
How to Use 6A AC BREAKER: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 6A AC BREAKER in Cirkit Designer
Design with 6A AC BREAKER in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 6A AC Breaker (Manufacturer: AC, Part ID: BREAKER) is a protective device designed to safeguard electrical circuits by automatically interrupting the flow of current when it detects an overload or short circuit. This ensures the safety of connected devices and prevents potential damage to the circuit.
Explore Projects Built with 6A AC BREAKER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer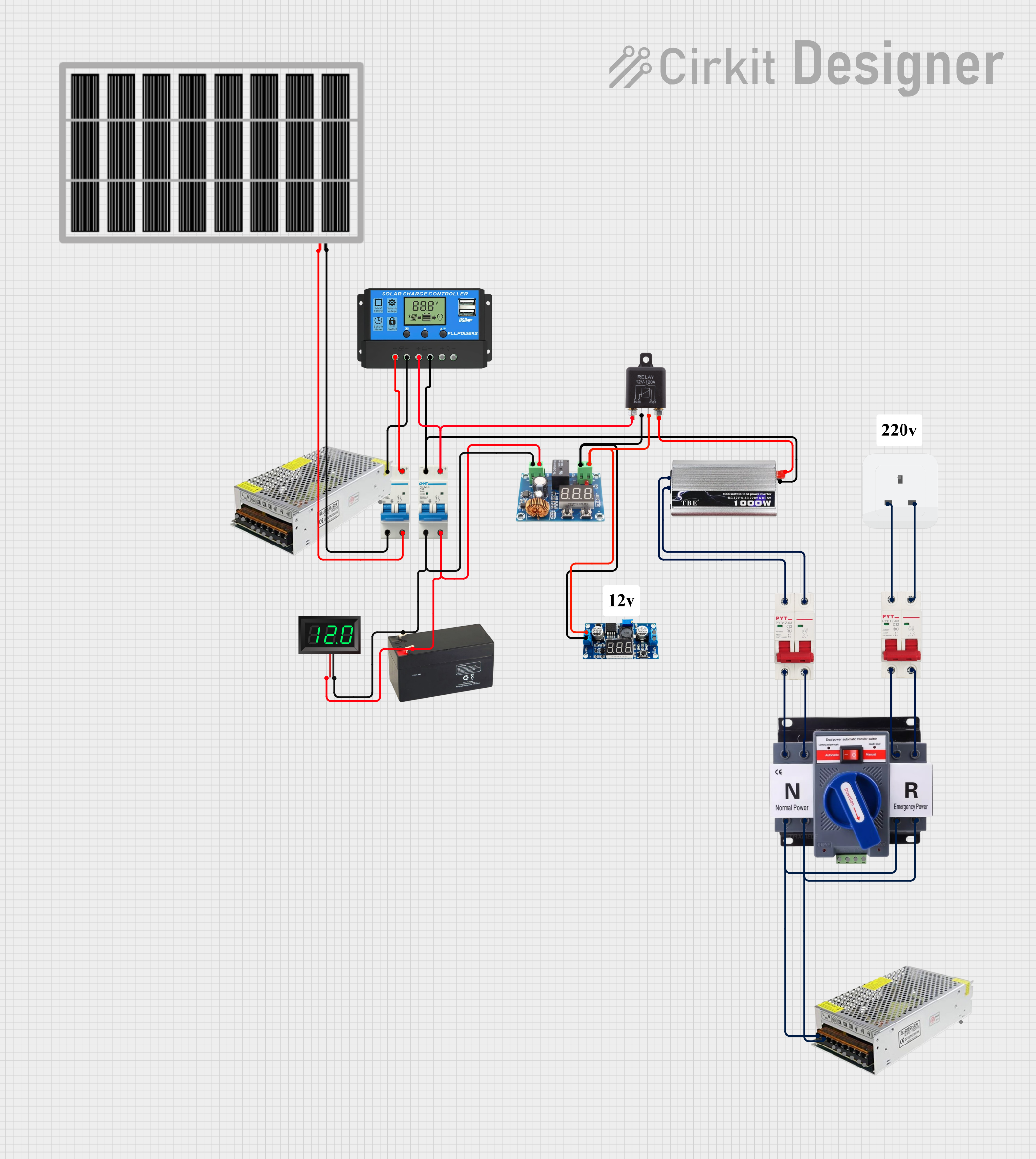
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer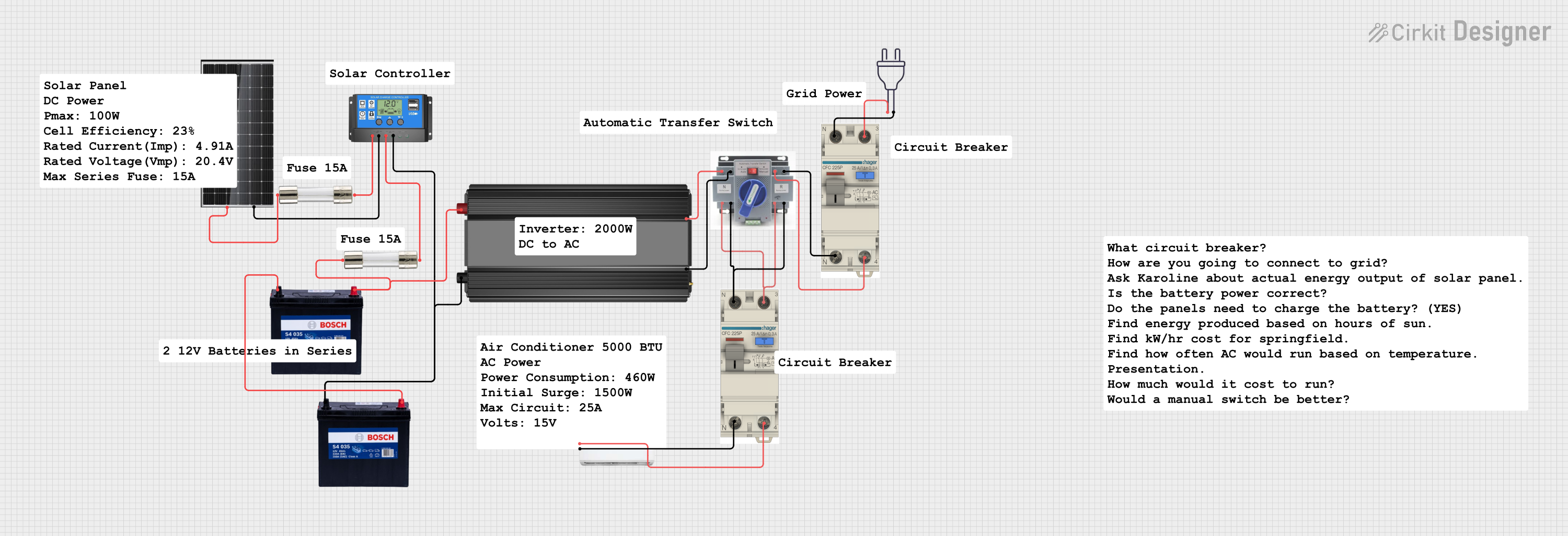
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer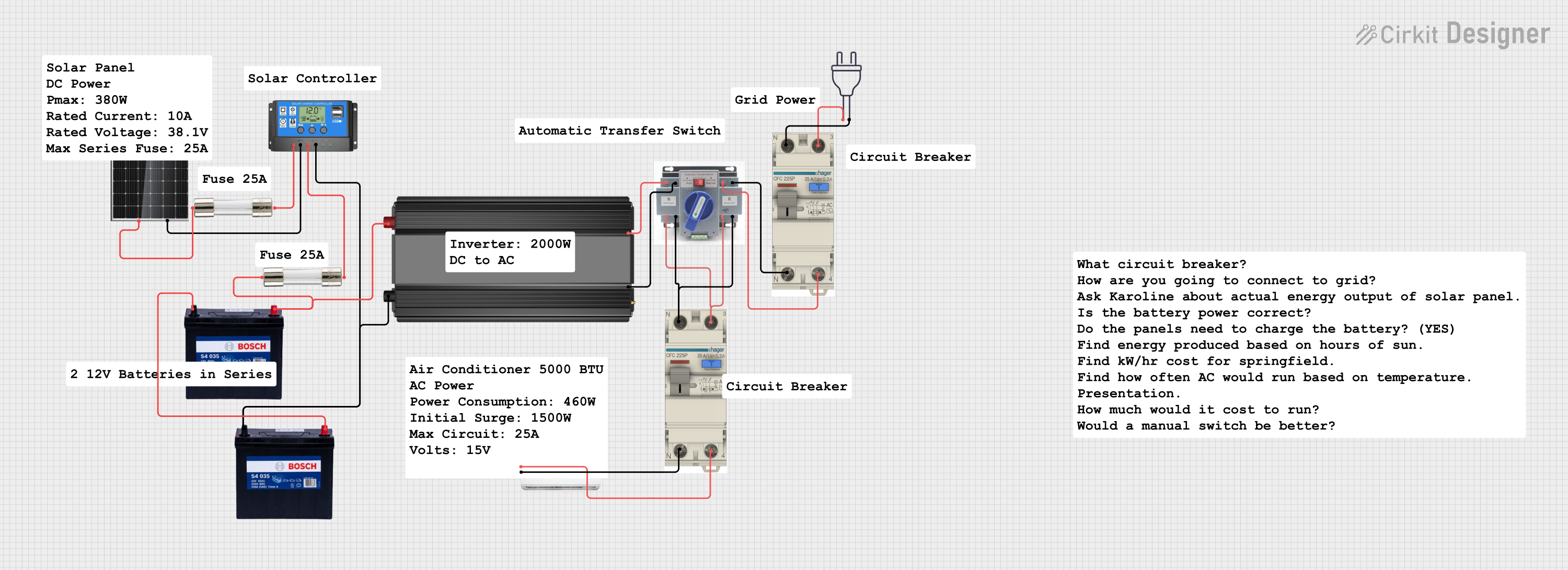
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 6A AC BREAKER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial electrical systems for circuit protection.
