
How to Use Polymer Lithium Ion Battery - Generic: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Polymer Lithium Ion Battery - Generic in Cirkit Designer
Design with Polymer Lithium Ion Battery - Generic in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
Polymer Lithium Ion Batteries (LiPo) are a subtype of lithium-ion batteries that use a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid one. This allows the batteries to be lightweight and have a very slim profile, which is why they are commonly used in portable electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, drones, and wearable technology. Their high energy density and ability to be shaped to fit various spaces make them highly versatile for both consumer and industrial applications.
Explore Projects Built with Polymer Lithium Ion Battery - Generic
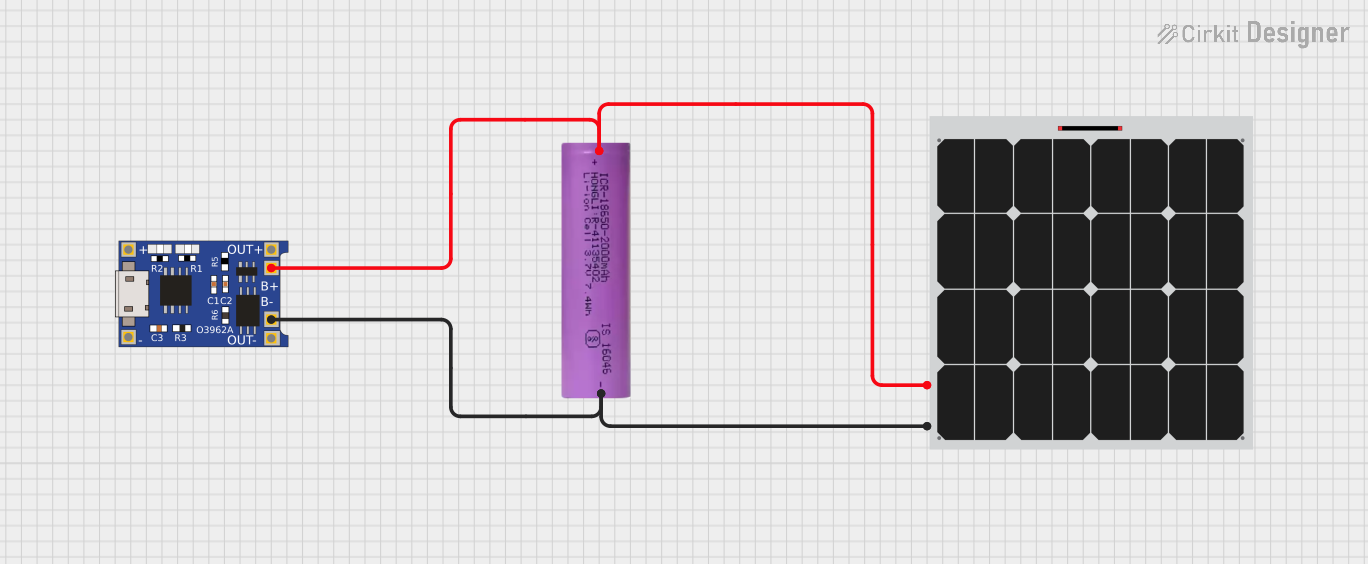
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer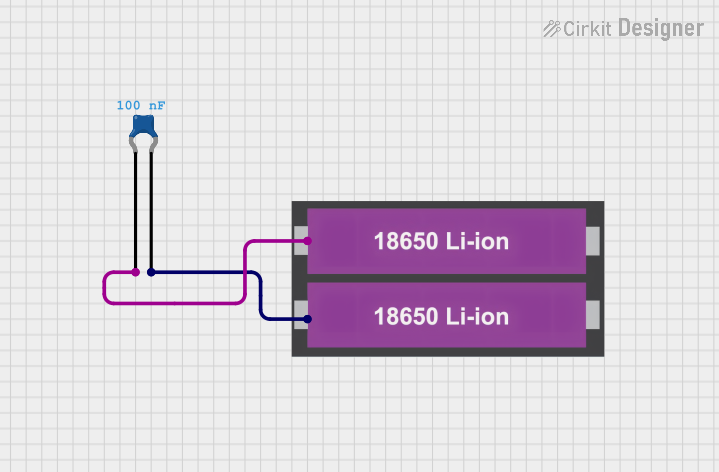
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Polymer Lithium Ion Battery - Generic

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Characteristics
- Chemistry: Lithium Polymer (LiPo)
- Nominal Voltage: 3.7V
- Charge Voltage: Typically 4.2V
- Cut-off Voltage: Typically 3.0V
- Energy Density: High
- Cycle Life: 500-1000 cycles (depending on usage and care)
- Operating Temperature: Charge 0°C to 45°C, Discharge -20°C to 60°C
Electrical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Capacity | X mAh (to be specified per model) |
| Max Continuous Discharge Current | Y A (to be specified per model) |
| Max Charge Current | Z A (to be specified per model) |
| Internal Resistance | <100 mΩ typically |
Replace X, Y, Z with the values specific to the battery model.
