
How to Use 7-20V to 5V: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 7-20V to 5V in Cirkit Designer
Design with 7-20V to 5V in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 7-20V to 5V voltage regulator is a compact and efficient electronic component designed to step down an input voltage ranging from 7 to 20 volts to a stable 5-volt output. This regulator is widely used in powering low-voltage devices such as microcontrollers, sensors, and communication modules. Its ability to provide a consistent 5V output makes it an essential component in embedded systems, robotics, and DIY electronics projects.
Explore Projects Built with 7-20V to 5V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer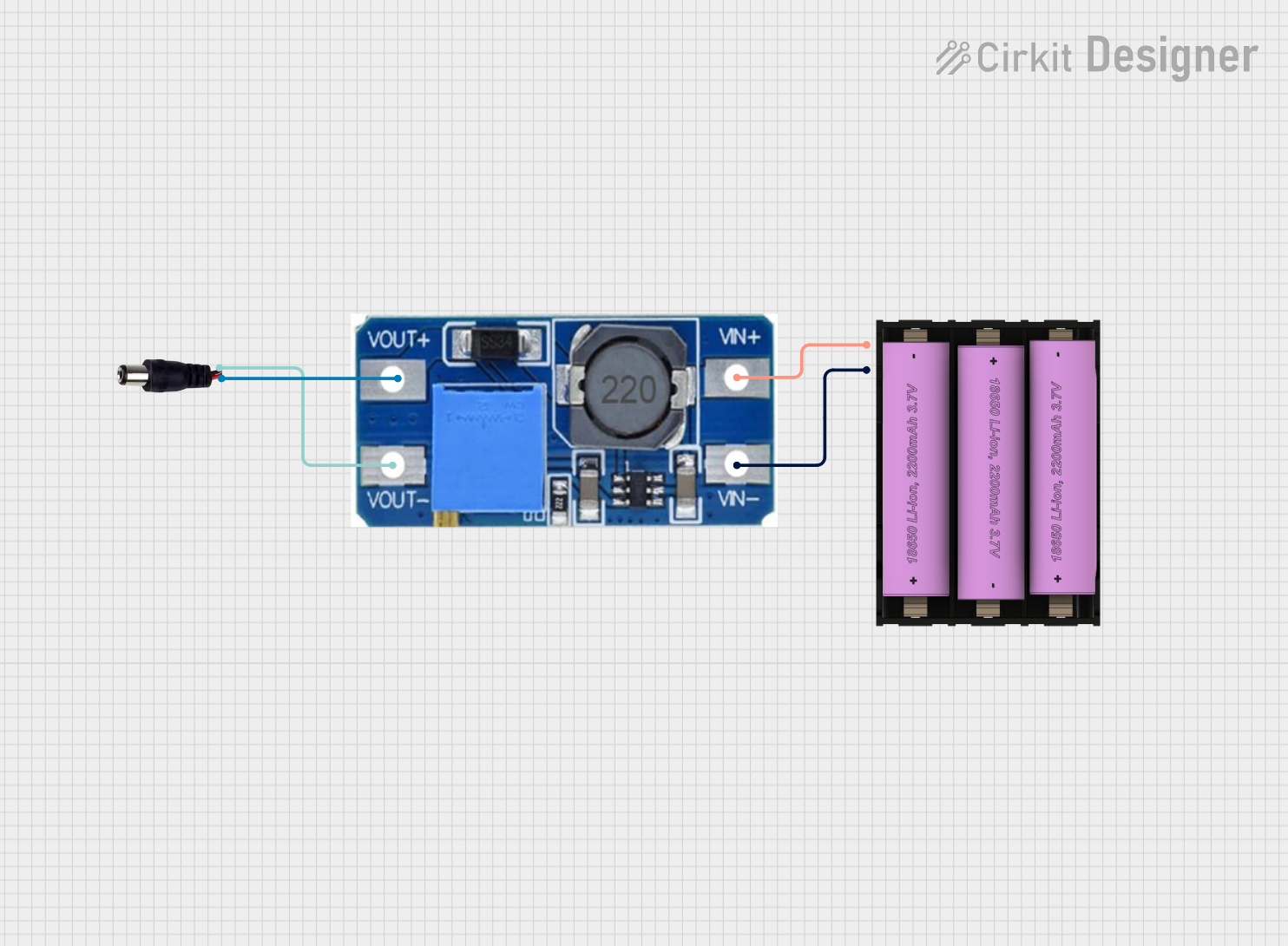
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer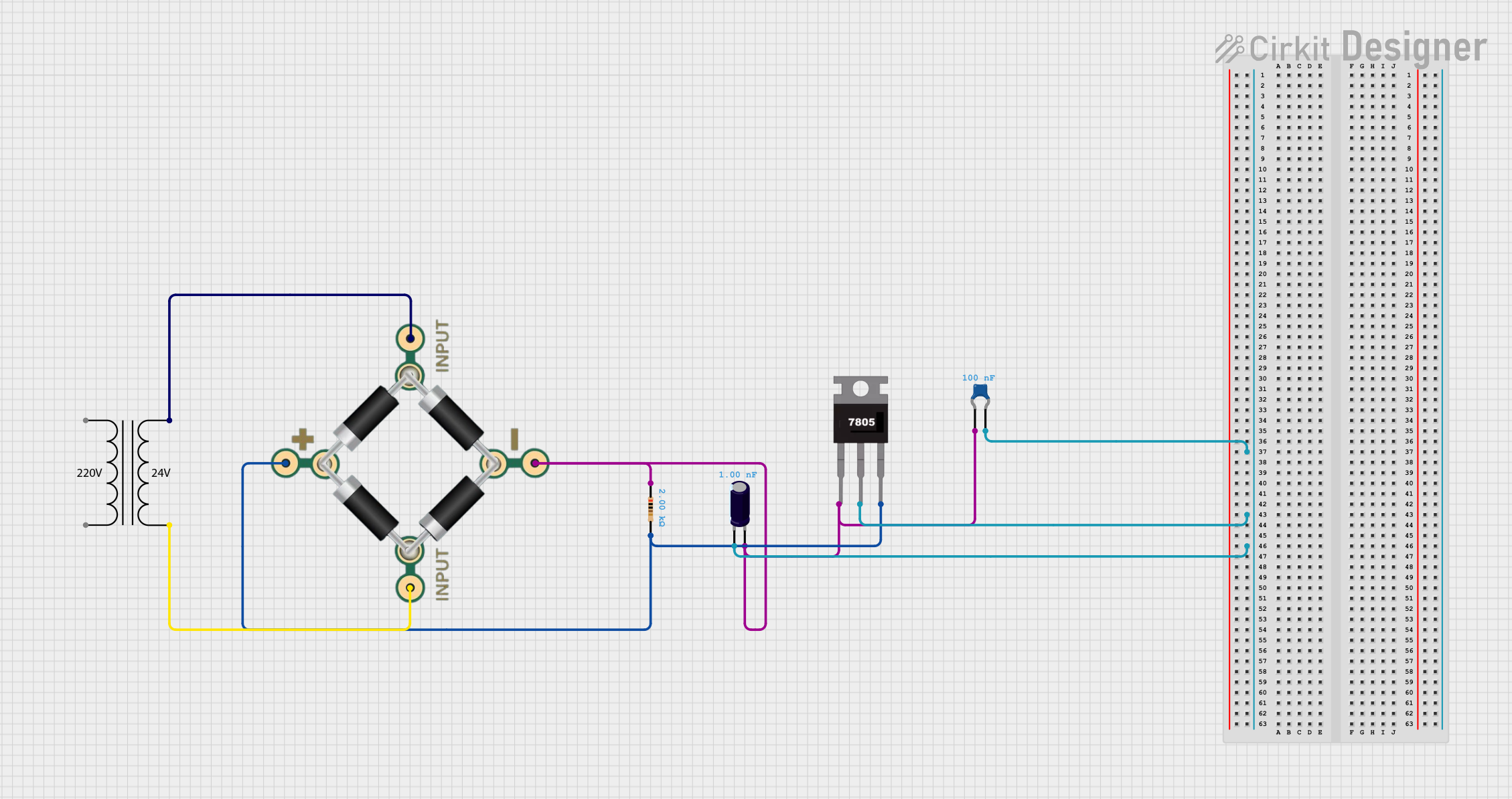
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer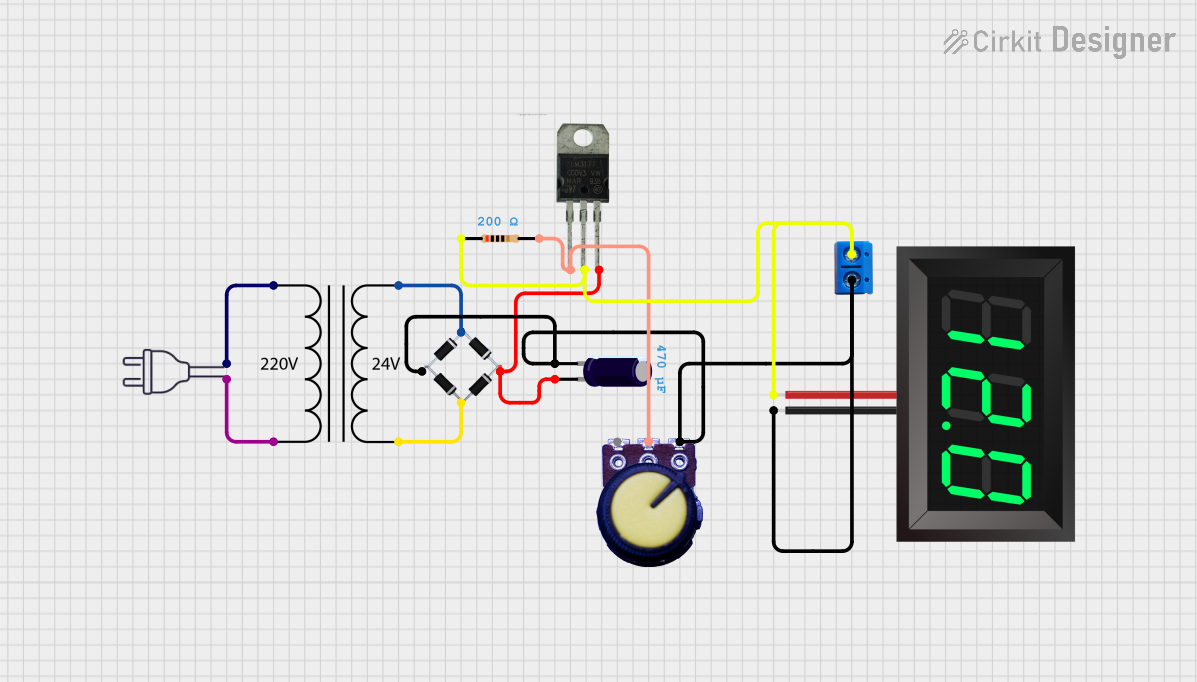
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 7-20V to 5V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi Pico.
- Supplying 5V to sensors, displays, and communication modules.
- Voltage regulation in battery-powered devices.
- DIY electronics projects requiring a stable 5V power source.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 7-20V to 5V voltage regulator:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 7V to 20V |
| Output Voltage | 5V ± 0.1V |
| Maximum Output Current | 1A (typical), 1.5A (peak) |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% (depending on load) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 25mm x 15mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The voltage regulator typically has three pins or terminals:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage pin. Connect to a DC voltage source between 7V and 20V. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 3 | VOUT | Output voltage pin. Provides a stable 5V output to power your devices. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (VIN):
