
How to Use Actuator Motor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Actuator Motor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Actuator Motor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An actuator motor is a type of motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It is commonly used to control mechanisms or systems in automation applications. Actuator motors are integral to a wide range of industries, including robotics, automotive systems, industrial machinery, and home automation. They are designed to provide precise control over movement, making them ideal for tasks such as opening valves, moving robotic arms, or adjusting positioning systems.
Explore Projects Built with Actuator Motor
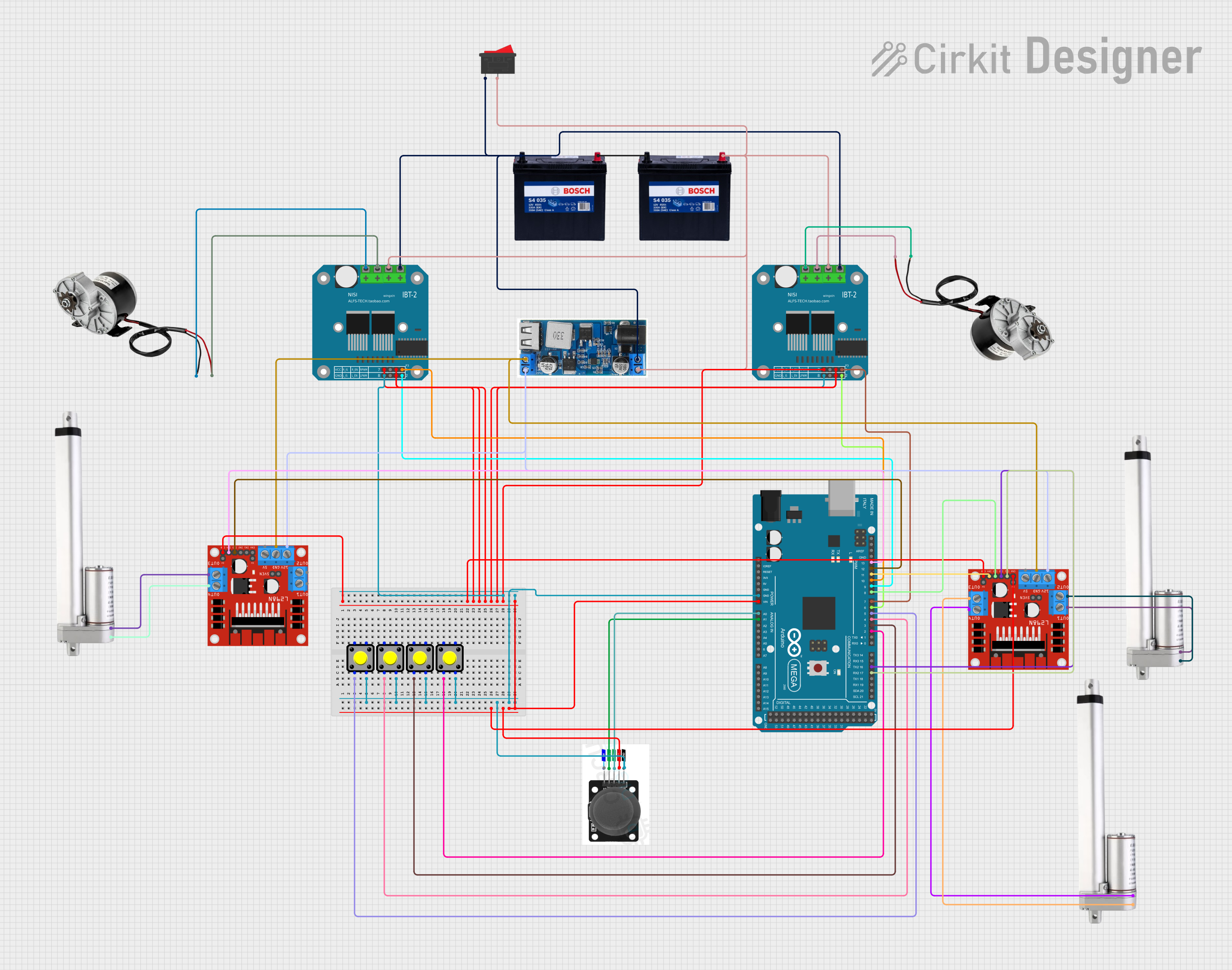
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer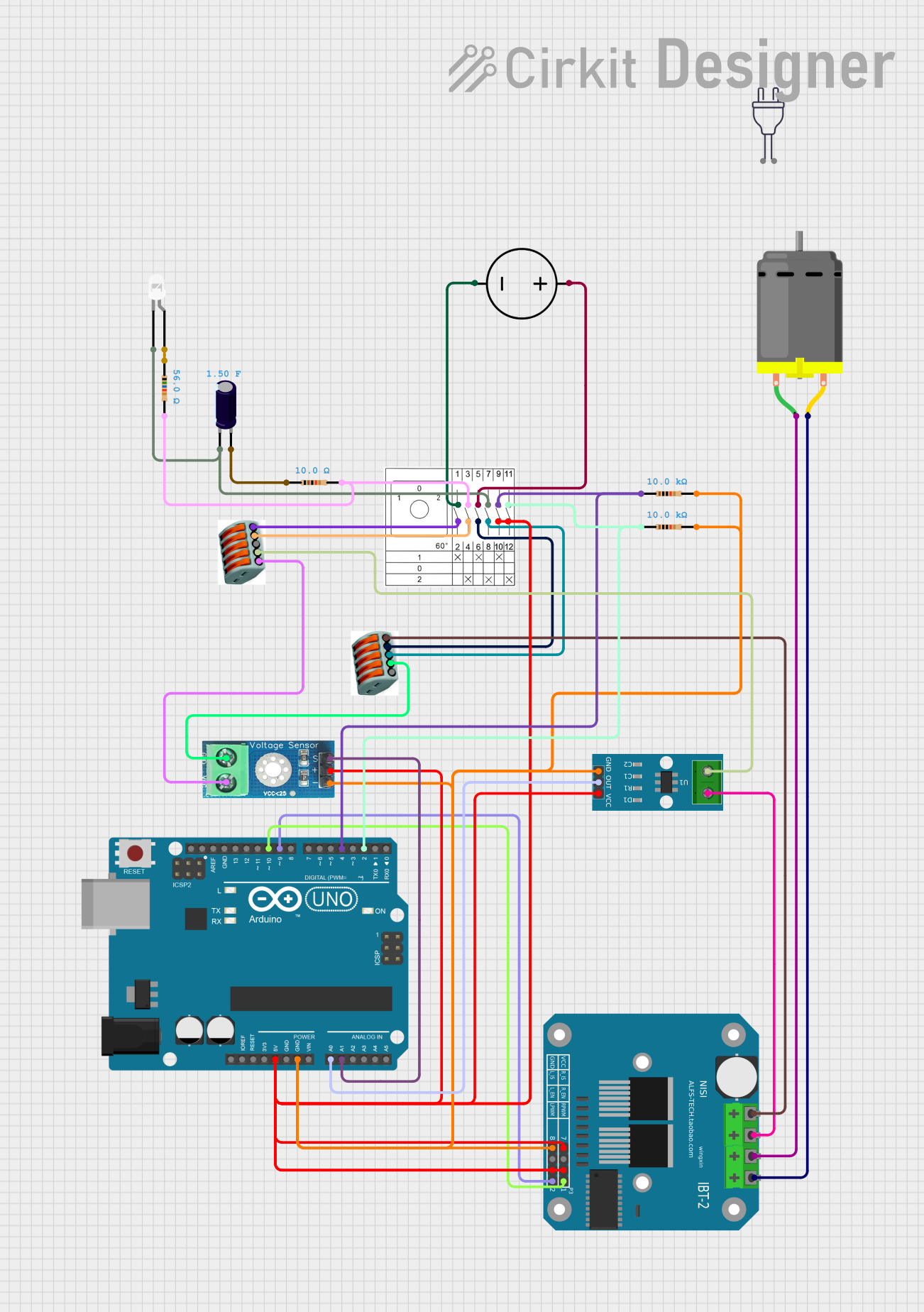
