
How to Use Zener Diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Zener Diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with Zener Diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Zener diode is a type of semiconductor device that allows current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific reverse voltage, known as the Zener voltage, is reached. Unlike regular diodes, which block reverse current, Zener diodes are designed to operate in the breakdown region without damage. This unique property makes them ideal for applications such as voltage regulation, overvoltage protection, and reference voltage generation.
Explore Projects Built with Zener Diode
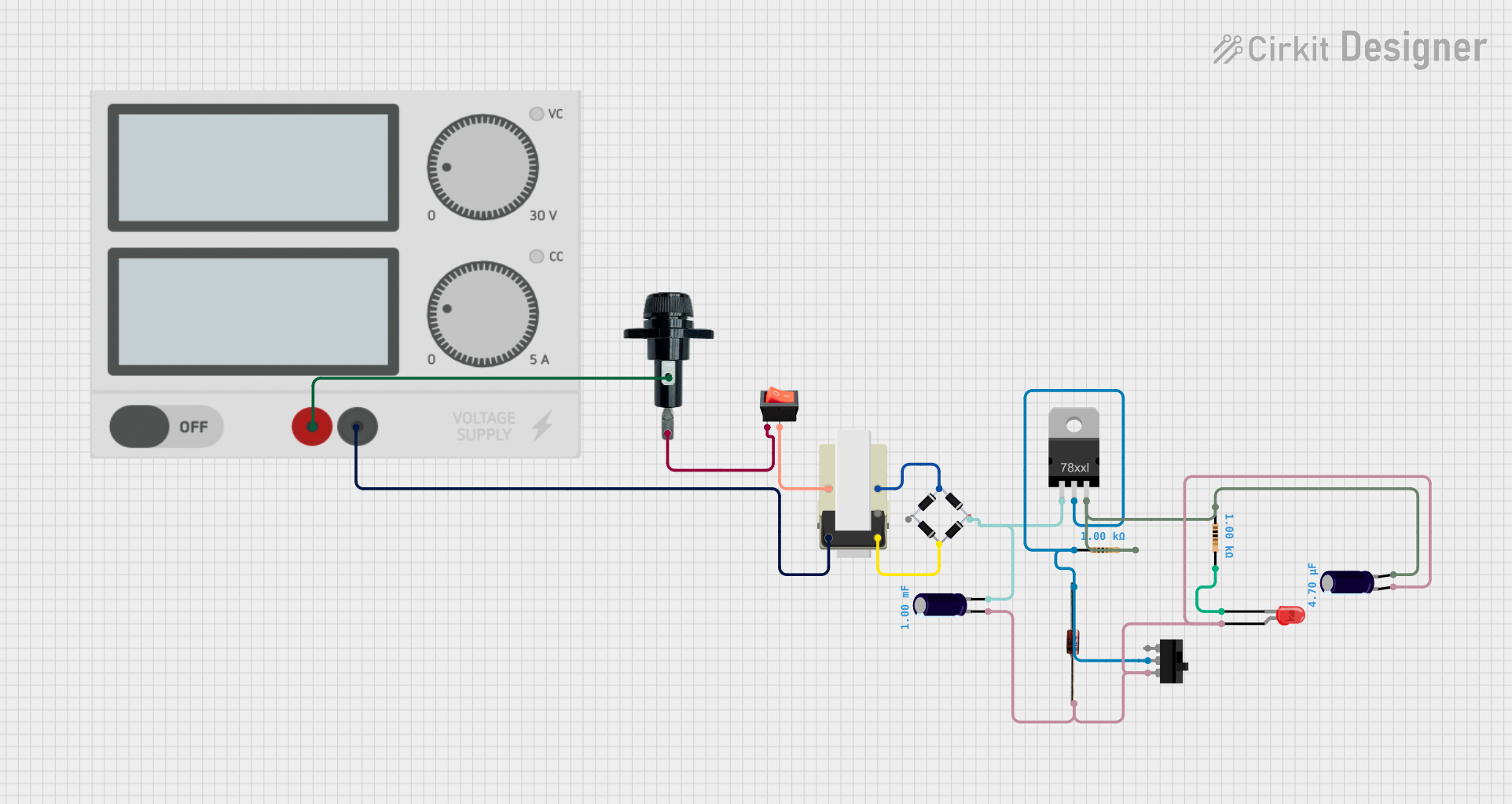
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer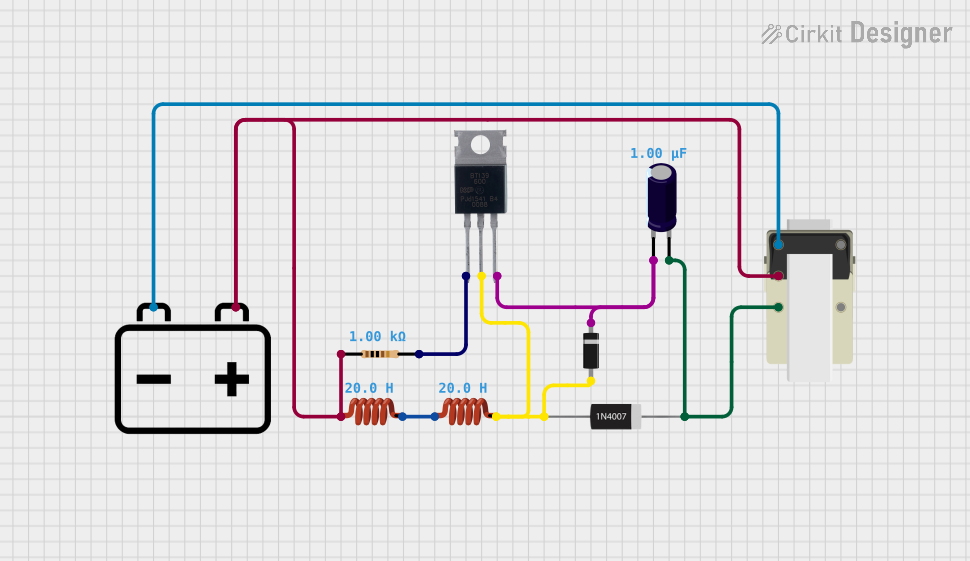
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer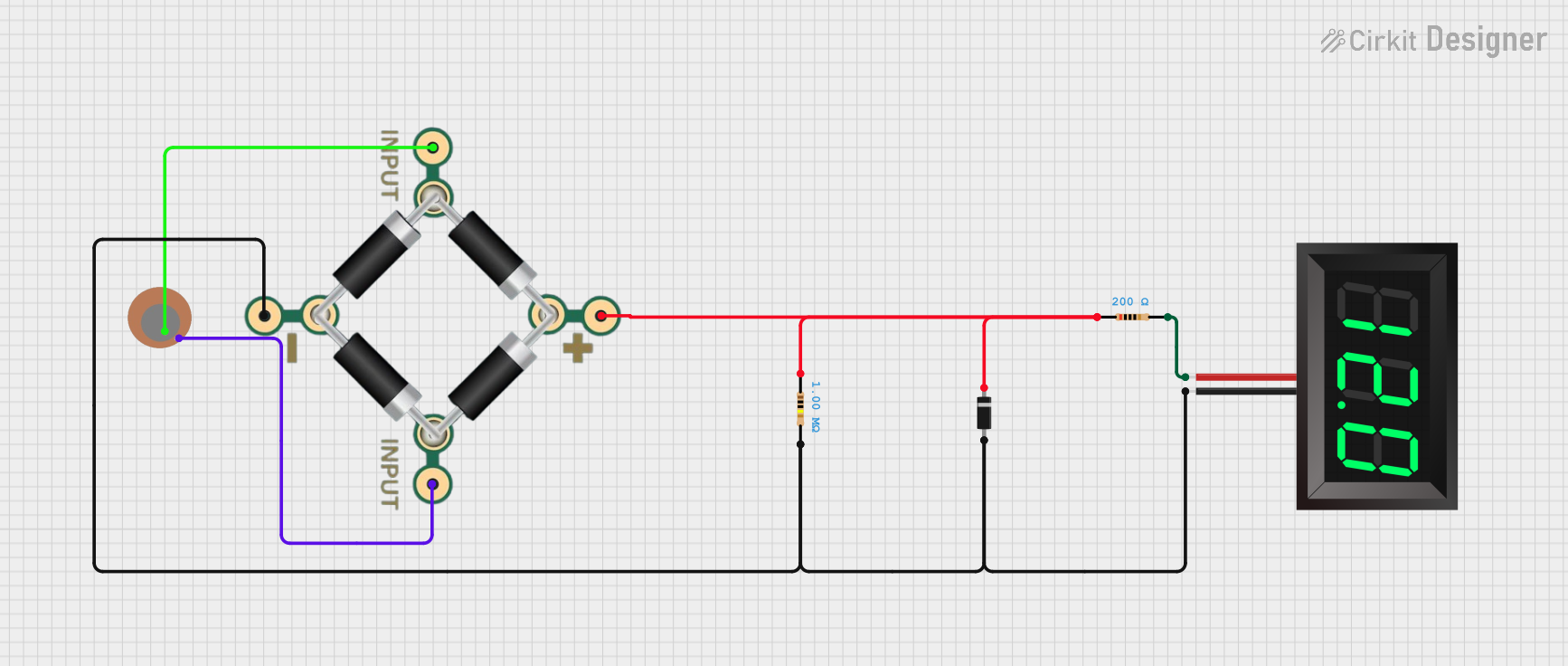
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer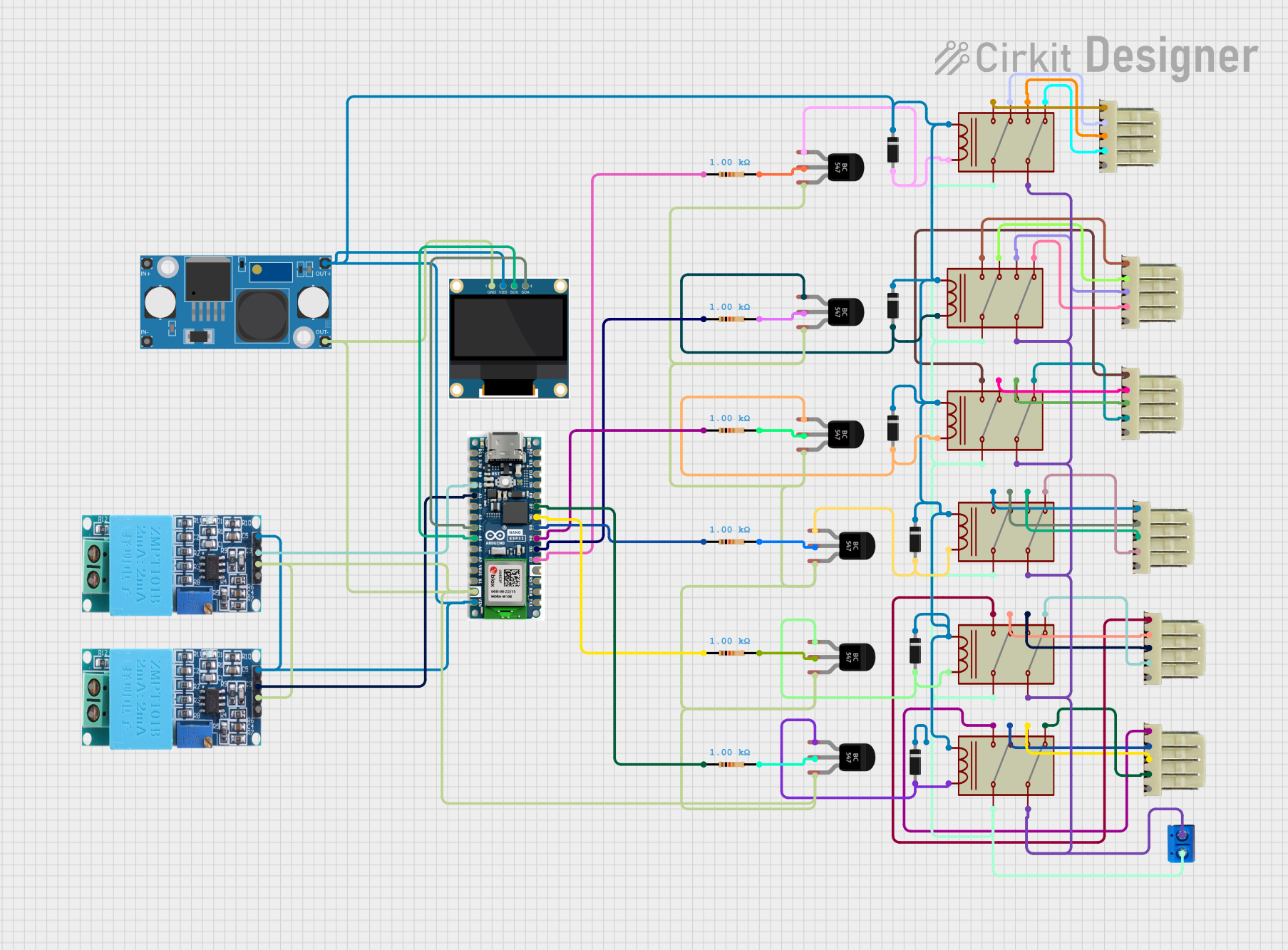
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Zener Diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Voltage regulation in power supplies
- Overvoltage protection for sensitive components
- Reference voltage generation in precision circuits
- Waveform clipping and shaping in signal processing
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications of a Zener diode. Note that specific values depend on the model and manufacturer.
