
How to Use Gearmotor DC / Motorreductor : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Gearmotor DC / Motorreductor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Gearmotor DC / Motorreductor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Gearmotor DC, or Motorreductor, is an integrated device that combines a direct current (DC) electric motor with a gearbox to enhance torque while reducing speed. This combination allows for precise control of large loads at low speeds, making gearmotors ideal for a wide range of applications such as robotics, industrial machinery, automotive systems, and consumer electronics.
Explore Projects Built with Gearmotor DC / Motorreductor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer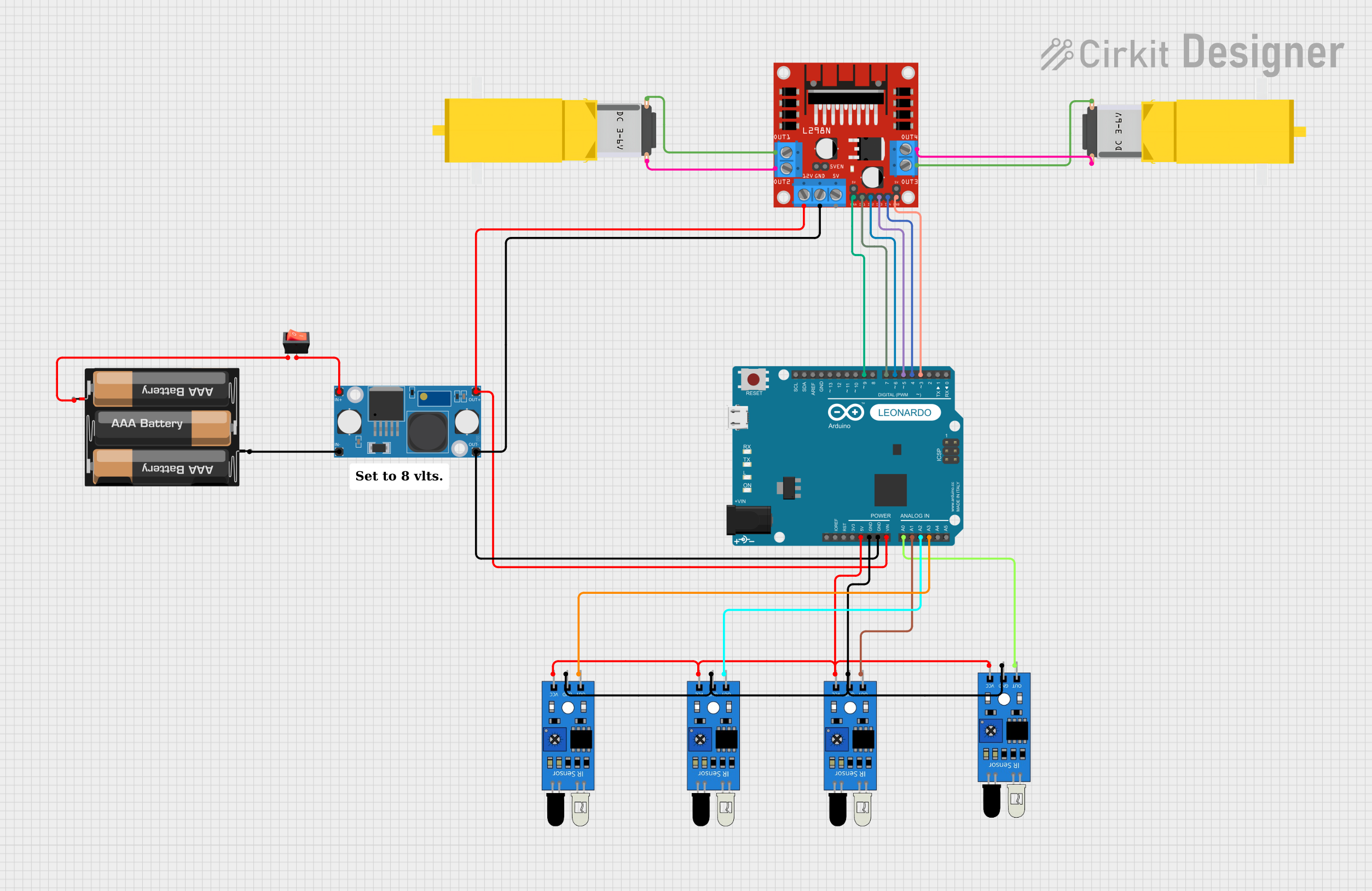
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer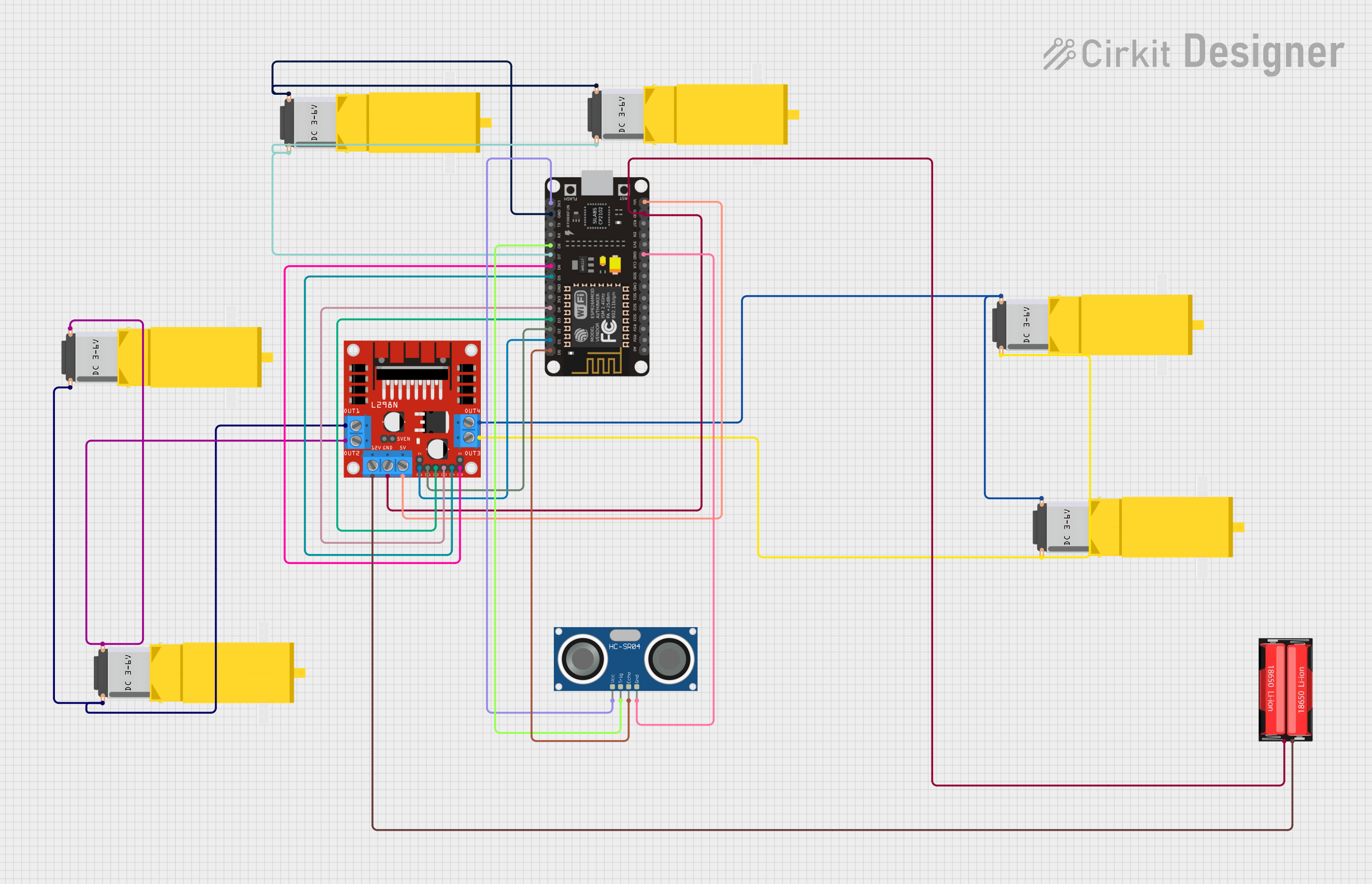
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer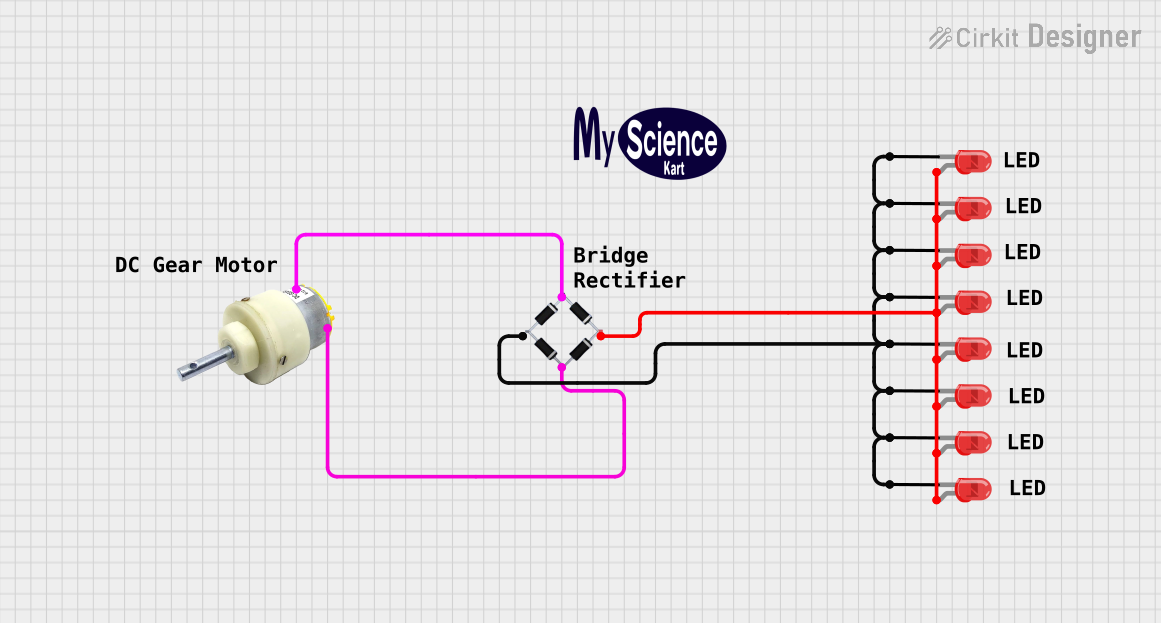
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Gearmotor DC / Motorreductor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Precise movement and positioning
- Automated machinery: Controlled operations requiring high torque
- Automotive: Electric window systems, seat adjustment
- Consumer electronics: Camera systems, smart home devices
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Range: Typically 3V to 24V DC
- Current Rating: Varies with model and load