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer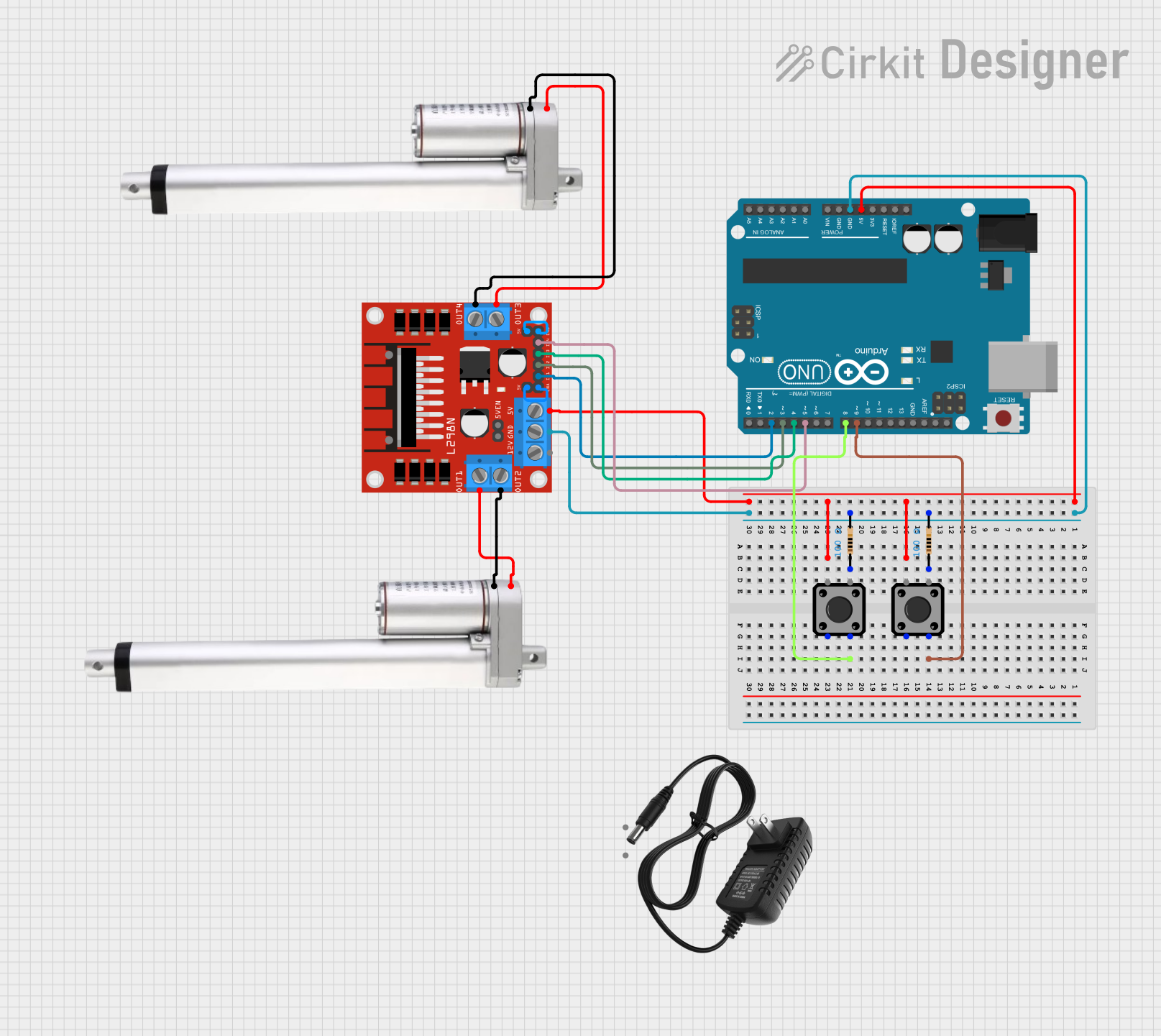
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer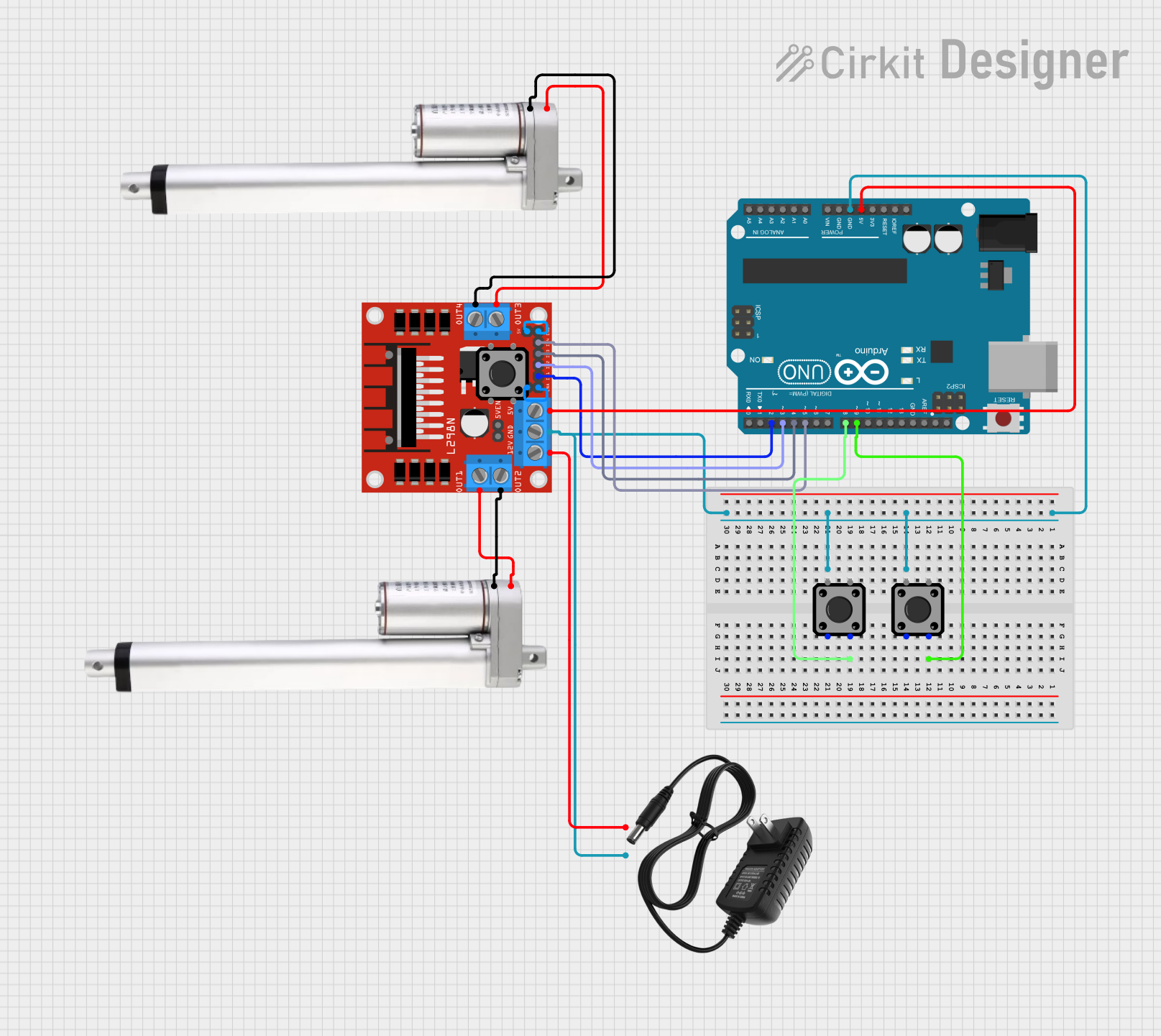
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Actuator Motor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Controlling robotic arms, grippers, and joints.
- Industrial Automation: Operating valves, conveyor belts, and assembly line equipment.
- Automotive Systems: Powering electric windows, seat adjustments, and throttle controls.
- Home Automation: Adjusting blinds, opening doors, and controlling HVAC systems.
- Medical Devices: Operating surgical tools and prosthetics.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard actuator motor. Note that specific models may vary, so always refer to the datasheet of your particular motor.