Attach the VIN pin to a DC power source with a voltage between 7V and 20V. Ensure the power source can supply sufficient current for your application.Connect the Ground (GND):
Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit. This establishes a common reference point for the input and output.Connect the Output Voltage (VOUT):
Use the VOUT pin to power your 5V devices. Ensure the total current draw of connected devices does not exceed the regulator's maximum output current.Add Capacitors (Optional but Recommended):
For improved stability, place a capacitor (e.g., 10µF) across the input (VIN and GND) and another across the output (VOUT and GND). This helps filter noise and maintain a stable voltage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: If the regulator is operating near its maximum current rating, it may generate heat. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Input Voltage Range: Do not exceed the 20V input limit, as this may damage the regulator.
- Load Current: Ensure the total current draw of connected devices does not exceed the regulator's maximum output current (1A typical, 1.5A peak).
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of your connections. Reversing the input voltage can damage the regulator.
Example: Using the Voltage Regulator with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the 7-20V to 5V voltage regulator to power an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect a 9V battery to the VIN and GND pins of the regulator.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the regulator to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND pin of the regulator to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Sample Code
Here is a simple Arduino sketch to blink an LED while powered by the regulator:
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
// Ensure the Arduino is powered via the 5V output of the voltage regulator.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient input voltage.
- Solution: Verify that the input voltage is within the 7-20V range and that all connections are secure.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or add a heatsink to the regulator.
Output Voltage Fluctuations:
- Cause: Insufficient input voltage or lack of filtering capacitors.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is stable and add capacitors across VIN and VOUT.
Regulator Not Working After Connection:
- Cause: Reversed polarity or input voltage exceeding 20V.
- Solution: Check the polarity of your connections and ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this regulator to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: No, most Raspberry Pi models require more than 1A of current, which exceeds the typical output capacity of this regulator.
Q: Do I need to use capacitors with this regulator?
A: While not mandatory, adding capacitors improves stability and reduces noise, especially in sensitive applications.
Q: Can I use this regulator with an AC power source?
A: No, this regulator is designed for DC input only. Use a rectifier and filter circuit to convert AC to DC before connecting to the regulator.
Q: What happens if I exceed the input voltage range?
A: Exceeding 20V can permanently damage the regulator. Always ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.