Key Technical Details
- Zener Voltage (Vz): Typically ranges from 2.4V to 200V
- Power Dissipation (Pz): Commonly 0.25W, 0.5W, 1W, or higher
- Maximum Reverse Current (Ir): Typically in the microampere range
- Temperature Coefficient: Indicates how the Zener voltage changes with temperature
- Forward Voltage (Vf): Around 0.7V for silicon-based Zener diodes
- Package Types: DO-35, SOD-123, SOT-23, etc.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Zener diodes are two-terminal devices with the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Anode | Positive terminal; connected to the lower potential in reverse bias mode |
| Cathode | Negative terminal; marked with a band and connected to the higher potential in reverse bias mode |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Zener Diode in a Circuit
Voltage Regulation:
- Connect the Zener diode in reverse bias (cathode to positive voltage, anode to ground).
- Place a current-limiting resistor in series with the Zener diode to prevent excessive current.
- The Zener diode will maintain a stable voltage across its terminals equal to its Zener voltage (Vz).
Overvoltage Protection:
- Place the Zener diode across the load in reverse bias.
- When the input voltage exceeds the Zener voltage, the diode conducts and clamps the voltage to the Zener voltage, protecting the load.
Reference Voltage:
- Use the Zener diode in reverse bias to provide a stable reference voltage for other circuit components.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a current-limiting resistor to prevent the Zener diode from exceeding its maximum power dissipation.
- Choose a Zener diode with a Zener voltage close to the desired regulated voltage.
- Ensure the power rating of the Zener diode is sufficient for the application.
- Be mindful of the temperature coefficient, especially in precision applications.
Example: Using a Zener Diode with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of using a Zener diode to regulate voltage for an Arduino UNO:
/*
Example: Using a Zener Diode for Voltage Regulation
This circuit uses a 5.1V Zener diode to regulate voltage for an Arduino UNO.
The Zener diode is connected in reverse bias with a 330-ohm resistor.
*/
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog pin to read the regulated voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read the voltage
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to actual voltage
Serial.print("Regulated Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Circuit Description:
- Connect the cathode of the Zener diode to the positive voltage source.
- Connect the anode to ground.
- Place a 330-ohm resistor in series with the Zener diode to limit current.
- Connect the regulated voltage to the Arduino's analog pin A0.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Zener Diode Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current through the diode.
- Solution: Use a higher-value current-limiting resistor or a Zener diode with a higher power rating.
Unstable Output Voltage:
- Cause: Insufficient current through the Zener diode.
- Solution: Ensure the current through the Zener diode is above its minimum operating current (Izmin).
No Voltage Regulation:
- Cause: Incorrect orientation of the Zener diode.
- Solution: Verify that the cathode is connected to the higher potential in reverse bias mode.
Arduino Reading Incorrect Voltage:
- Cause: Incorrect resistor value or poor connections.
- Solution: Double-check the resistor value and ensure all connections are secure.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Zener diode without a resistor?
A: No, a current-limiting resistor is essential to prevent the Zener diode from exceeding its maximum power dissipation.
Q: How do I select the right Zener diode for my application?
A: Choose a Zener diode with a Zener voltage close to your desired regulated voltage and ensure its power rating is sufficient for the expected current.
Q: Can Zener diodes be used in forward bias?
A: Yes, but they behave like regular diodes in forward bias, with a typical forward voltage drop of around 0.7V.
Q: What happens if the input voltage is lower than the Zener voltage?
A: The Zener diode will not conduct, and the output voltage will be equal to the input voltage.