
How to Use MicroSD Card Adapter dengan regulator onboard: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with MicroSD Card Adapter dengan regulator onboard in Cirkit Designer
Design with MicroSD Card Adapter dengan regulator onboard in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
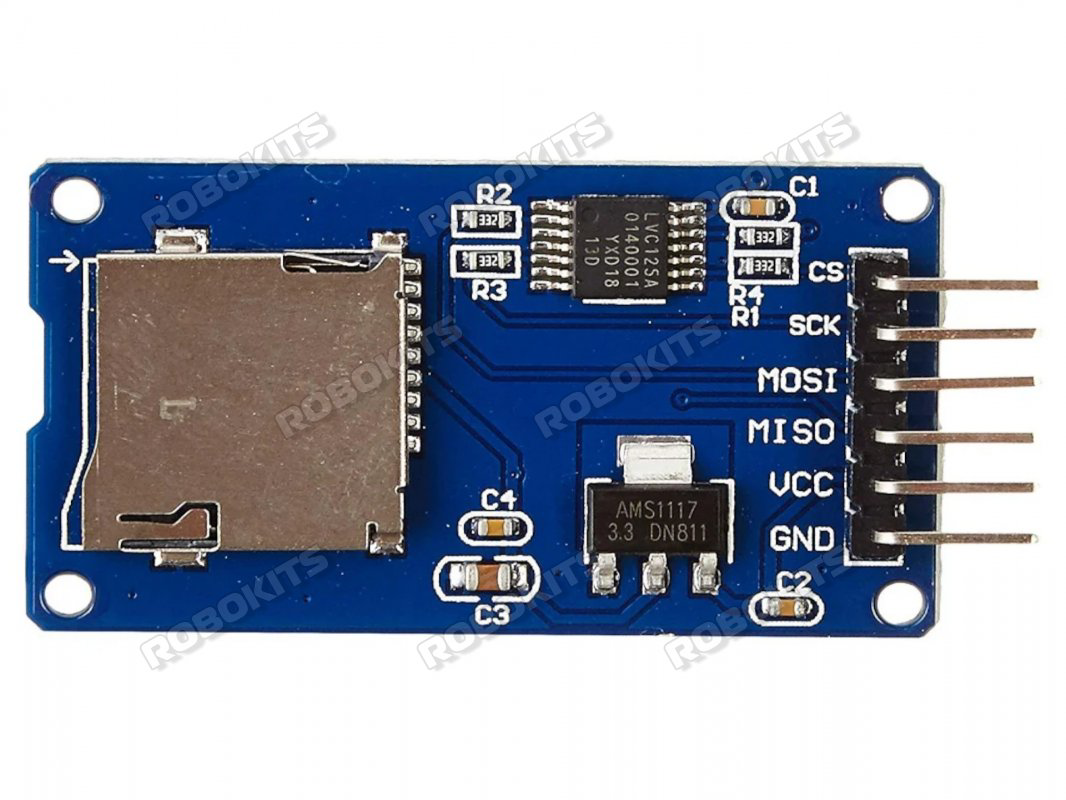
The MicroSD Card Adapter dengan Regulator Onboard is a versatile module designed to interface MicroSD cards with microcontrollers, development boards, or other electronic systems. It features an onboard voltage regulator, enabling compatibility with both 5V and 3.3V systems while ensuring a stable power supply to the MicroSD card. This adapter simplifies the process of adding storage capabilities to your projects, making it ideal for data logging, file storage, and multimedia applications.
