
How to Use NRF24 Adapter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
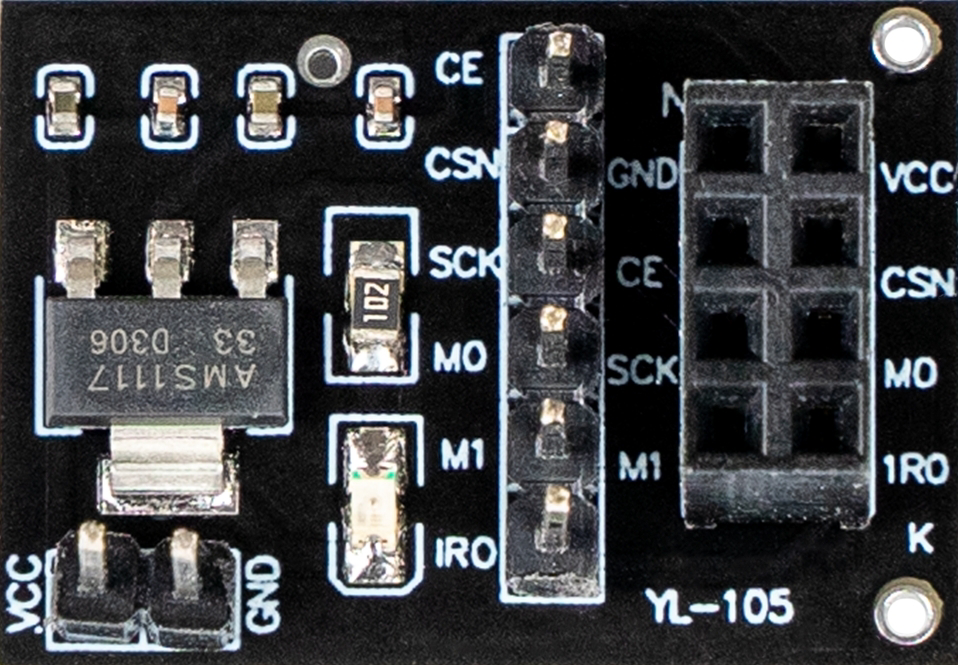
 Design with NRF24 Adapter in Cirkit Designer
Design with NRF24 Adapter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The NRF24 Adapter is a wireless transceiver module designed to operate in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Manufactured by NRF24, this module is widely used for short-range communication in applications such as remote controls, wireless sensors, and IoT devices. Its compact design and low power consumption make it an ideal choice for battery-powered devices and embedded systems.
The NRF24 Adapter is commonly paired with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO to enable wireless communication between devices. It supports multiple communication channels and features a robust data transmission protocol, ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
Explore Projects Built with NRF24 Adapter
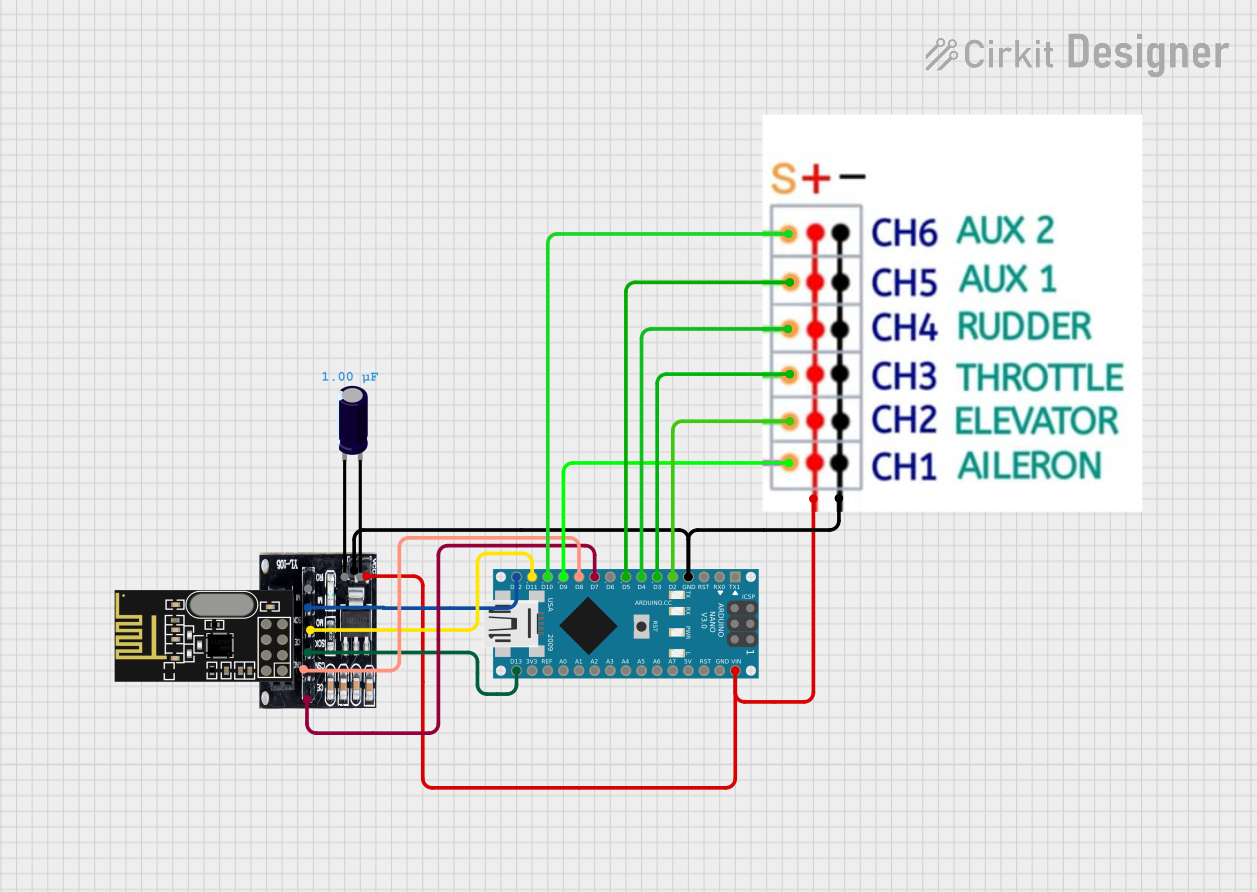
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer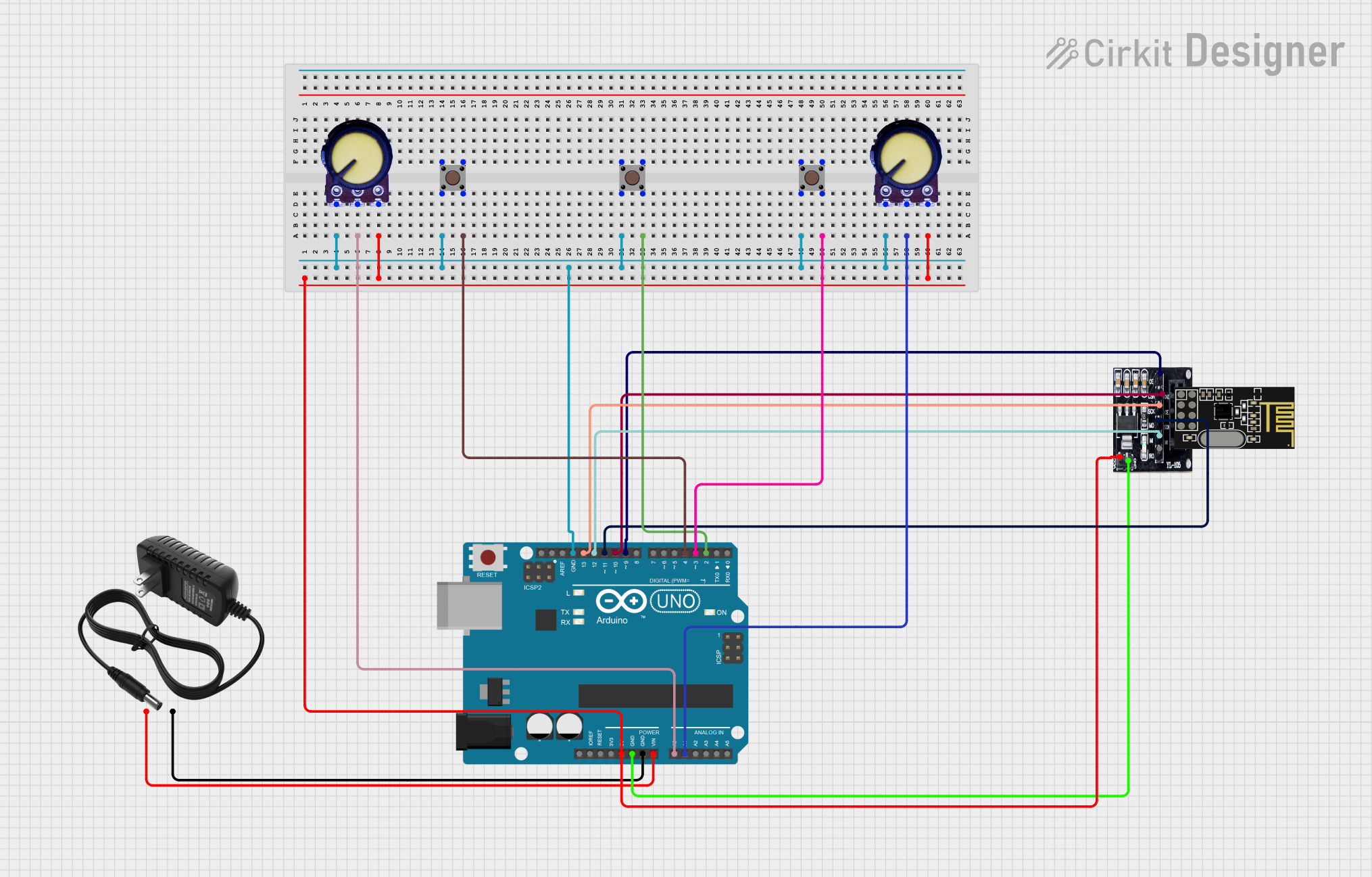
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer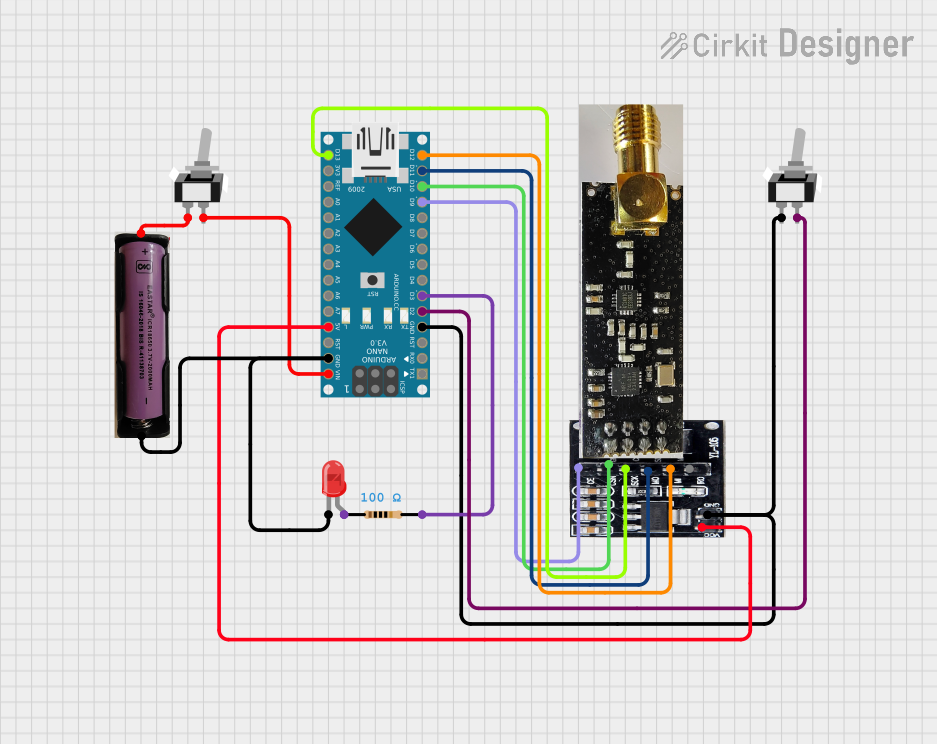
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with NRF24 Adapter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the NRF24 Adapter:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 2.4 GHz ISM Band |
| Operating Voltage | 1.9V to 3.6V |
| Communication Protocol | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
