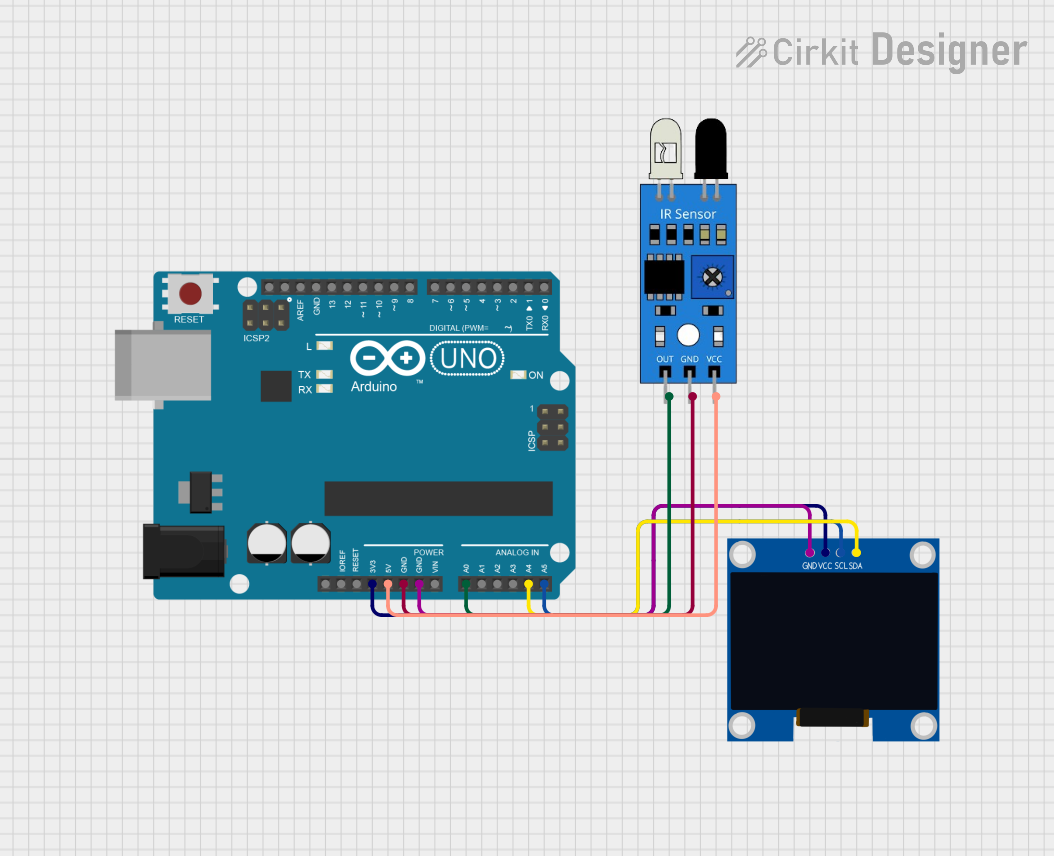
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with IR Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Current Consumption: 20mA (typical)
- Detection Range: 2cm to 30cm (varies by model and environment)
- Output Type: Digital (High/Low) or Analog (depending on the model)
- Wavelength: 700nm to 1mm (infrared spectrum)
- Operating Temperature: -25°C to 85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V DC. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | OUT (Digital) | Digital output pin. Outputs HIGH or LOW based on object detection. |
| 4 | OUT (Analog)* | Analog output pin (if available). Provides a voltage proportional to distance. |
*Note: Some IR sensors may not have an analog output pin. Check your specific model's datasheet.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Connect the Output:
- For digital output, connect the OUT pin to a microcontroller's digital input pin.
- For analog output (if available), connect the analog OUT pin to an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) pin on the microcontroller.
- Position the Sensor: Place the sensor so that it faces the area where object detection is required. Ensure there are no obstructions in its line of sight.
- Read the Output:
- A HIGH signal on the digital OUT pin indicates no object detected.
- A LOW signal indicates an object is within the detection range.
- For analog output, read the voltage to determine the distance.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ambient Light: IR sensors can be affected by ambient light. Use them in controlled lighting conditions for better accuracy.
- Reflective Surfaces: Highly reflective surfaces may cause false readings. Test the sensor with the target material.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply to avoid erratic behavior.
- Interference: Avoid placing multiple IR sensors close to each other to prevent interference.
Example: Connecting an IR Sensor to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a digital IR sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the IR sensor's digital output
const int irSensorPin = 2; // Connect the OUT pin of the IR sensor to pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED on Arduino for visual feedback
void setup() {
pinMode(irSensorPin, INPUT); // Set the IR sensor pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = digitalRead(irSensorPin); // Read the IR sensor's output
if (sensorValue == LOW) {
// Object detected
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
Serial.println("Object detected!");
} else {
// No object detected
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED
Serial.println("No object detected.");
}
delay(100); // Small delay to stabilize readings
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Sensor Not Detecting Objects
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply matches the sensor's requirements.
False Readings in Bright Light
- Cause: Ambient light interference.
- Solution: Use the sensor in a shaded area or add an IR filter to block visible light.
Multiple Sensors Interfering with Each Other
- Cause: Overlapping IR signals from nearby sensors.
- Solution: Space the sensors apart or use modulation techniques to differentiate signals.
Output Always HIGH or LOW
- Cause: Faulty sensor or incorrect placement.
- Solution: Test the sensor with a known object and ensure it is positioned correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can the IR sensor detect transparent objects?
A: IR sensors may struggle with transparent objects like glass. Use a specialized sensor for such applications.Q: What is the maximum range of an IR sensor?
A: The range depends on the model, typically between 2cm and 30cm. Check the datasheet for exact specifications.Q: Can I use an IR sensor outdoors?
A: Yes, but performance may be affected by sunlight. Consider using an IR sensor with ambient light compensation.Q: How do I clean the sensor?
A: Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the sensor lens. Avoid using liquids or abrasive materials.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and using an IR sensor effectively.