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 5V to 24V DC (varies by model)
- Current Rating: 0.5A to 5A (depending on load and motor type)
- Torque: 0.1 Nm to 10 Nm (varies by application)
- Speed: 10 RPM to 5000 RPM
- Control Signal: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) or analog input
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 60°C
- Lifespan: 10,000 to 100,000 cycles (depending on usage)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration for an actuator motor depends on the type of motor (e.g., DC motor, stepper motor, or servo motor). Below is a general example for a DC actuator motor with an integrated driver.
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (e.g., 5V, 12V, or 24V DC). |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 3 | PWM/Control | Input for controlling motor speed or position using a PWM signal. |
| 4 | Direction/IN1 | Input to control the direction of motor rotation (e.g., HIGH for forward). |
| 5 | Direction/IN2 | Input to control the direction of motor rotation (e.g., HIGH for reverse). |
| 6 | Feedback (optional) | Output for position or speed feedback (e.g., encoder signal). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a suitable DC power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Control Signal: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to generate a PWM signal for speed or position control.
- Direction Control: Use the IN1 and IN2 pins to set the motor's rotation direction. For example:
- Set IN1 HIGH and IN2 LOW for forward rotation.
- Set IN1 LOW and IN2 HIGH for reverse rotation.
- Feedback (if available): Connect the feedback pin to an analog or digital input on your microcontroller to monitor the motor's position or speed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Matching: Ensure the motor's operating voltage matches your power supply to avoid damage.
- Current Requirements: Use a motor driver or H-bridge circuit to handle the motor's current demands.
- Heat Management: Actuator motors can generate heat during operation. Use proper ventilation or heat sinks if necessary.
- Load Limits: Avoid exceeding the motor's torque or speed ratings to prevent mechanical or electrical failure.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Add capacitors near the motor's power pins to reduce electrical noise.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an actuator motor using an Arduino UNO and a PWM signal.
// Define motor control pins
const int pwmPin = 9; // PWM pin for speed control
const int in1Pin = 7; // Direction control pin 1
const int in2Pin = 8; // Direction control pin 2
void setup() {
// Set motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(pwmPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2Pin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor forward at 50% speed
digitalWrite(in1Pin, HIGH); // Set direction to forward
digitalWrite(in2Pin, LOW);
analogWrite(pwmPin, 128); // Set speed (128/255 = 50%)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Rotate motor backward at 75% speed
digitalWrite(in1Pin, LOW); // Set direction to reverse
digitalWrite(in2Pin, HIGH);
analogWrite(pwmPin, 192); // Set speed (192/255 = 75%)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
digitalWrite(in1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2Pin, LOW);
analogWrite(pwmPin, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Spinning
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the power supply meets the motor's voltage and current requirements.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction
- Cause: Direction control pins (IN1 and IN2) are incorrectly set.
- Solution: Swap the HIGH/LOW states of IN1 and IN2 to reverse the direction.
Motor Overheats
- Cause: Excessive load or prolonged operation at high speed.
- Solution: Reduce the load, lower the speed, or add a heat sink.
Noisy Operation
- Cause: Electrical noise or mechanical issues.
- Solution: Add decoupling capacitors to the power lines and check for mechanical obstructions.
Feedback Signal Not Working
- Cause: Incorrect connection or incompatible microcontroller input.
- Solution: Verify the feedback pin connection and ensure the microcontroller can read the signal type (analog or digital).
FAQs
Can I use an actuator motor with an AC power supply? No, actuator motors are typically designed for DC power. Using an AC supply may damage the motor.
What is the difference between a DC motor and an actuator motor? An actuator motor is a type of DC motor specifically designed for precise control of motion in automation systems.
Do I need a motor driver to use an actuator motor? Yes, a motor driver or H-bridge circuit is recommended to safely control the motor's speed and direction.
Can I control multiple actuator motors with one Arduino? Yes, but ensure the Arduino has enough PWM pins and that the power supply can handle the total current draw.
How do I calculate the required torque for my application? Use the formula: Torque = Force × Distance. Consider the load, friction, and any additional forces acting on the motor.