
How to Use TMC2209: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TMC2209 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TMC2209 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TMC2209, manufactured by BIGTREETECH, is a highly efficient and versatile stepper motor driver designed for applications requiring precise motor control. It is widely used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and other motion control systems. The TMC2209 is known for its silent operation, thanks to StealthChop2 technology, and advanced features such as stall detection (StallGuard4) and microstepping control. It supports up to 256 microsteps, ensuring smooth and accurate motor movement.
Explore Projects Built with TMC2209

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer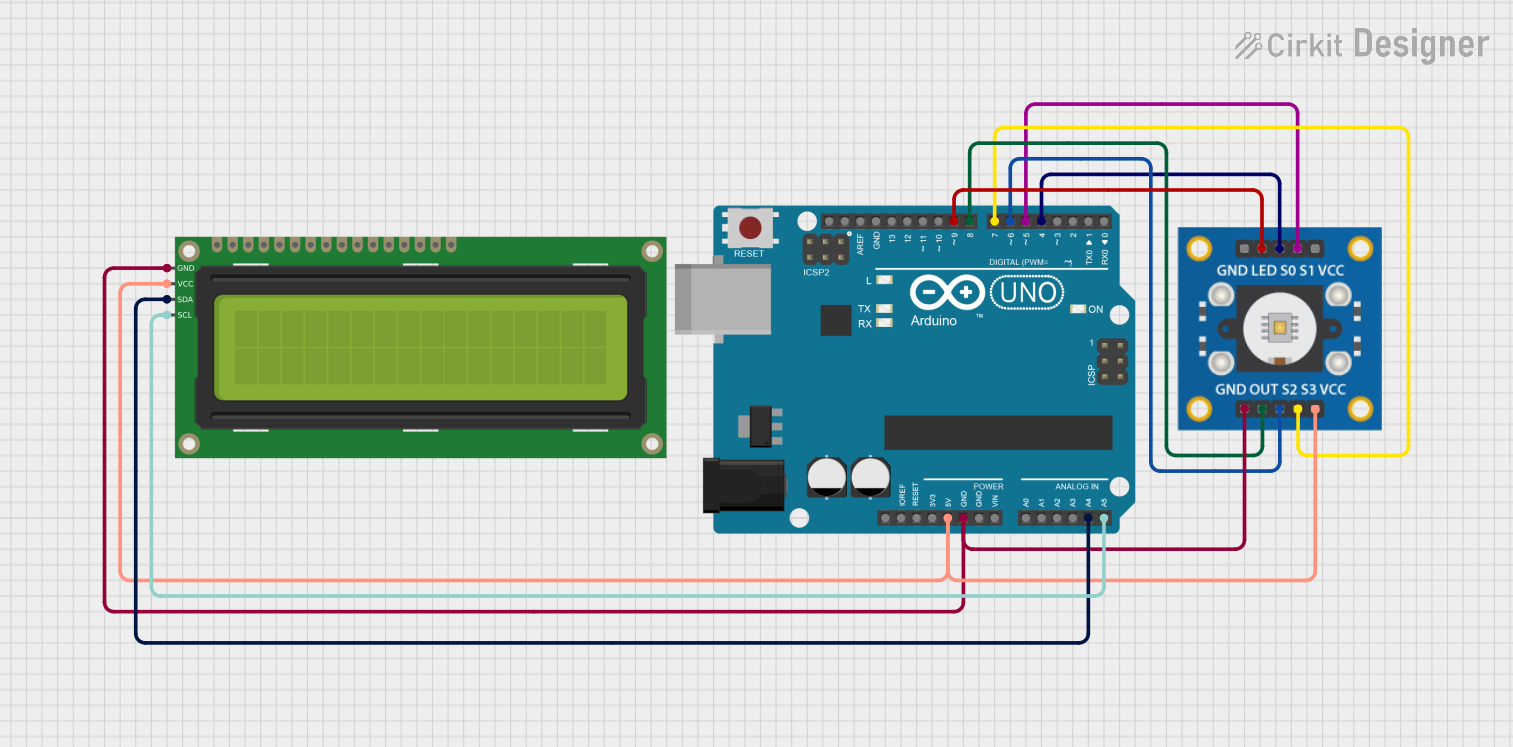
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer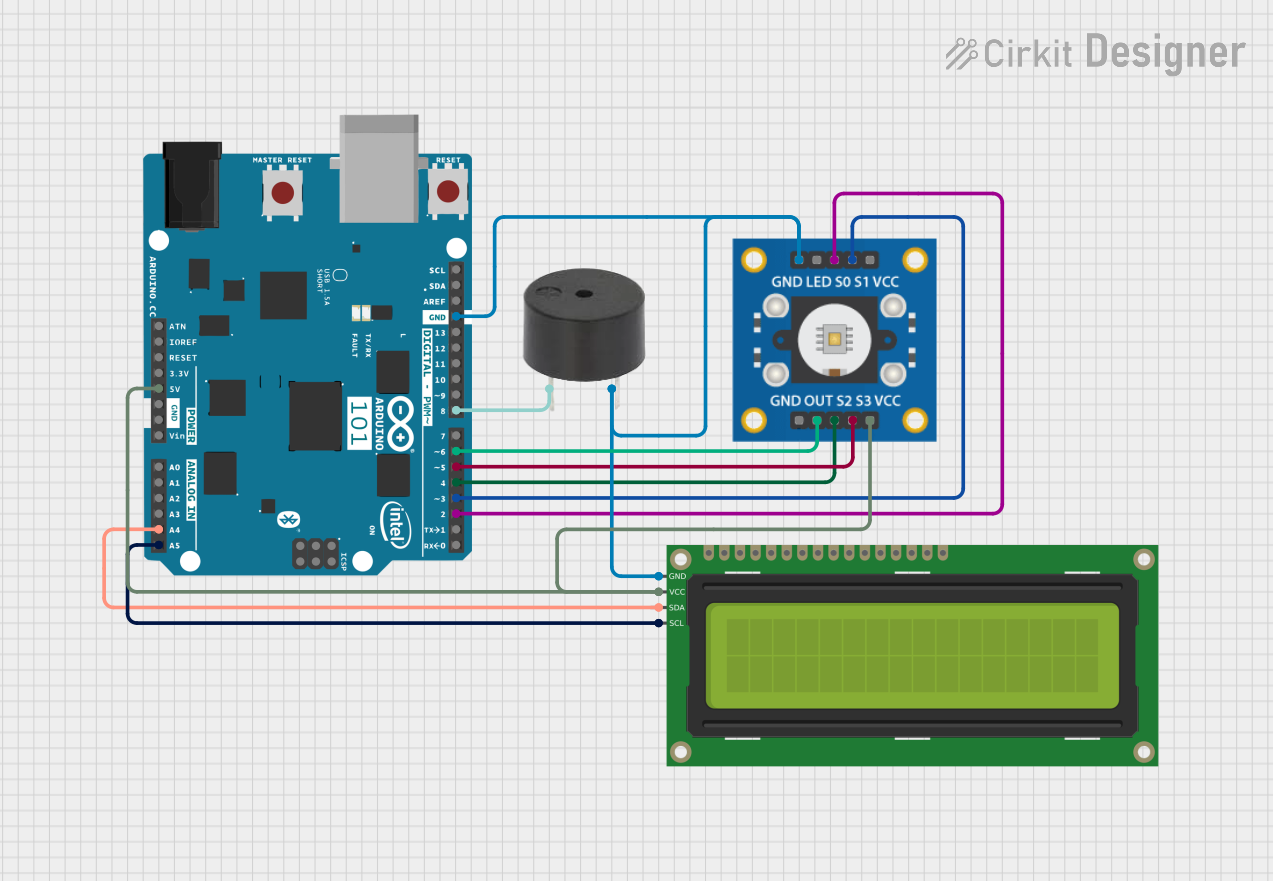
