
How to Use BTS7960 Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
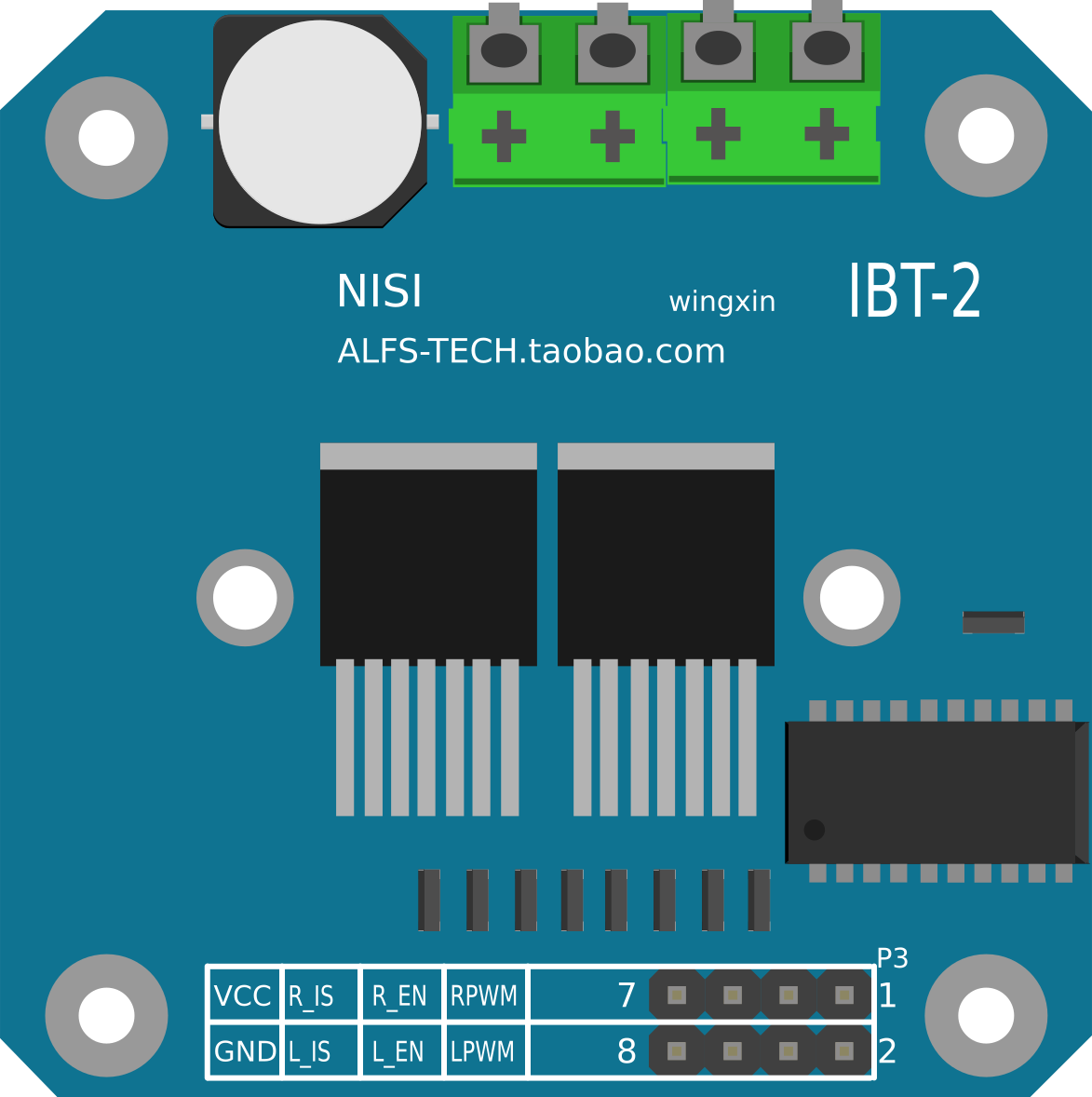
 Design with BTS7960 Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with BTS7960 Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BTS7960 Motor Driver is a high-current H-bridge motor driver designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors. It is capable of handling high currents, making it suitable for driving large motors in industrial, robotic, and automotive applications. The module features built-in protection