
How to Use greyboard: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with greyboard in Cirkit Designer
Design with greyboard in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A greyboard, manufactured by Greycode (Part ID: Greycode), is a type of cardboard commonly used in electronics for prototyping circuits. It provides a sturdy, non-conductive base for mounting components, making it ideal for DIY projects, educational purposes, and temporary circuit setups. Greyboards are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to cut or shape, making them a popular choice for hobbyists and students.
Explore Projects Built with greyboard

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer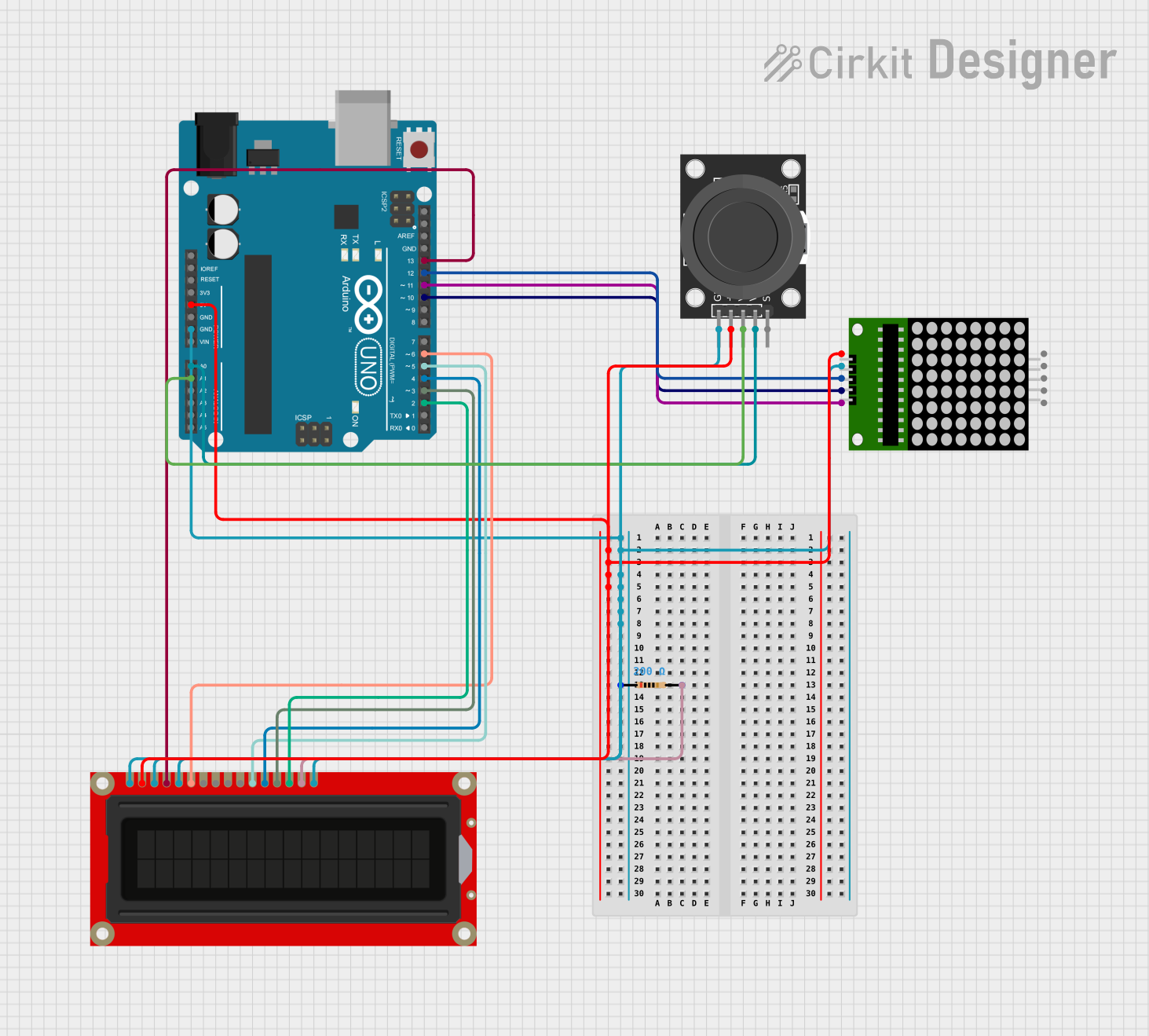
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer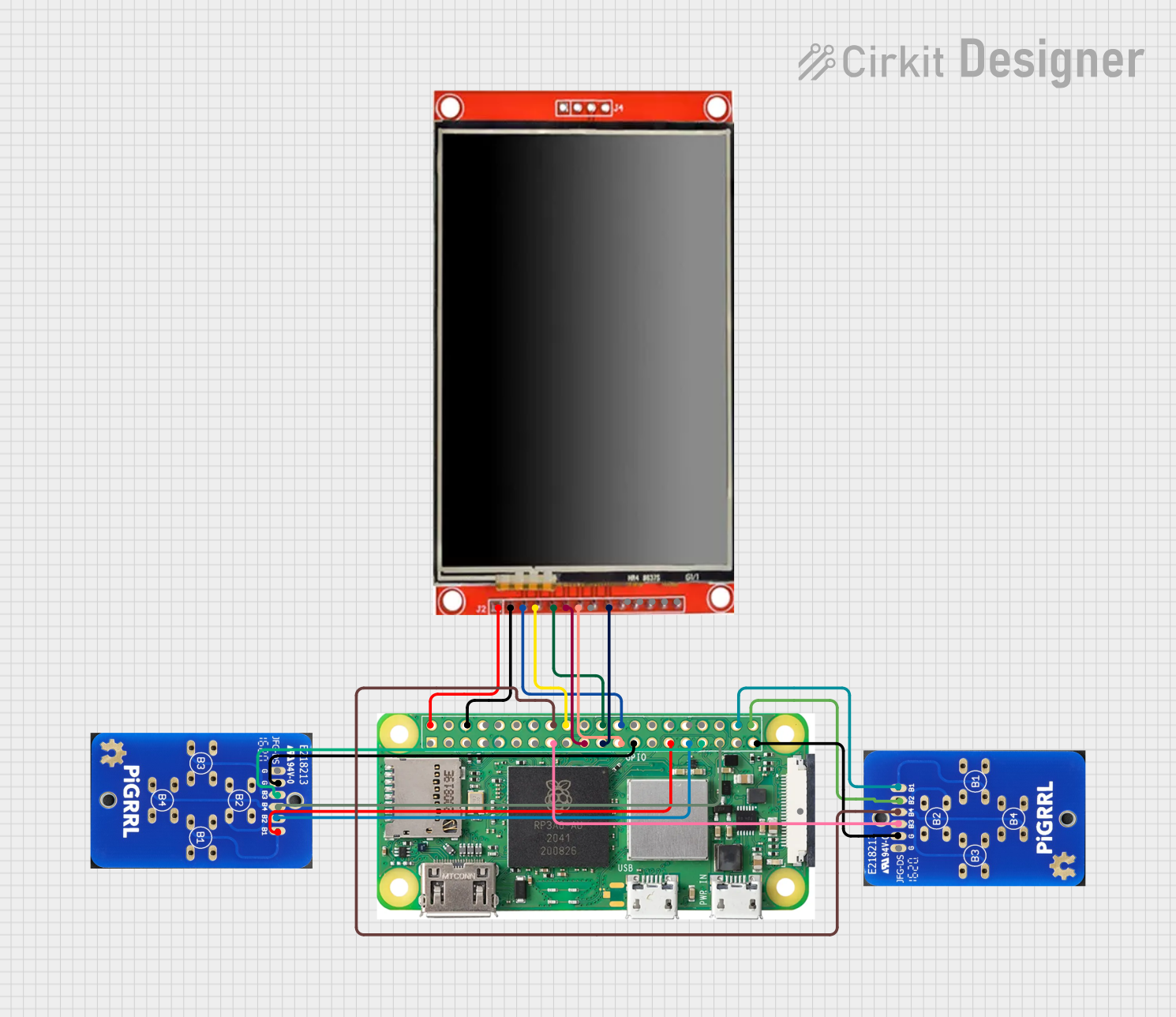
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer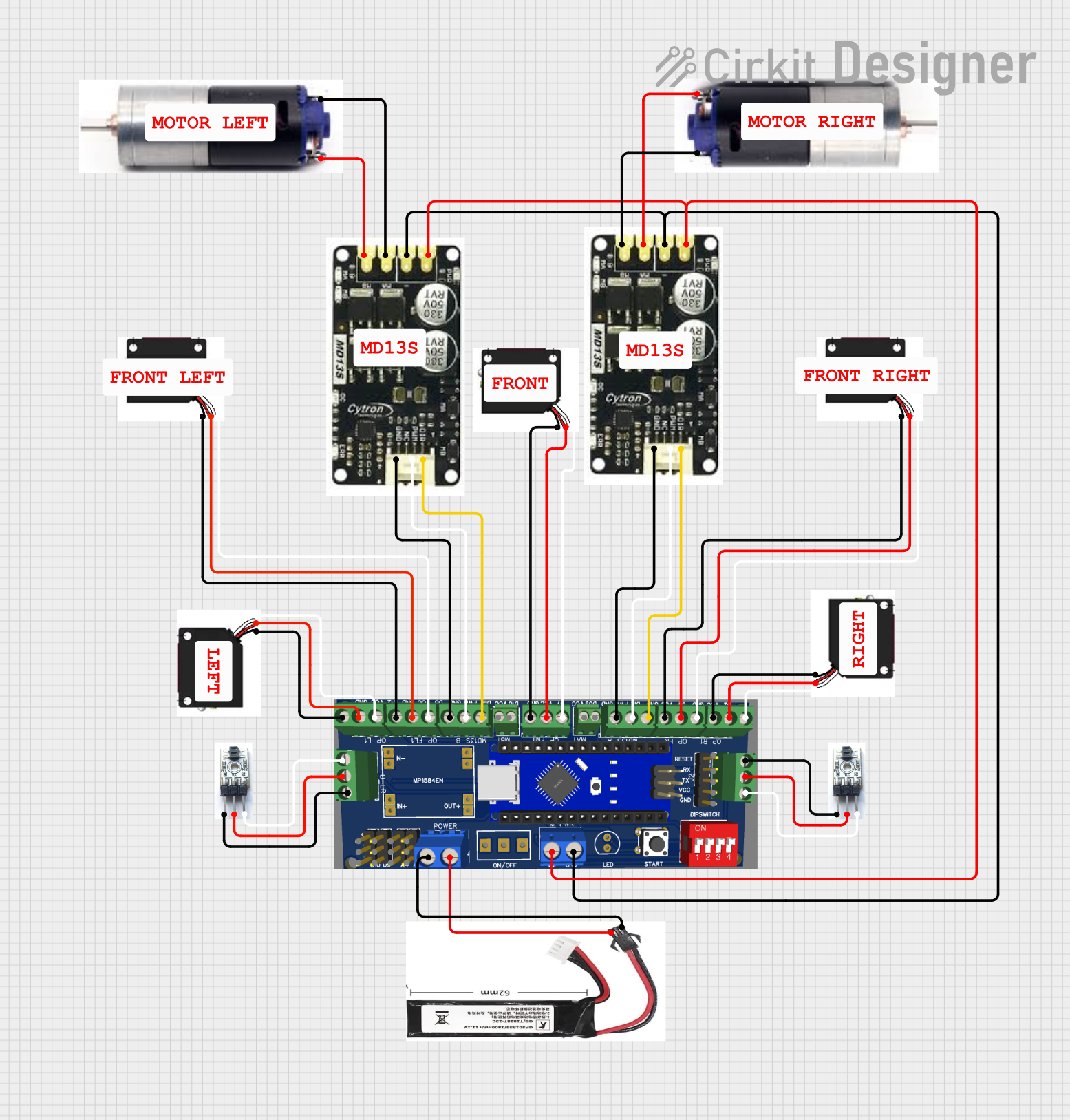
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with greyboard

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Prototyping simple electronic circuits
- Educational demonstrations and workshops
- DIY electronics projects
- Temporary mounting of components for testing
- Creating custom enclosures or supports for small devices
Technical Specifications