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer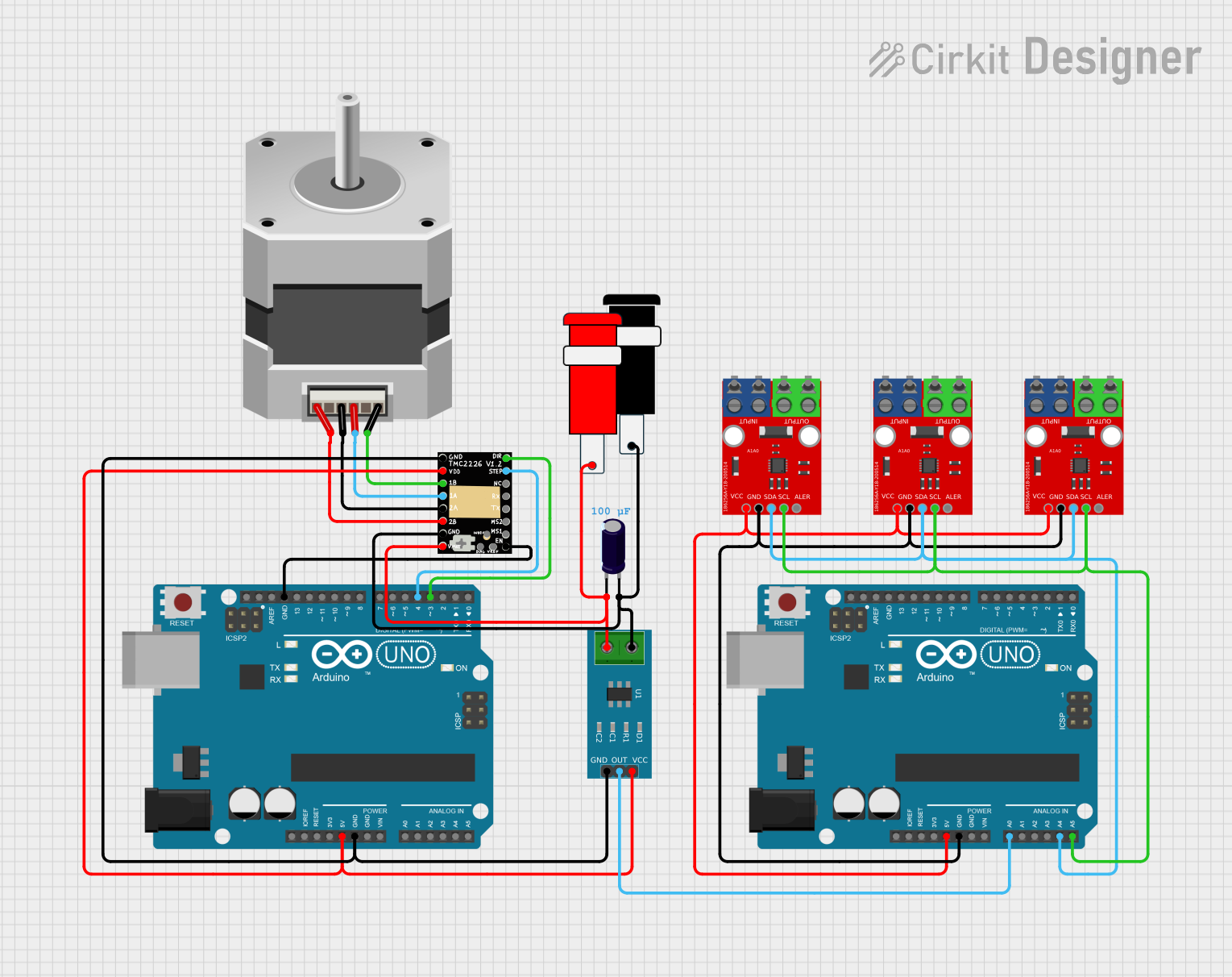
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TMC2209

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- 3D printers for precise and quiet motor control
- CNC machines for high-precision motion
- Robotics and automation systems
- Laser engravers and plotters
- Any application requiring silent and efficient stepper motor operation
Technical Specifications
The TMC2209 offers a range of features and specifications that make it suitable for demanding applications. Below are the key technical details:
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | 4.75V to 29V |
| Maximum Motor Current | 2.0A RMS (2.8A peak) |
| Microstepping Resolution | Up to 256 microsteps |
| Communication Interface | UART |
| Logic Voltage | 3.3V or 5V compatible |
| Features | StealthChop2, StallGuard4, |
| CoolStep, SpreadCycle | |
| Package Type | QFN28 |
Pin Configuration
The TMC2209 comes in a 28-pin QFN package. Below is the pin configuration and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | VM | Motor power supply (4.75V to 29V) |
| 3 | VCC_IO | Logic voltage input (3.3V or 5V) |
| 4 | ENN | Enable input (active low) |
| 5 | DIR | Direction control input |
| 6 | STEP | Step pulse input |
| 7 | UART | UART communication pin |
| 8 | MS1 | Microstep resolution selection |
| 9 | MS2 | Microstep resolution selection |
| 10 | DIAG | Diagnostic output |
| 11 | INDEX | Microstep index output |
| 12 | GND | Ground |
| 13-28 | Various | Motor coil connections and other functions |
Usage Instructions
The TMC2209 is designed to be easy to integrate into a variety of systems. Below are the steps and best practices for using the TMC2209 in a circuit.
