
How to Use DC Generator: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DC Generator in Cirkit Designer
Design with DC Generator in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A DC Generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into direct current (DC) electrical energy based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. These generators are widely used in various applications such as charging batteries, providing power for electronic systems in off-grid locations, and as a power source for motors, lights, and other electrical devices in vehicles and industrial settings.
Explore Projects Built with DC Generator

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer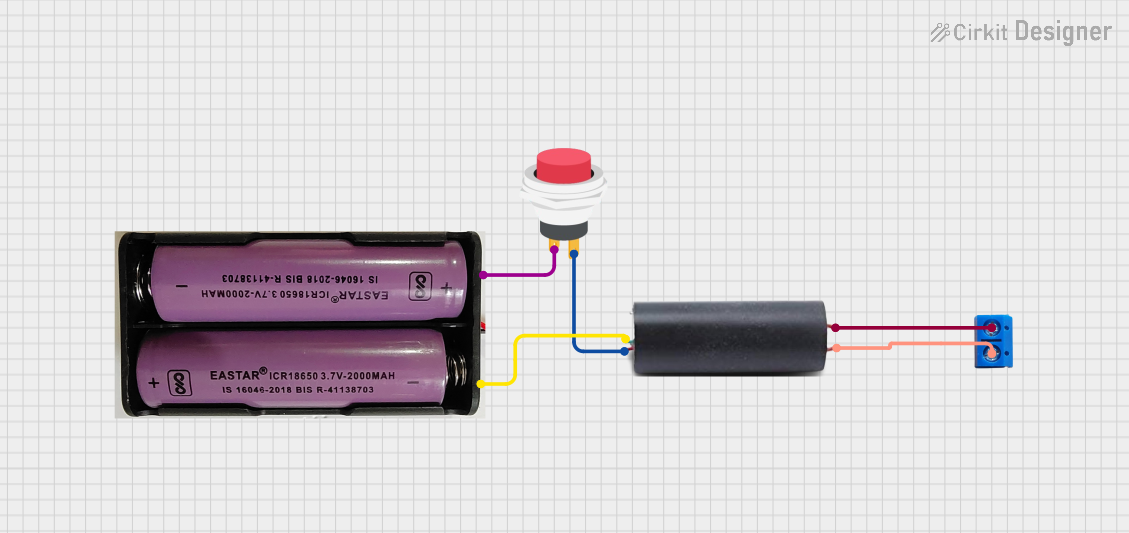
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DC Generator

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Battery charging systems
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., wind turbines, hand-crank generators)
- Automotive alternators
- Backup power supplies
- Power generation in remote locations
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Output: Typically ranges from a few volts to several hundred volts
- Current Output: Depends on the load and design, can range from milliamps to several hundred amps
- Power Ratings: Varies widely, from a few watts to megawatts
- Speed (RPM): The rotational speed at which the generator operates efficiently
- Efficiency: Percentage of mechanical power converted to electrical power
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Output | Connects to the positive load |
| 2 | Negative Output | Connects to the negative load |
| 3 | Field Winding (+) | Excitation positive |
| 4 | Field Winding (-) | Excitation negative |
| 5 | Tachometer Output | Optional, for speed measurement |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Load: Attach the positive and negative outputs of the DC Generator to the respective terminals of the load.
- Excitation: Provide the field windings with the necessary excitation current. This can be done using a battery or another DC source.
- Start the Generator: Initiate the mechanical motion to start generating electricity. The mechanical input can be from an engine, turbine, or manual effort.
- Regulation: Use a voltage regulator to maintain a steady output voltage, especially if the load varies.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Load Matching: Ensure that the generator's output matches the requirements of the load.
- Cooling: Provide adequate cooling for the generator to prevent overheating.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect brushes and bearings for wear and tear.
- Safety: Always follow electrical safety protocols when working with generators.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Low Output Voltage: This could be due to low speed, poor excitation, or high resistance in the windings.
- Overheating: Caused by excessive load, inadequate cooling, or mechanical friction.
- Unusual Noises: Often a sign of mechanical issues such as worn bearings or misalignment.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check the Speed: Ensure the generator is running at the correct RPM.
- Inspect the Excitation Circuit: Verify that the field windings are receiving the correct current.
- Load Reduction: If overheating, reduce the load and check for proper ventilation.
- Mechanical Inspection: Regularly inspect and maintain mechanical parts to prevent noise and wear.
FAQs
Q: Can a DC Generator charge a battery? A: Yes, a DC Generator can charge a battery. Ensure the voltage output is appropriate for the battery.
Q: What is the role of the field winding? A: The field winding creates a magnetic field necessary for the operation of the generator.
Q: How can I increase the output voltage of my DC Generator? A: Increase the speed of the mechanical input or improve the excitation current.
Q: Is it possible to use a DC Generator as a motor? A: Yes, many DC machines are reversible, but additional circuitry may be required for optimal operation as a motor.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Connection
// This example assumes the use of a DC Generator as an input to an Arduino UNO for monitoring purposes.
int generatorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the DC Generator output
int generatorValue = 0; // Variable to store the value read from the generator
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
generatorValue = analogRead(generatorPin); // Read the voltage from the generator
float voltage = generatorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert the reading to voltage
Serial.println(voltage); // Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for a second before reading again
}
Note: The above code is for demonstration purposes and assumes that the DC Generator's output voltage is within the range that the Arduino's analog input can handle (0-5V). If the generator's output exceeds this range, a voltage divider or level shifter is required to bring the voltage within a safe range for the Arduino.