| Data Rate | 250 kbps, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps |
| Maximum Range | Up to 100 meters (line of sight) |
| Power Consumption | 11.3 mA (transmit mode, 0 dBm) |
| Number of Channels | 125 |
| Modulation Technique | GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) |
| Dimensions | 15 mm x 29 mm x 1.5 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The NRF24 Adapter has 8 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (1.9V to 3.6V) |
| 3 | CE | Chip Enable: Activates the module for data transmission or reception |
| 4 | CSN | Chip Select Not: Used to enable or disable SPI communication |
| 5 | SCK | Serial Clock: Clock signal for SPI communication |
| 6 | MOSI | Master Out Slave In: Data line for sending data from the microcontroller |
| 7 | MISO | Master In Slave Out: Data line for receiving data from the NRF24 module |
| 8 | IRQ | Interrupt Request: Indicates when data is available or an event has occurred |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the NRF24 Adapter in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground. Avoid connecting the module directly to 5V as it may damage the component.
- SPI Communication: Connect the SPI pins (CSN, SCK, MOSI, MISO) to the corresponding SPI pins on your microcontroller. For example, on an Arduino UNO:
- CSN → Pin 10
- SCK → Pin 13
- MOSI → Pin 11
- MISO → Pin 12
- CE Pin: Connect the CE pin to a digital pin on the microcontroller (e.g., Pin 9 on Arduino UNO). This pin is used to toggle between standby and active modes.