- Industrial equipment to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions.
- Electrical panels and distribution boards.
- Protection of sensitive devices such as motors, transformers, and appliances.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 6A AC Breaker:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Current | 6A |
| Rated Voltage | 230V AC (single-phase) |
| Breaking Capacity | 6 kA |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Trip Mechanism | Thermal-Magnetic |
| Operating Temperature | -5°C to 40°C |
| Mounting Type | DIN Rail |
| Dimensions | 18mm width (standard module) |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 60898-1 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 6A AC Breaker does not have traditional pins but instead features terminal connections for input and output. The table below describes these terminals:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Line (Input) | Connects to the incoming live wire from the power source. |
| Load (Output) | Connects to the live wire of the circuit to be protected. |
| Neutral | Optional terminal for neutral wire connection (if applicable). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 6A AC Breaker in a Circuit
Mounting the Breaker:
- Install the breaker on a standard DIN rail in the distribution panel.
- Ensure the breaker is securely locked into place.
Wiring:
- Connect the Line (Input) terminal to the live wire from the power source.
- Connect the Load (Output) terminal to the live wire of the circuit to be protected.
- If the breaker includes a neutral terminal, connect the neutral wire accordingly.
Testing:
- After installation, switch the breaker to the "ON" position.
- Test the breaker by simulating an overload or short circuit to ensure proper functionality.
Operation:
- In normal conditions, the breaker remains in the "ON" position, allowing current to flow.
- In case of an overload or short circuit, the breaker trips to the "OFF" position, interrupting the circuit.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the breaker is rated for the voltage and current of your application.
- Do not exceed the 6A current rating to avoid nuisance tripping.
- Regularly inspect the breaker for signs of wear or damage.
- Use appropriate wire sizes for the connected circuit to prevent overheating.
- Always turn off the main power supply before installing or servicing the breaker.
Arduino Integration
While the 6A AC Breaker is not directly connected to an Arduino, it can be used in conjunction with an Arduino-based monitoring system. For example, you can use a current sensor (e.g., ACS712) to monitor the current flowing through the breaker and trigger alerts if the current approaches the breaker's limit.
Here is an example Arduino code snippet for monitoring current:
#include <Wire.h>
// Define the analog pin connected to the current sensor
const int currentSensorPin = A0;
// Calibration factor for the ACS712 sensor (adjust as needed)
const float calibrationFactor = 0.185; // For 5A ACS712 module
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
Serial.println("6A AC Breaker Current Monitoring");
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(currentSensorPin); // Read sensor value
float voltage = (sensorValue / 1023.0) * 5.0; // Convert to voltage
float current = voltage / calibrationFactor; // Calculate current in Amps
// Print the current value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
// Add a delay for readability
delay(1000);
}
Note: This code is for monitoring purposes only and does not directly control the breaker.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Breaker trips frequently without load. | Check for wiring faults or short circuits in the connected circuit. |
| Breaker does not trip during an overload. | Verify the breaker's current rating and ensure it matches the circuit's load. |
| Breaker is difficult to switch on. | Inspect for mechanical damage or debris in the breaker mechanism. |
| Overheating of terminals. | Ensure proper tightening of terminal screws and use appropriate wire sizes. |
FAQs
Can I use the 6A AC Breaker for DC circuits?
- No, this breaker is designed for AC circuits only. Using it in a DC circuit may result in improper operation or damage.
What happens if the breaker trips?
- The breaker will move to the "OFF" position, interrupting the circuit. You can reset it by switching it back to the "ON" position after resolving the issue.
How do I know if the breaker is faulty?
- If the breaker does not trip during an overload or short circuit, or if it trips under normal conditions, it may be faulty and should be replaced.
Can I use this breaker for motor protection?
- Yes, but ensure the motor's starting current does not exceed the breaker's rated current.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the 6A AC Breaker to protect your electrical circuits and devices.