
How to Use Main Switch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
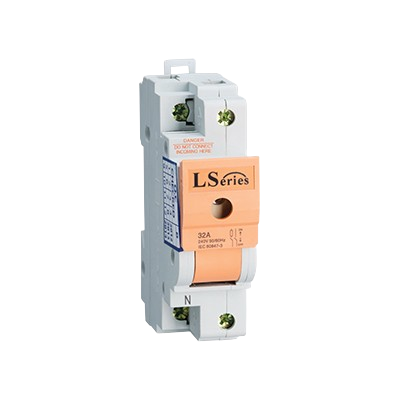

 Design with Main Switch in Cirkit Designer
Design with Main Switch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Main Switch is a critical component in electrical systems, serving as the primary control mechanism for connecting or disconnecting the flow of electricity in a circuit. It is manually operated and is often used to control the main power supply to a building, machinery, or an electronic device. Common applications include residential and commercial electrical distribution panels, industrial control systems, and as a safety mechanism in various electronic projects.
Explore Projects Built with Main Switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer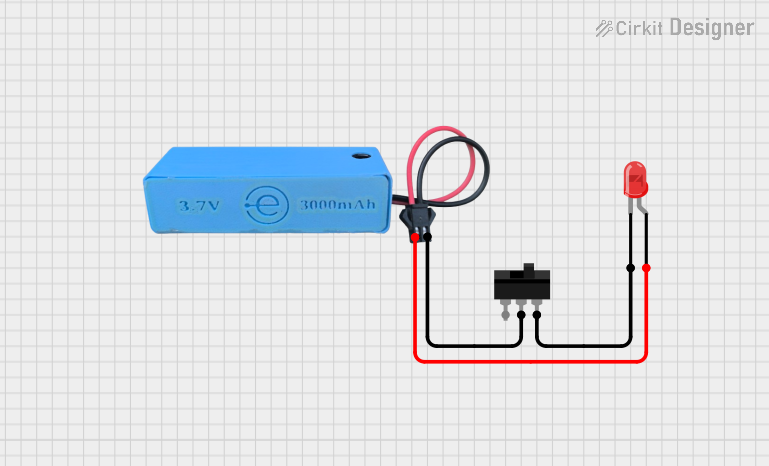
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer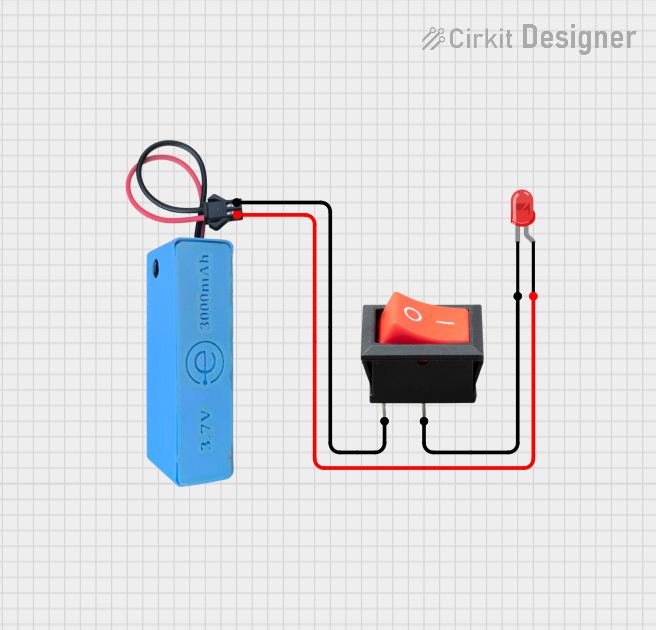
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer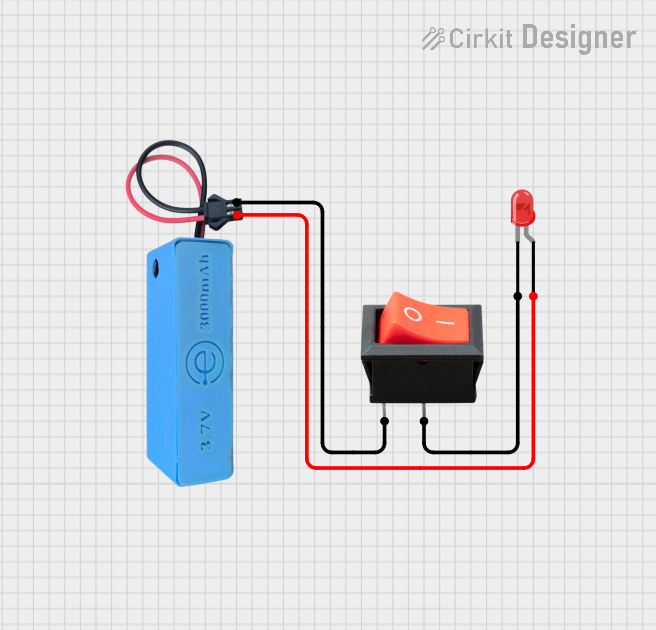
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Main Switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Characteristics
- Type: Mechanical Switch
- Function: Make or Break Electrical Connection
- Operation: Manual
Electrical Ratings
- Rated Voltage: Specified in volts (V), typically ranges from 110V to 600V depending on the model.
- Rated Current: Specified in amperes (A), commonly from 10A to several hundred amperes.
- Power Handling: Specified in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), relevant to the switch's voltage and current ratings.
Mechanical Ratings
- Endurance: Number of operation cycles before failure, typically in the tens of thousands.
- Operating Temperature: Range in which the switch can operate reliably, e.g., -20°C to 60°C.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Line In (Live Input) | Connects to the live supply line |
| 2 | Load Out (Live Output) | Connects to the load or device |
| - | Earth/Ground | Safety connection (if applicable) |
| - | Neutral | Neutral line (if applicable) |
Note: The actual pin configuration may vary based on the design and manufacturer of the Main Switch. Always refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for the exact pinout.
Usage Instructions
