
How to Use TDs sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
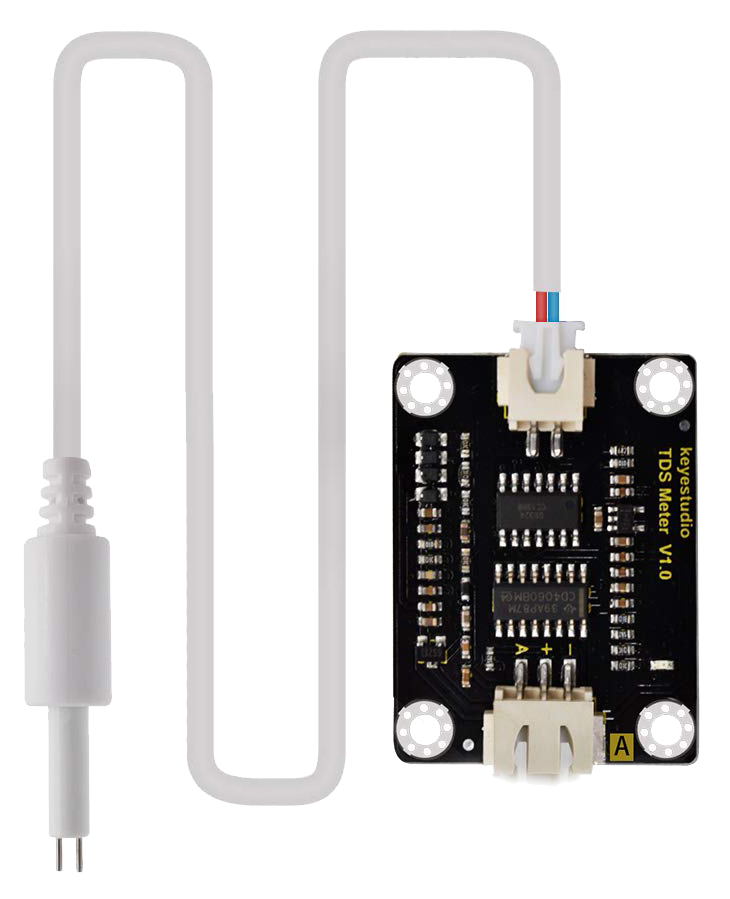
 Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with TDs sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) sensor measures the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid, typically expressed in parts per million (ppm). It is widely used in water quality monitoring, aquariums, hydroponics, and water treatment systems to ensure the liquid's purity and suitability for specific applications. By detecting the electrical conductivity of the liquid, the sensor estimates the total dissolved solids present.
Explore Projects Built with TDs sensor
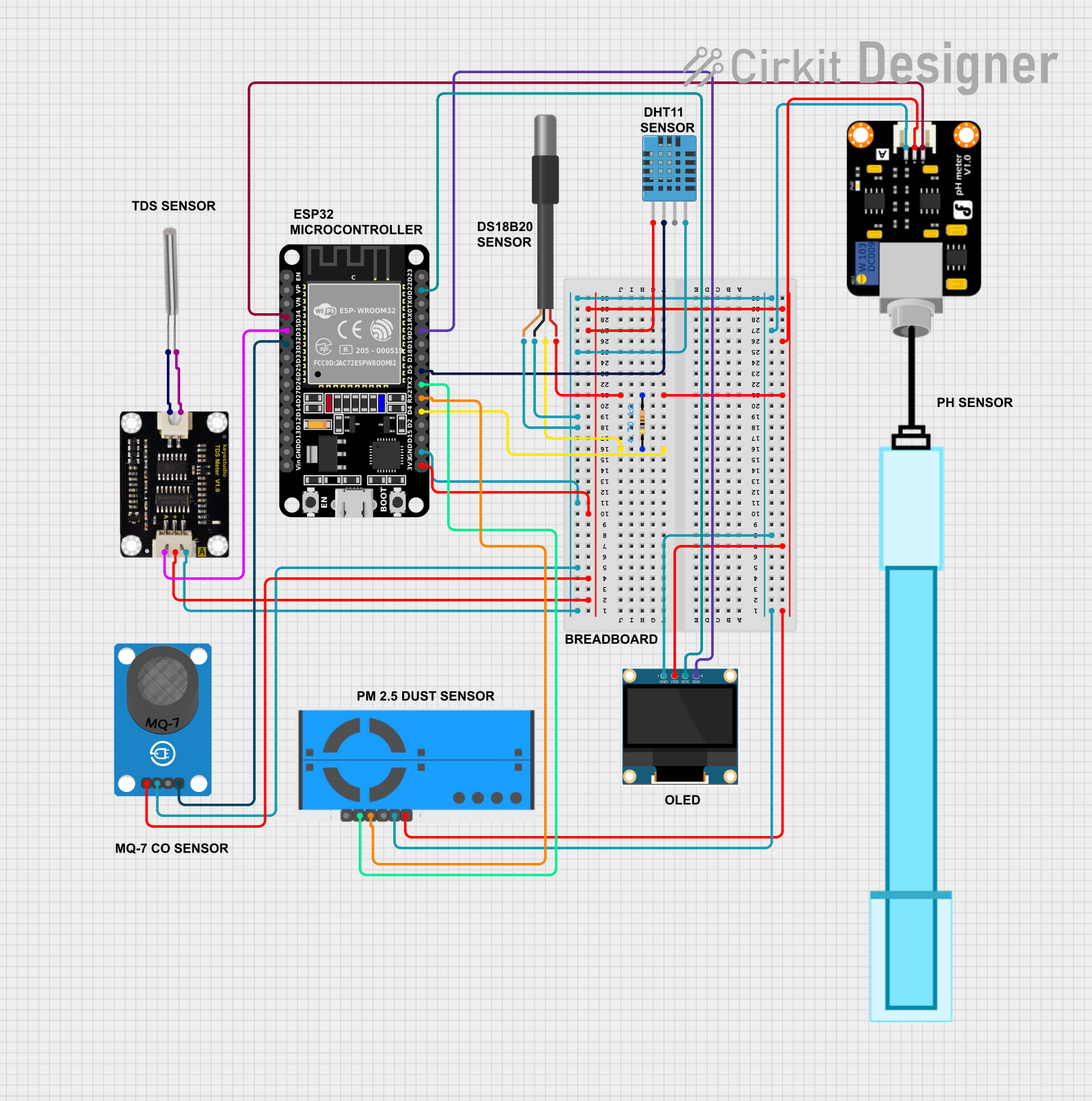
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer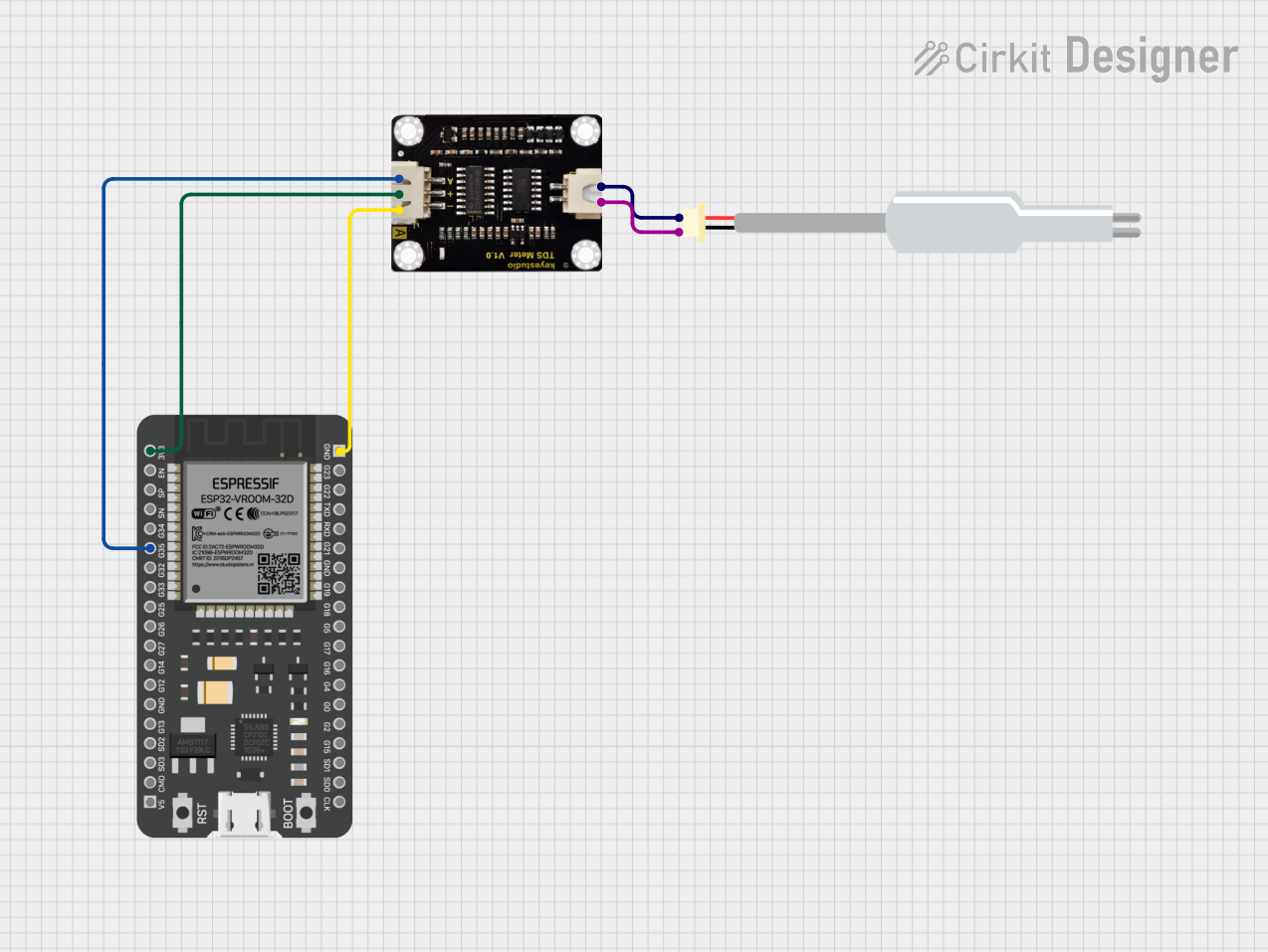
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer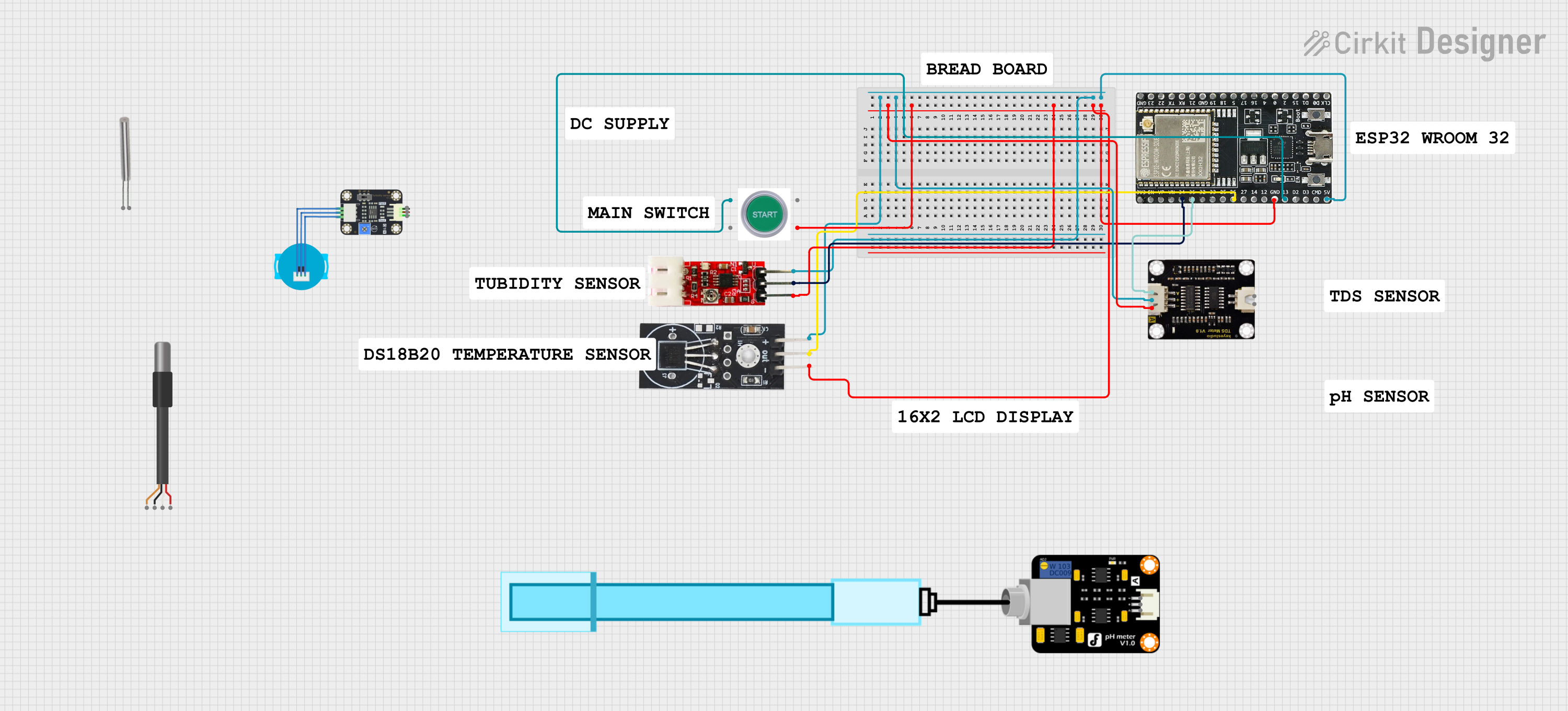
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer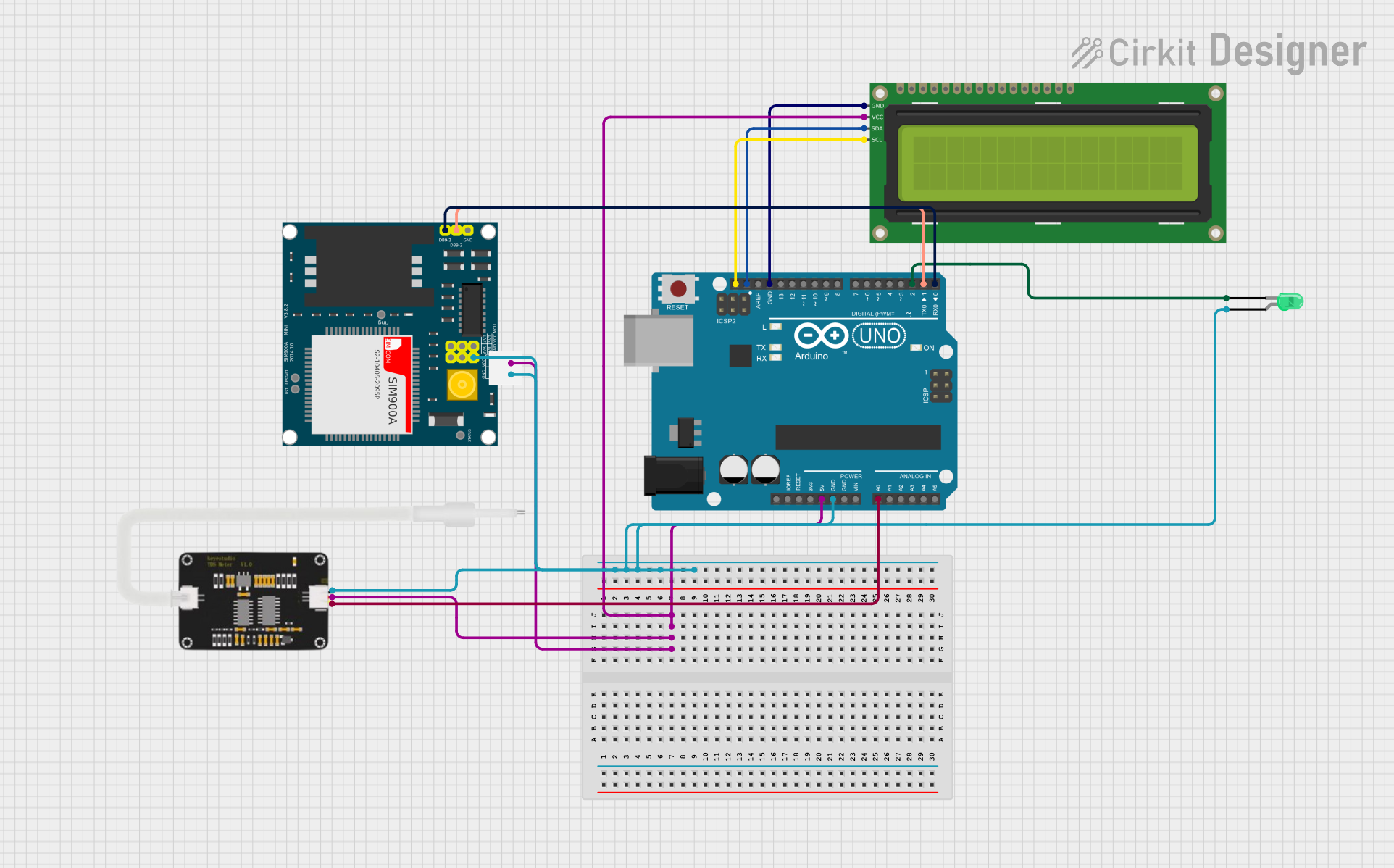
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TDs sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Monitoring water quality in drinking water systems