Basic Circuit Connection
- Power Supply: Connect the motor power supply (VM) to a voltage source between 4.75V and 29V. Ensure the power supply can handle the current requirements of your stepper motor.
- Logic Voltage: Connect the VCC_IO pin to the logic voltage of your microcontroller (3.3V or 5V).
- Control Pins: Connect the STEP and DIR pins to the corresponding outputs of your microcontroller for step and direction control.
- UART Communication: If using UART, connect the UART pin to the microcontroller's UART TX pin. Ensure proper configuration of the UART baud rate.
- Microstepping: Use the MS1 and MS2 pins to set the desired microstepping resolution. Refer to the datasheet for the microstepping configuration table.
- Enable Pin: Connect the ENN pin to ground to enable the driver.
Important Considerations
- Cooling: The TMC2209 can generate heat during operation. Use a heatsink or active cooling if necessary to prevent overheating.
- Current Limiting: Set the motor current limit using the UART interface or external resistors to protect the motor and driver.
- StealthChop2: Enable StealthChop2 for silent operation, especially in noise-sensitive applications.
- Stall Detection: Use StallGuard4 for sensorless homing and stall detection.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the TMC2209 using an Arduino UNO:
// Example code to control a stepper motor with the TMC2209 driver
// Ensure the TMC2209 is properly connected to the Arduino UNO
#define STEP_PIN 3 // Pin connected to the STEP pin of TMC2209
#define DIR_PIN 4 // Pin connected to the DIR pin of TMC2209
#define EN_PIN 5 // Pin connected to the ENN pin of TMC2209
void setup() {
pinMode(STEP_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set STEP pin as output
pinMode(DIR_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set DIR pin as output
pinMode(EN_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set ENN pin as output
digitalWrite(EN_PIN, LOW); // Enable the driver (ENN is active low)
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, HIGH); // Set initial direction
}
void loop() {
// Generate step pulses to move the motor
digitalWrite(STEP_PIN, HIGH); // Step pulse high
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
digitalWrite(STEP_PIN, LOW); // Step pulse low
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
}
Notes:
- Adjust the
delayMicroseconds()value to control the motor speed. - Ensure the motor current limit is set appropriately to avoid overheating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Motor Not Moving
- Check the power supply connections and ensure the voltage is within the specified range.
- Verify the STEP and DIR signals from the microcontroller.
- Ensure the ENN pin is connected to ground to enable the driver.
Overheating
- Ensure proper cooling with a heatsink or fan.
- Check the motor current limit and reduce it if necessary.
Noisy Operation
- Enable StealthChop2 mode for silent operation.
- Verify the microstepping configuration.
Stall Detection Not Working
- Ensure StallGuard4 is enabled via UART.
- Check the motor load and adjust the sensitivity settings.
FAQs
Q: Can the TMC2209 be used with 12V or 24V power supplies?
A: Yes, the TMC2209 supports a wide voltage range of 4.75V to 29V, making it compatible with 12V and 24V systems.
Q: How do I set the motor current limit?
A: The motor current limit can be set via the UART interface or by adjusting external resistors. Refer to the datasheet for detailed instructions.
Q: Is the TMC2209 compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the TMC2209 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
Q: Can I use the TMC2209 for sensorless homing?
A: Yes, the TMC2209 supports sensorless homing using the StallGuard4 feature. Ensure proper configuration via UART.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate and operate the TMC2209 in their projects.