Explore Projects Built with MicroSD Card Adapter dengan regulator onboard
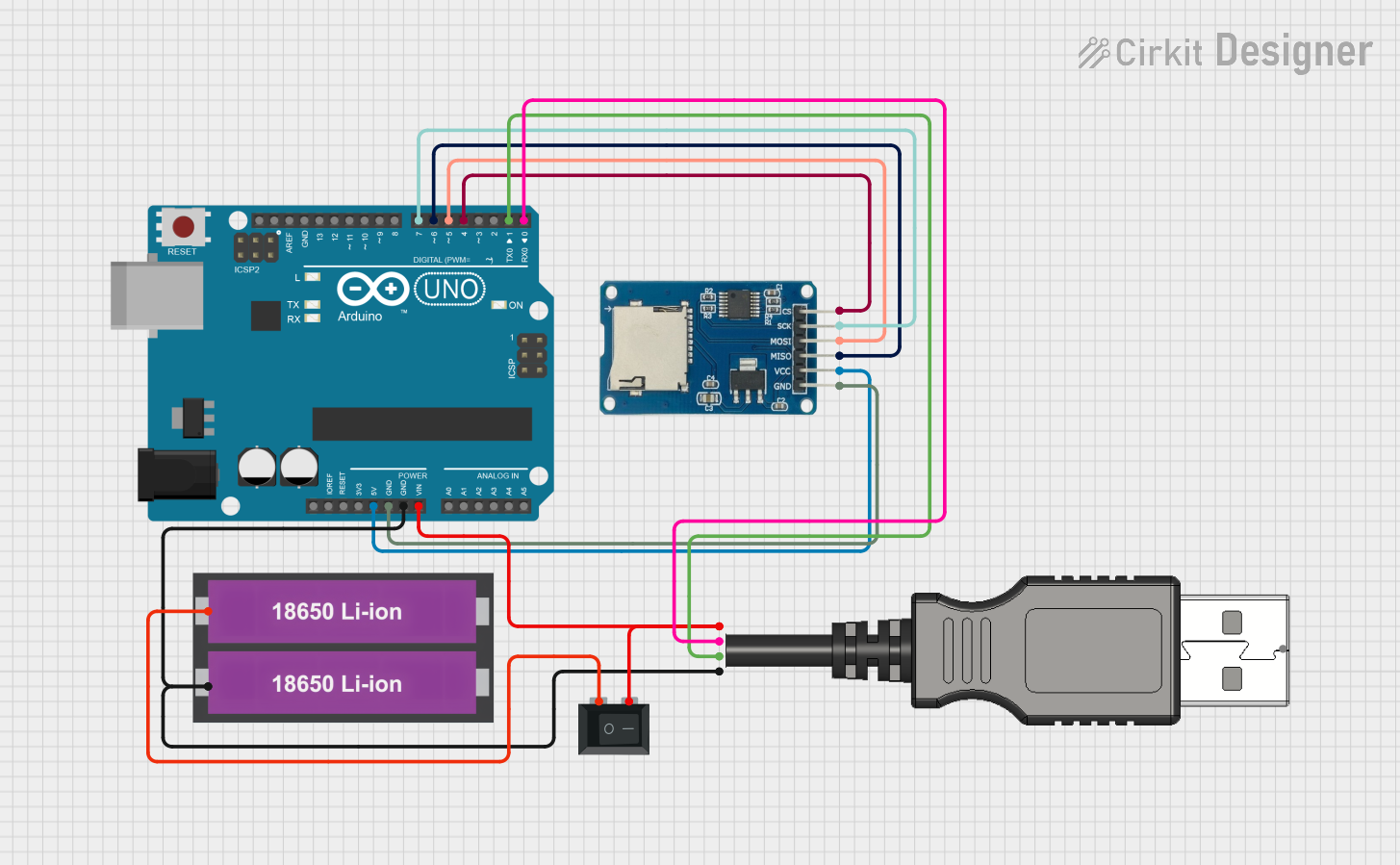
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer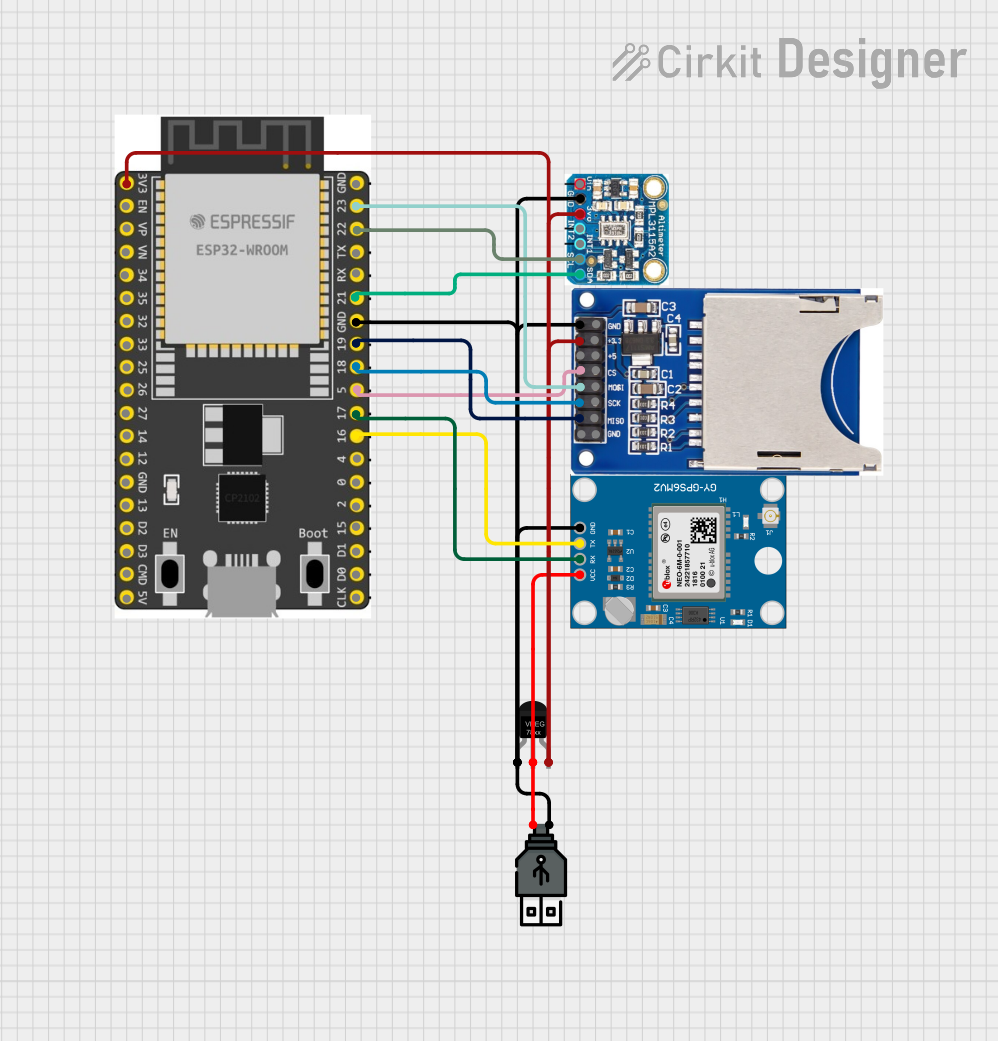
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer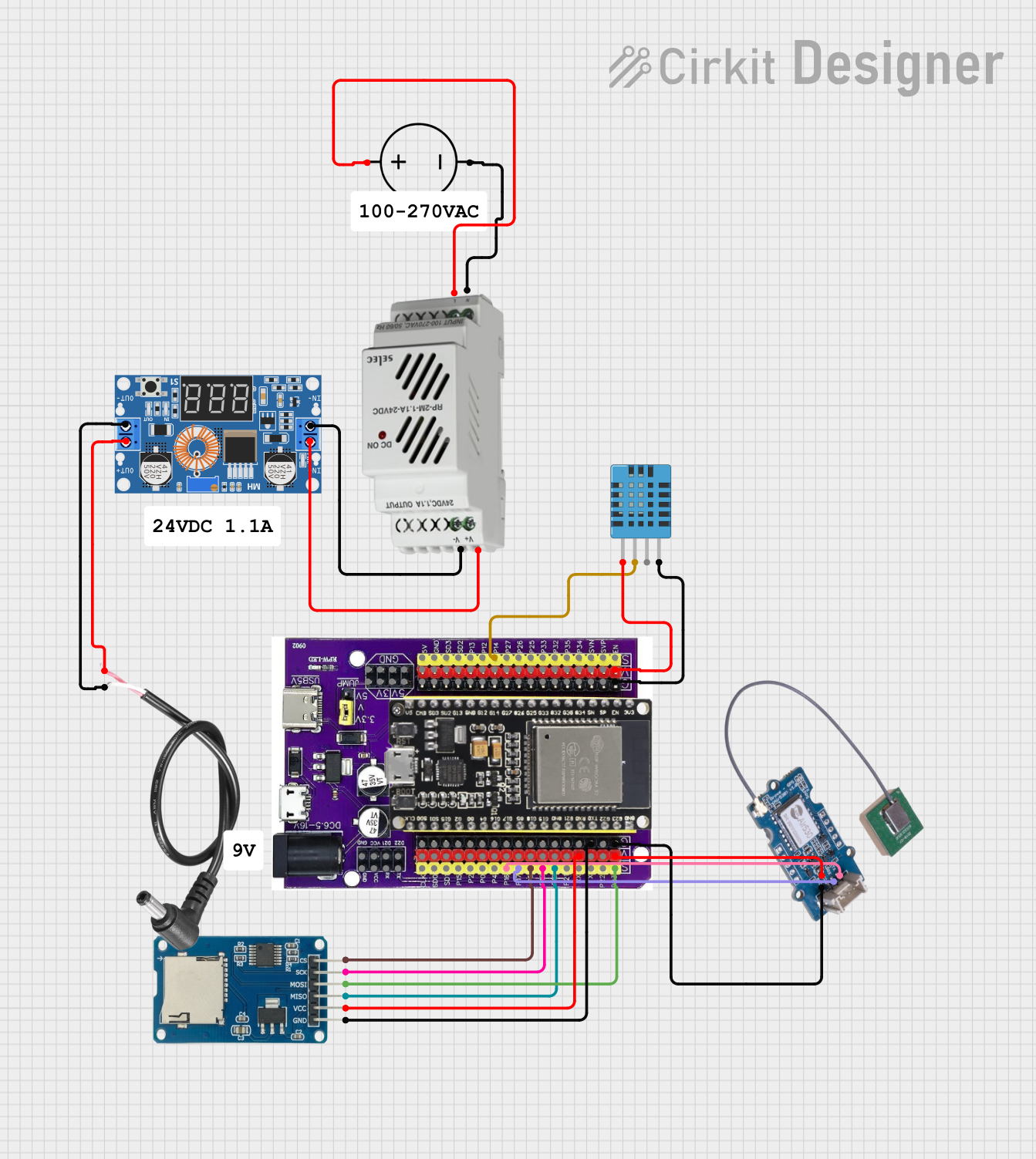
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer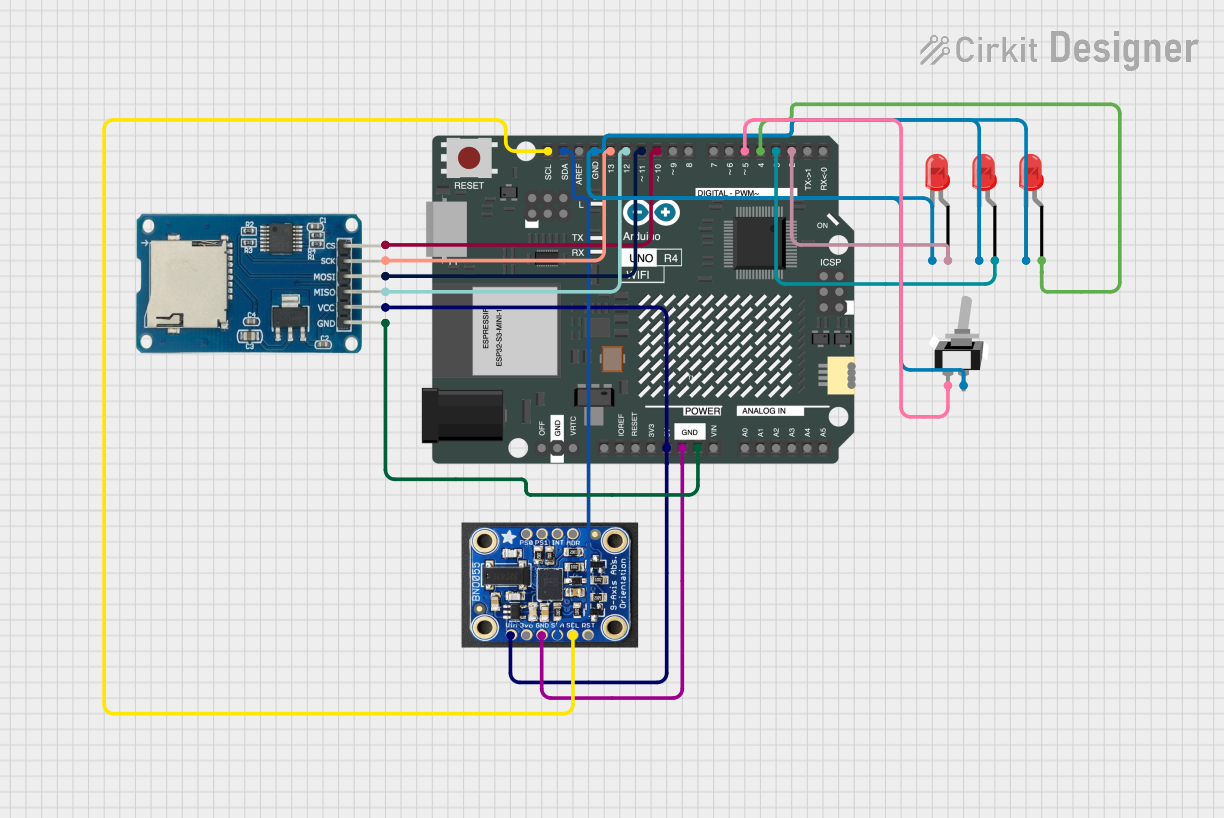
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MicroSD Card Adapter dengan regulator onboard

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Data logging for IoT devices and sensors
- File storage for embedded systems
- Multimedia storage for audio, video, or image files
- Bootable storage for microcontroller-based systems
- Projects requiring expandable memory
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the MicroSD Card Adapter dengan Regulator Onboard:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 4.5V to 5.5V (input) |
| Output Voltage | 3.3V (regulated for MicroSD card) |
| Current Consumption | ~100mA (typical, depending on card) |
| Supported Card Types | MicroSD, MicroSDHC |
| Communication Protocol | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
| Dimensions | 42mm x 24mm x 12mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The adapter has a standard 6-pin interface for easy connection to microcontrollers or development boards. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