mechanisms, including overcurrent and thermal overload protection, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Explore Projects Built with BTS7960 Motor Driver
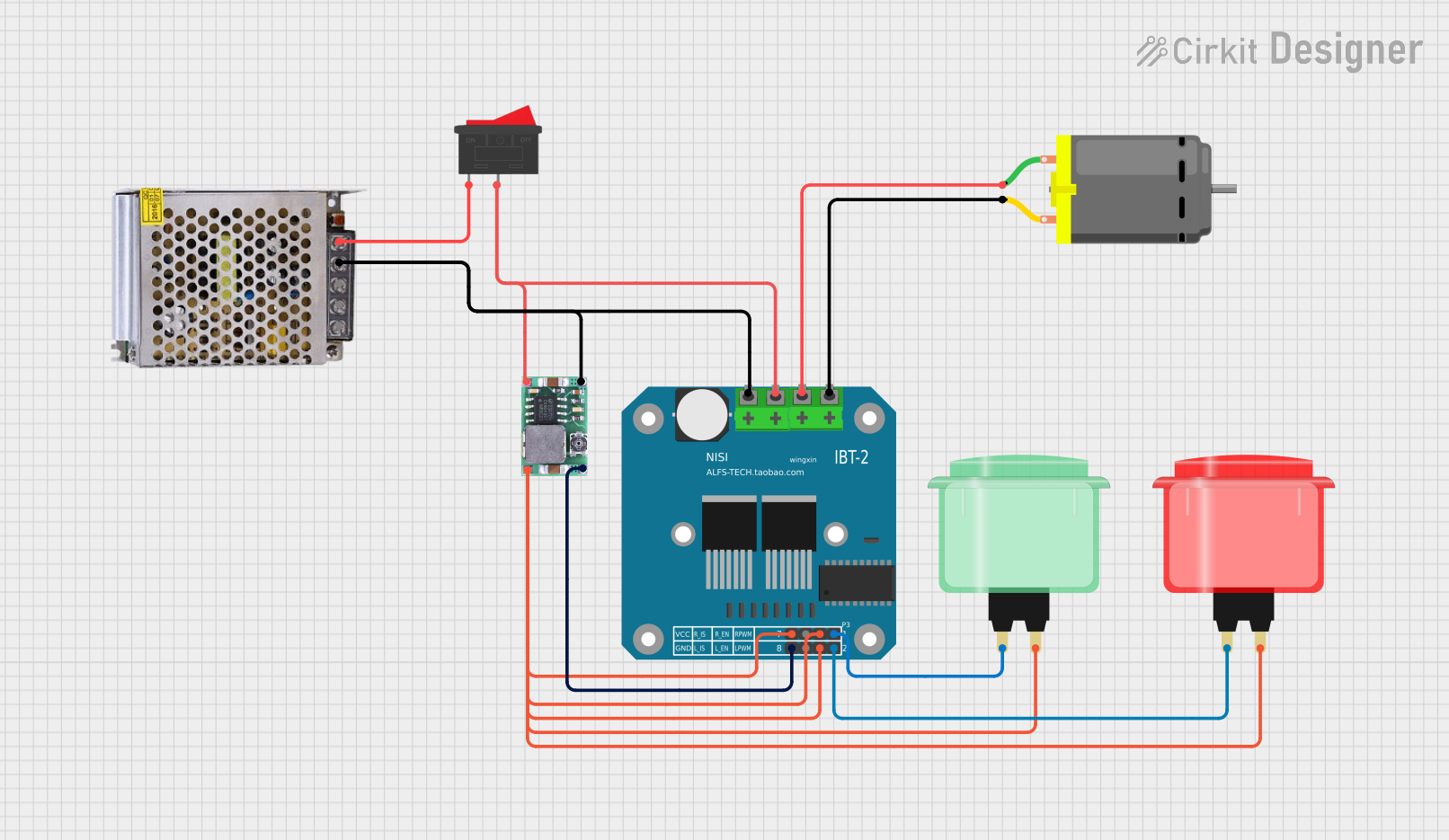
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer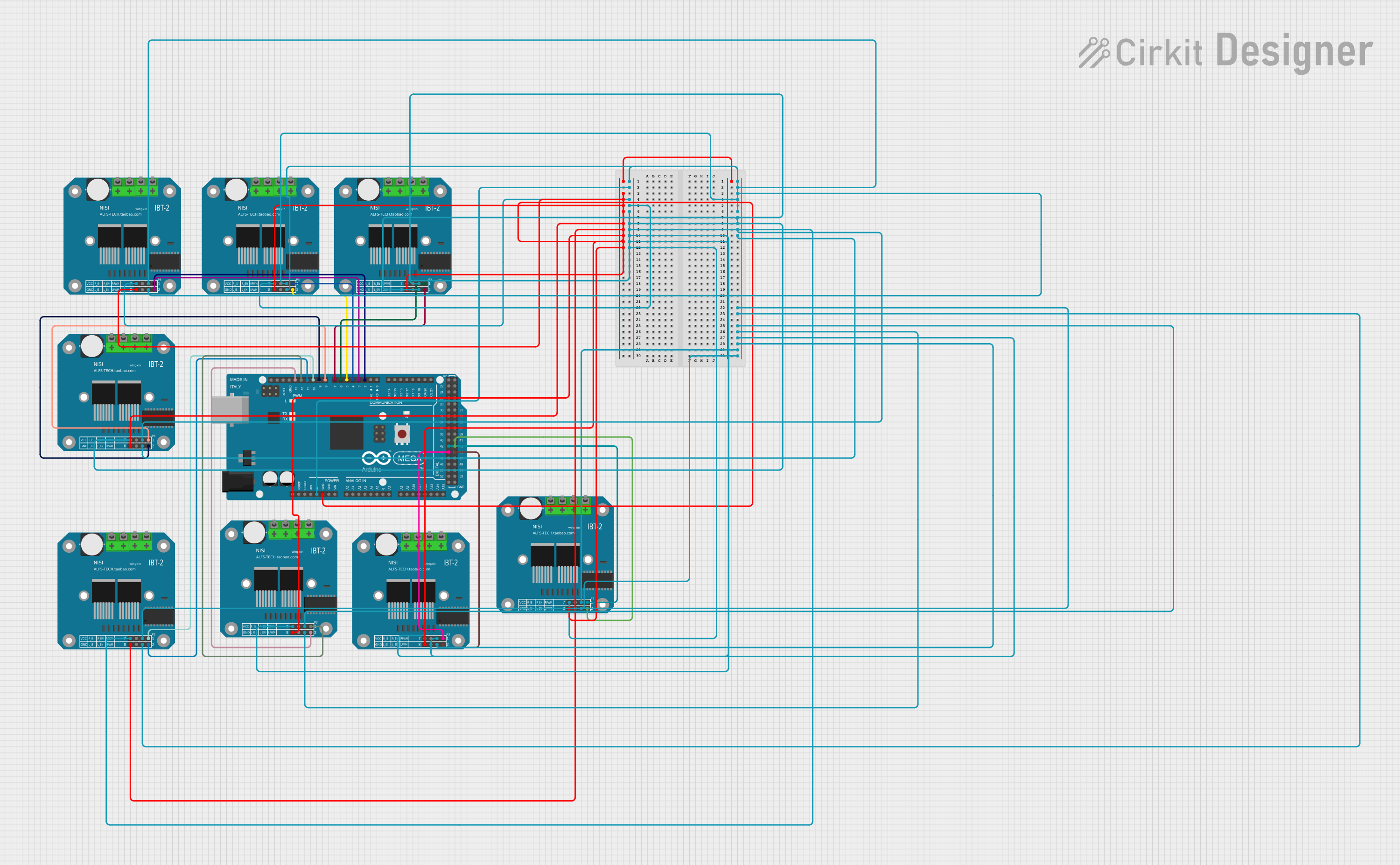
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer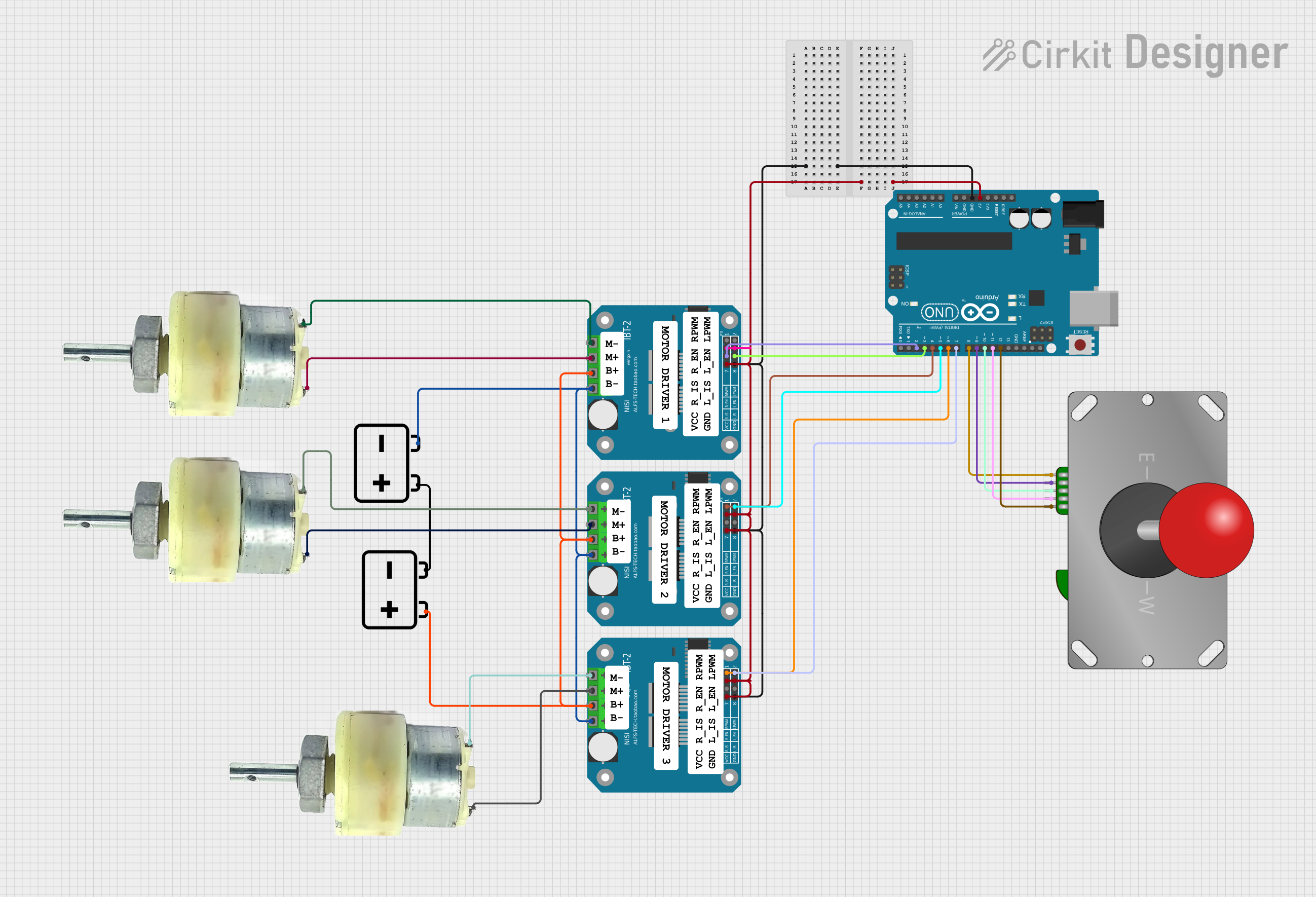
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer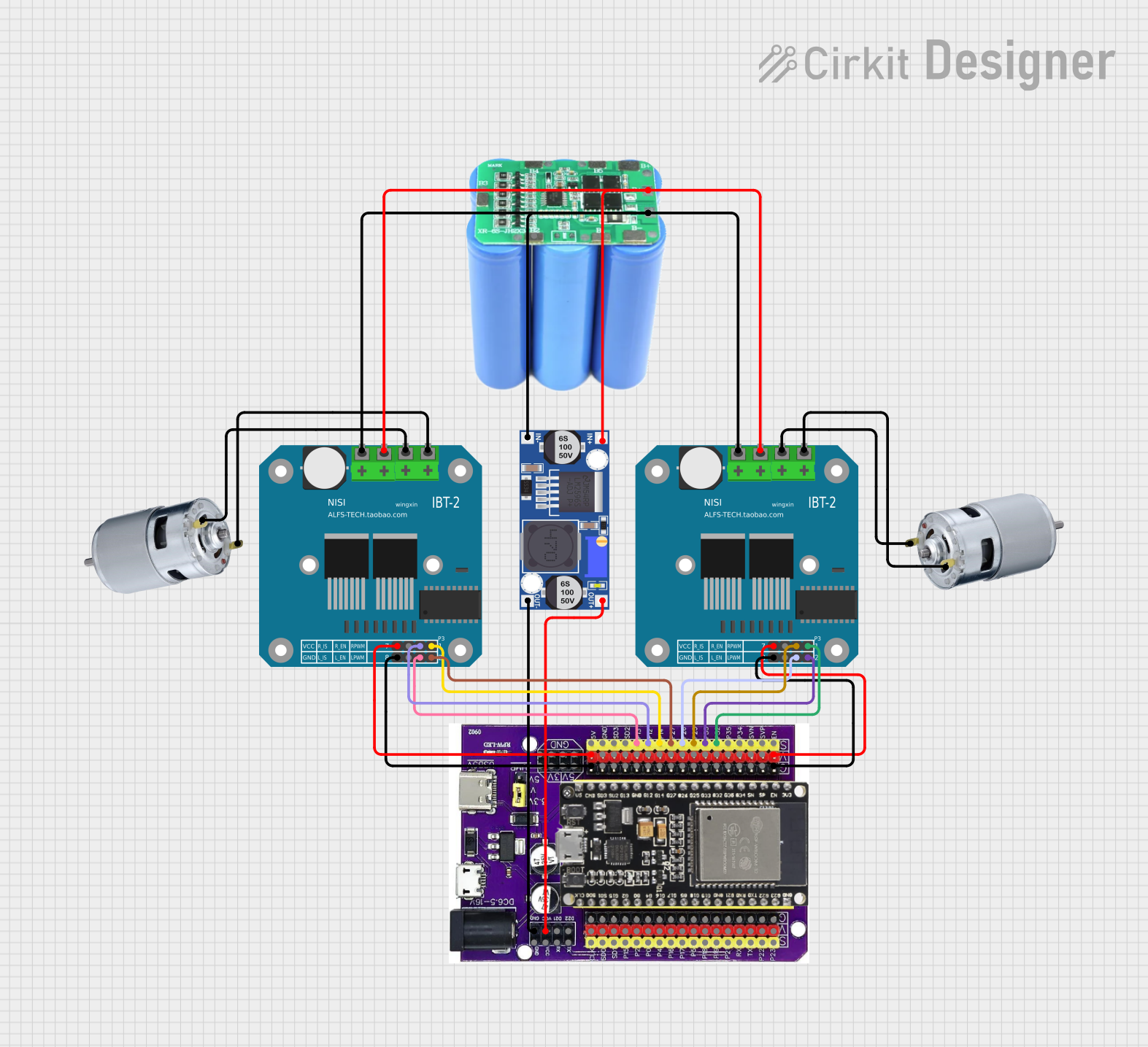