- Measuring nutrient levels in hydroponic systems
- Ensuring proper water conditions in aquariums
- Industrial water treatment and wastewater management
- Testing water purity in laboratories
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical TDS sensor module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V DC |
| Operating Current | 10mA (typical) |
| Measurement Range | 0 - 1000 ppm |
| Accuracy | ±10% (25°C calibration) |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0 - 2.3V) |
| Temperature Compensation | Supported (via external circuitry) |
| Probe Material | Stainless steel |
| Cable Length | ~1 meter |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C - 60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TDS sensor module typically has three pins for connection:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V - 5V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | AOUT | Analog output signal proportional to the TDS value |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TDS Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor Module:
- Connect the
VCCpin to the 5V or 3.3V power supply of your microcontroller. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the
AOUTpin to an analog input pin of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Connect the
Calibrate the Sensor:
- Use a standard solution with a known TDS value (e.g., 342 ppm calibration solution).
- Adjust the potentiometer on the module to match the expected output voltage for the known TDS value.
Place the Probe:
- Submerge the stainless steel probe into the liquid to be tested.
- Ensure the probe is fully immersed but avoid submerging the module itself.
Read the Output:
- Use the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of your microcontroller to read the voltage from the
AOUTpin. - Convert the voltage reading to a TDS value using the formula provided in the sensor's datasheet.
- Use the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of your microcontroller to read the voltage from the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Corrosion: Clean the probe regularly to prevent buildup of contaminants that may affect accuracy.
- Temperature Compensation: Use a temperature sensor to account for temperature variations, as TDS readings are temperature-dependent.