- IRQ Pin: Optionally, connect the IRQ pin to a digital pin on the microcontroller to handle interrupts.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a 10 µF capacitor between VCC and GND to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
- Ensure proper antenna placement for optimal range and signal strength.
- Avoid placing the module near high-frequency components or metal surfaces that may interfere with the signal.
- Use libraries like
RF24for Arduino to simplify communication with the module.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the NRF24 Adapter with an Arduino UNO to send and receive data:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
// Define the CE and CSN pins for the NRF24 module
#define CE_PIN 9
#define CSN_PIN 10
// Create an RF24 object
RF24 radio(CE_PIN, CSN_PIN);
// Define the address for communication
const byte address[6] = "00001";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
radio.begin(); // Initialize the NRF24 module
radio.openWritingPipe(address); // Set the address for transmission
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_LOW); // Set power level to low
radio.stopListening(); // Set the module to transmit mode
}
void loop() {
const char text[] = "Hello, World!"; // Data to send
bool success = radio.write(&text, sizeof(text)); // Send data
if (success) {
Serial.println("Data sent successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Data transmission failed.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before sending again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Not Responding:
- Ensure the power supply is stable and within the specified range (1.9V to 3.6V).
- Verify the SPI connections and ensure they match the microcontroller's pinout.
Short Communication Range:
- Check the antenna placement and ensure there are no obstructions.
- Increase the power level using the
setPALevel()function in the RF24 library.
Data Transmission Fails:
- Verify that both the transmitter and receiver modules are using the same address and channel.
- Ensure the CE pin is properly toggled to activate the module.
Interference with Other Devices:
- Change the communication channel to avoid conflicts with other 2.4 GHz devices.
- Use a lower data rate (e.g., 250 kbps) for better reliability in noisy environments.
FAQs
Q: Can the NRF24 Adapter be powered with 5V?
A: No, the module operates at 1.9V to 3.6V. Use a 3.3V regulator if your system provides only 5V.
Q: What is the maximum range of the NRF24 Adapter?
A: The maximum range is up to 100 meters in line-of-sight conditions. Obstacles and interference may reduce the range.
Q: Can multiple NRF24 modules communicate simultaneously?
A: Yes, the module supports up to 6 simultaneous data pipes for multi-device communication.
Q: How do I debug communication issues?
A: Use the printDetails() function from the RF24 library to check the module's configuration and status.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the NRF24 Adapter into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.