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BTS7960 Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotic systems and motorized platforms
- Electric vehicles and motorized carts
- Conveyor belts and industrial automation
- High-power DC motor control in hobbyist projects
- Smart home devices requiring motorized movement
Technical Specifications
The BTS7960 Motor Driver is designed to handle high-power applications with robust performance. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | 5.5V to 27V |
| Maximum Continuous Current | 43A |
| Peak Current | 50A |
| PWM Frequency | Up to 25kHz |
| Logic Voltage | 3.3V or 5V (compatible) |
| Overcurrent Protection | Yes |
| Thermal Shutdown | Yes |
| Dimensions | 43mm x 45mm x 28mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BTS7960 module has several pins for motor control and power input. Below is the pinout:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | Logic voltage input (3.3V or 5V). |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for logic and motor power. |
| RPWM | Input | PWM signal for controlling motor speed in one direction. |
| LPWM | Input | PWM signal for controlling motor speed in the opposite direction. |
| R_EN | Input | Enable pin for the right side of the H-bridge. |
| L_EN | Input | Enable pin for the left side of the H-bridge. |
| IS | Output | Current sensing output (optional, for monitoring motor current). |
| V+ | Power Input | Motor power supply (5.5V to 27V). |
| OUT1 | Output | Motor terminal 1. |
| OUT2 | Output | Motor terminal 2. |
Usage Instructions
The BTS7960 Motor Driver is straightforward to use in a circuit. Below are the steps and best practices for integrating it into your project.