Physical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | Length x Width x Height (mm) |
| Weight | X grams (to be specified per model) |
| Connector Type | JST/XT60/others (to be specified per model) |
Replace Length x Width x Height and X with the values specific to the battery model.
Usage Instructions
Charging
- Use a LiPo-compatible charger. Always charge LiPo batteries with a charger specifically designed for lithium polymer chemistry.
- Monitor the charging process. Never leave the battery unattended while charging.
- Set the correct voltage and current. Ensure the charger is set to the correct voltage (4.2V per cell) and does not exceed the maximum charge current of the battery.
- Balance charging is recommended. If the battery has multiple cells, use a balance charger to ensure all cells are charged equally.
Discharging
- Do not over-discharge. Never allow the voltage of the battery to drop below the cut-off voltage (typically 3.0V per cell).
- Avoid high discharge rates. Do not exceed the maximum continuous discharge current rating.
- Use a battery management system (BMS). For multi-cell packs, a BMS is recommended to protect the cells from over-discharge and over-current conditions.
Storage
- Store at half-charge. If storing the battery for an extended period, do so at approximately 50% charge.
- Keep in a cool, dry place. Avoid storing the battery in hot or humid environments.
- Check periodically. If stored for long periods, check the battery every few months and recharge to 50% if necessary.
Safety Precautions
- Do not puncture or damage the battery.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight.
- In case of swelling, stop using immediately and dispose of properly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Battery won't charge: Ensure the charger is functioning and set to the correct settings. Check the battery's voltage; if it's below the cut-off voltage, the battery may be damaged.
- Battery swells during use or charging: Discontinue use immediately. Swelling can indicate overcharging, deep discharging, or a damaged cell.
- Reduced capacity or runtime: This can be a sign of aging or that the battery has been cycled many times. It may be time to replace the battery.
FAQs
Q: Can I charge a LiPo battery with a regular lithium-ion charger? A: No, you must use a charger that is specifically designed for LiPo batteries to ensure safe and proper charging.
Q: How do I dispose of a LiPo battery? A: LiPo batteries should be fully discharged and then taken to a battery recycling facility. Do not throw them in the trash.
Q: What should I do if my LiPo battery gets wet? A: Immediately disconnect any power, remove the battery from the device, and allow it to dry completely. Inspect for damage before using again.
Q: Can I repair a damaged LiPo battery? A: No, damaged LiPo batteries are hazardous and should not be repaired. They should be replaced and disposed of properly.
Example Arduino UNO Connection
LiPo batteries can be used to power an Arduino UNO via the VIN pin. Here's a simple example of how to connect a LiPo battery to an Arduino UNO:
// No specific code is required for powering Arduino with LiPo battery.
// Just ensure that the battery voltage is within the acceptable range for the Arduino VIN pin (6-12V).
// Always check the Arduino specifications for the recommended input voltage range.
// Connecting a LiPo battery with a higher voltage than recommended can damage the Arduino.
// Connect the positive terminal of the LiPo battery to the VIN pin on the Arduino.
// Connect the negative terminal of the LiPo battery to one of the GND pins on the Arduino.
Note: This is a generic connection guide. Always refer to the specific battery and Arduino UNO documentation for any additional considerations or instructions.