Installation
- Power Off: Ensure that the power supply to the circuit where the Main Switch will be installed is turned off.
- Mounting: Secure the Main Switch to a suitable location, ensuring it is accessible for operation.
- Wiring: Connect the live supply line to the 'Line In' terminal and the load to the 'Load Out' terminal. If provided, connect the neutral and ground wires to their respective terminals.
- Inspection: Double-check all connections for correctness and tightness.
Operation
- To energize the circuit, manually toggle the switch to the 'ON' position.
- To de-energize the circuit, toggle the switch to the 'OFF' position.
Best Practices
- Always install a Main Switch with a current rating that exceeds the maximum expected load.
- Use appropriate cable sizes to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
- Regularly inspect the Main Switch for signs of wear or damage and replace if necessary.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Switch Does Not Operate: Check if the switch is jammed or if there is a mechanical failure.
- No Power to Load: Ensure the connections are secure and the switch is in the 'ON' position. Check for a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker upstream of the Main Switch.
FAQs
Q: Can I replace a Main Switch myself? A: Replacing a Main Switch involves working with high-voltage electrical systems. It is recommended to hire a qualified electrician unless you have the proper training and experience.
Q: How do I know if my Main Switch is rated for my application? A: Check the switch's voltage and current ratings against the requirements of your electrical system. The ratings should meet or exceed your system's maximum operating parameters.
Q: What should I do if the Main Switch gets hot during operation? A: A hot switch may indicate an overloaded circuit or a loose connection. Turn off the power and inspect the switch and connections. If the issue persists, consult an electrician.
Note: This documentation is for informational purposes only. Always follow local codes and regulations when working with electrical components.
Since a Main Switch is not typically a component that would be connected to an Arduino UNO or similar microcontroller, code examples are not applicable for this documentation.