How to Use the BTS7960 in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the motor power supply to the
V+pin and ground to theGNDpin. - Ensure the power supply voltage is within the range of 5.5V to 27V.
- Connect the logic voltage (3.3V or 5V) to the
VCCpin.
- Connect the motor power supply to the
Motor Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to the
OUT1andOUT2pins.
- Connect the motor terminals to the
Control Pins:
- Use the
RPWMandLPWMpins to control the motor's speed and direction via PWM signals. - Enable the H-bridge sides by setting
R_ENandL_ENto HIGH.
- Use the
PWM Control:
- To move the motor in one direction, send a PWM signal to
RPWMand setLPWMto LOW. - To reverse the motor direction, send a PWM signal to
LPWMand setRPWMto LOW.
- To move the motor in one direction, send a PWM signal to
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the BTS7960 Motor Driver using an Arduino UNO:
// Define control pins for the BTS7960
#define RPWM 9 // PWM pin for forward direction
#define LPWM 10 // PWM pin for reverse direction
#define R_EN 7 // Enable pin for right H-bridge
#define L_EN 8 // Enable pin for left H-bridge
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(RPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_EN, OUTPUT);
// Enable both sides of the H-bridge
digitalWrite(R_EN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_EN, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Move motor forward at 50% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 128); // 50% duty cycle
analogWrite(LPWM, 0); // No reverse signal
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(RPWM, 0);
analogWrite(LPWM, 0);
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
// Move motor in reverse at 75% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 0); // No forward signal
analogWrite(LPWM, 192); // 75% duty cycle
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(RPWM, 0);
analogWrite(LPWM, 0);
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: The BTS7960 can handle high currents, but it may generate heat. Use a heatsink or active cooling for prolonged high-current operation.
- Power Supply: Ensure the motor power supply can provide sufficient current for your motor.
- Logic Voltage: The module is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels, making it suitable for most microcontrollers.
- Current Monitoring: Use the
ISpin to monitor motor current if needed.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Running:
- Check power supply connections and ensure the voltage is within the specified range.
- Verify that the
R_ENandL_ENpins are set to HIGH.
Motor Running in Only One Direction:
- Ensure the PWM signals are being sent to the correct pins (
RPWMandLPWM). - Check for loose or incorrect wiring.
- Ensure the PWM signals are being sent to the correct pins (
Overheating:
- Ensure proper heat dissipation using a heatsink or fan.
- Reduce the motor load if it exceeds the driver's current rating.
Erratic Motor Behavior:
- Verify that the power supply is stable and not dropping under load.
- Check for noise or interference in the PWM signals.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the BTS7960 with a 3.3V microcontroller like the ESP32?
A: Yes, the BTS7960 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
Q: What is the maximum motor voltage I can use?
A: The maximum motor voltage is 27V. Ensure your power supply does not exceed this limit.
Q: How do I stop the motor?
A: To stop the motor, set both RPWM and LPWM to LOW or send a 0% duty cycle PWM signal.
Q: Can I control two motors with one BTS7960 module?
A: No, the BTS7960 is designed to control a single DC motor. For dual-motor control, use two modules.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the BTS7960 Motor Driver into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.