VCC |
Power input (4.5V to 5.5V). Connect to the 5V pin of your microcontroller. |
GND |
Ground connection. Connect to the ground of your circuit. |
MISO |
Master In Slave Out. Data output from the MicroSD card to the microcontroller. |
MOSI |
Master Out Slave In. Data input from the microcontroller to the MicroSD card. |
SCK |
Serial Clock. Clock signal for SPI communication. |
CS |
Chip Select. Used to enable or disable the MicroSD card module. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Adapter: Connect the
VCCpin to a 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect SPI Pins: Link the
MISO,MOSI,SCK, andCSpins to the corresponding SPI pins on your microcontroller or development board. - Insert the MicroSD Card: Gently insert a compatible MicroSD card into the slot on the adapter.
- Initialize the Card: Use appropriate software libraries (e.g., Arduino SD library) to initialize and communicate with the card.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the MicroSD card is formatted to FAT16 or FAT32 for compatibility.
- Avoid removing the MicroSD card while the system is powered to prevent data corruption.
- Use short and properly shielded wires for SPI connections to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- If using with a 3.3V system, ensure the onboard regulator is bypassed or not overloaded.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the adapter with an Arduino UNO to read and write data to a MicroSD card:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// Define the Chip Select (CS) pin for the MicroSD card module
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // Wait for the serial port to connect (for native USB boards)
}
Serial.println("Initializing MicroSD card...");
// Initialize the SD card
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("Card initialization failed!");
return; // Stop if the card cannot be initialized
}
Serial.println("Card initialized successfully.");
// Create or open a file on the MicroSD card
File dataFile = SD.open("example.txt", FILE_WRITE);
// Check if the file opened successfully
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.println("Hello, MicroSD card!"); // Write data to the file
dataFile.close(); // Close the file to save changes
Serial.println("Data written to file.");
} else {
Serial.println("Error opening file for writing.");
}
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
MicroSD Card Not Detected
- Ensure the card is properly inserted into the adapter.
- Verify that the
CSpin is correctly defined in your code and connected to the correct pin on your microcontroller. - Check the card's format (use FAT16 or FAT32).
Data Corruption
- Avoid removing the card while the system is powered.
- Ensure proper shutdown of file operations using
file.close()in your code.
Communication Errors
- Verify SPI connections and ensure they are secure.
- Use shorter wires to reduce noise and interference.
Power Issues
- Confirm that the
VCCpin is receiving a stable 5V supply. - Check the onboard regulator for overheating or damage.
- Confirm that the
FAQs
Q: Can this adapter work with 3.3V systems?
A: Yes, the onboard regulator ensures compatibility with 3.3V systems. However, ensure the regulator is not bypassed or overloaded.
Q: What is the maximum storage capacity supported?
A: The adapter supports MicroSD cards up to 32GB (MicroSDHC). For larger cards, ensure your microcontroller and software library support exFAT.
Q: Can I use this adapter with a Raspberry Pi?
A: While the adapter is designed for microcontrollers, it can be used with a Raspberry Pi if SPI communication is properly configured.
Q: How do I format the MicroSD card?
A: Use a computer to format the card to FAT16 or FAT32. Avoid using NTFS or exFAT unless supported by your system.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the MicroSD Card Adapter dengan Regulator Onboard into your projects for reliable and efficient storage solutions.