- Power Output: Depends on gear ratio and motor efficiency
- Torque: Enhanced due to gear reduction
- Speed (RPM): Reduced proportionally to gear ratio
- Gear Ratio: Varies, common ratios include 10:1, 50:1, 100:1, etc.
- Efficiency: Dependent on gear type and quality
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Motor Positive (+) | Connect to positive voltage |
| 2 | Motor Negative (-) | Connect to ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply matches the voltage requirements of the gearmotor. Overvoltage can damage the motor, while undervoltage may result in insufficient performance.
- Motor Controller: Use a motor controller or H-bridge to control the direction and speed of the gearmotor.
- Load Considerations: Do not exceed the rated torque of the gearmotor as it can lead to gear failure or motor burnout.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Mounting: Securely mount the gearmotor to prevent misalignment of gears and potential damage.
- Lubrication: Ensure gears are properly lubricated to reduce wear and noise.
- Heat Dissipation: Provide adequate cooling if the motor is expected to operate continuously or under high load.
- Electrical Noise: Use appropriate filtering to minimize electrical noise, which can interfere with other electronics.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Motor not turning: Check power supply and connections. Ensure the motor controller is functioning correctly.
- Excessive noise or vibration: Inspect gears for wear or misalignment. Check if the motor is securely mounted.
- Overheating: Ensure the motor is not overloaded and has proper ventilation.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Intermittent Operation: Verify connections for any loose wires or poor solder joints.
- Reduced Torque: Check if the gearbox is clogged or requires lubrication.
- Direction Control Issues: Confirm that the motor controller or H-bridge is correctly programmed and wired.
Example Arduino UNO Code
// Example code to control a Gearmotor DC with an Arduino UNO
#include <Arduino.h>
const int motorPin1 = 3; // H-bridge leg 1 (pin 2, 1A)
const int motorPin2 = 4; // H-bridge leg 2 (pin 7, 2A)
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorPin2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, HIGH);
delay(1000);
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(motorPin1, LOW);
digitalWrite(motorPin2, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
Note: This example assumes the use of an H-bridge for direction control. The motorPin1 and motorPin2 are connected to the H-bridge inputs, and the gearmotor is connected to the H-bridge outputs. Adjust the pin numbers and logic according to your specific H-bridge module and wiring. Always ensure that the power supply voltage and current are within the specifications of the gearmotor.