- Avoid Immersion of the Module: Only the probe is waterproof; the module should remain dry.
- Power Supply Stability: Use a stable power source to avoid fluctuations in readings.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a TDS sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the TDS sensor
const int tdsPin = A0; // Analog pin A0 is used for the sensor's output
const float vRef = 5.0; // Reference voltage of the Arduino (5V for UNO)
const int adcResolution = 1024; // ADC resolution (10-bit for Arduino UNO)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(tdsPin); // Read the analog value from the sensor
float voltage = (sensorValue / float(adcResolution)) * vRef;
// Convert ADC value to voltage
float tdsValue = (voltage / 2.3) * 1000;
// Convert voltage to TDS value (assuming 0-2.3V maps to 0-1000 ppm)
Serial.print("TDS Value: ");
Serial.print(tdsValue);
Serial.println(" ppm"); // Print the TDS value in ppm
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Inaccurate Readings:
- Cause: Probe contamination or improper calibration.
- Solution: Clean the probe with distilled water and recalibrate using a standard solution.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the module is powered correctly.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Unstable power supply or electrical noise.
- Solution: Use a decoupling capacitor near the module's power pins and ensure a stable power source.
Temperature Dependency:
- Cause: TDS readings vary with temperature.
- Solution: Implement temperature compensation using a temperature sensor.
FAQs
Q: Can the TDS sensor measure salinity?
A: While the TDS sensor is not specifically designed for salinity, it can provide an approximate measurement since salinity contributes to the total dissolved solids.
Q: How often should I calibrate the sensor?
A: Calibration is recommended every few weeks or whenever the sensor is used in a new liquid.
Q: Can I use the TDS sensor in hot liquids?
A: The sensor is rated for temperatures up to 60°C. Avoid using it in liquids above this temperature to prevent damage.
Q: Is the TDS sensor suitable for measuring pure water?
A: Pure water has very low TDS levels, which may be below the sensor's detection range. It is better suited for measuring water with dissolved solids.