While greyboards are not electronic components themselves, their physical properties are important for their use in electronics. Below are the key specifications:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material | Compressed cardboard (non-conductive) |
| Thickness | 1.5 mm to 3 mm (varies by model) |
| Dimensions | Typically 300 mm x 300 mm (customizable) |
| Weight | ~0.5 kg/m² |
| Surface Finish | Matte |
| Temperature Tolerance | Up to 80°C (short-term exposure) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Non-conductive |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
As a non-electronic component, the greyboard does not have pins or electrical connections. However, it serves as a physical base for mounting components such as resistors, capacitors, and ICs.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Greyboard in a Circuit
- Prepare the Greyboard: Cut the greyboard to the desired size using a utility knife or scissors. Ensure the edges are smooth to avoid damage to components.
- Plan the Layout: Sketch the circuit layout on the greyboard using a pencil or marker. This helps in organizing components and wires.
- Mount Components:
- Use adhesive (e.g., double-sided tape or glue) to secure components to the greyboard.
- Alternatively, use small screws or zip ties for heavier components.
- Connect the Circuit: Use jumper wires, breadboards, or soldered connections to complete the circuit. Ensure wires are properly insulated to prevent short circuits.
- Test the Circuit: Once the components are mounted and connected, test the circuit functionality. Make adjustments as needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overheating: Do not solder directly onto the greyboard, as it is not heat-resistant and may deform or catch fire.
- Use Insulation: Ensure all exposed wires are insulated to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Secure Components: Use appropriate adhesives or fasteners to prevent components from shifting during use.
- Environmental Conditions: Keep the greyboard away from moisture, as it can weaken the material and compromise its structural integrity.
Example: Using Greyboard with an Arduino UNO
Greyboards are often used as a base for Arduino projects. Below is an example of how to mount an Arduino UNO and connect an LED circuit:
- Mount the Arduino UNO on the greyboard using screws or adhesive.
- Connect an LED to pin 13 of the Arduino using a 220-ohm resistor.
- Use jumper wires to complete the circuit.
Sample Arduino Code
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
// Ensure the LED's longer leg (anode) is connected to pin 13, and the shorter
// leg (cathode) is connected to GND through a 220-ohm resistor.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Components Falling Off:
- Cause: Insufficient adhesive or improper mounting.
- Solution: Use stronger adhesive or mechanical fasteners like screws or zip ties.
Circuit Malfunction:
- Cause: Loose connections or short circuits.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure wires are properly insulated.
Greyboard Warping:
- Cause: Exposure to moisture or excessive heat.
- Solution: Store the greyboard in a dry, cool environment and avoid soldering directly on it.
Difficulty Cutting the Greyboard:
- Cause: Using dull tools or improper technique.
- Solution: Use a sharp utility knife and a straight edge for clean cuts.
FAQs
Q: Can I reuse a greyboard for multiple projects?
A: Yes, as long as the greyboard is not damaged or warped, it can be reused. Remove old components carefully to avoid tearing the surface.
Q: Is the greyboard safe for high-voltage circuits?
A: Greyboards are non-conductive but not designed for high-voltage applications. Use caution and ensure proper insulation.
Q: Can I paint or decorate the greyboard?
A: Yes, you can paint or decorate the greyboard to enhance its appearance. Use non-conductive paints to avoid affecting the circuit.
Q: How do I clean a greyboard?
A: Use a dry cloth or a soft brush to remove dust. Avoid using water or cleaning solutions, as they can damage the material.